Medications are a cornerstone of modern healthcare, providing relief from pain, managing chronic conditions, and treating infections. However, many common medications come with hidden health risks, especially when used frequently or over long periods. Understanding these risks can help you make informed decisions about your health.
Sleeping Pills

While sleeping pills can be a lifesaver for those struggling with insomnia, long-term use can lead to dependency, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. Common side effects include constipation, diarrhea, headache, and fatigue. It’s crucial to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Ibuprofen and NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are widely used for pain relief. However, excessive use can cause stomach ulcers, bleeding, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. It’s important to follow dosage recommendations and consult a doctor if you need long-term pain management.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Acetaminophen is a popular over-the-counter pain reliever, but overuse can lead to severe liver damage. Always adhere to the recommended dosage and be cautious of combining multiple medications that contain acetaminophen.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, but misuse or overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance that negatively impacts gut health. It’s vital to complete the prescribed course and avoid using antibiotics for viral infections like the common cold.
Antidepressants

Antidepressants can be life-changing for those with depression. Still, long-term use can lead to weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and withdrawal symptoms. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider can help manage these side effects.
Statins
Statins are used to lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease. However, they can cause muscle pain, liver damage, and increased blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
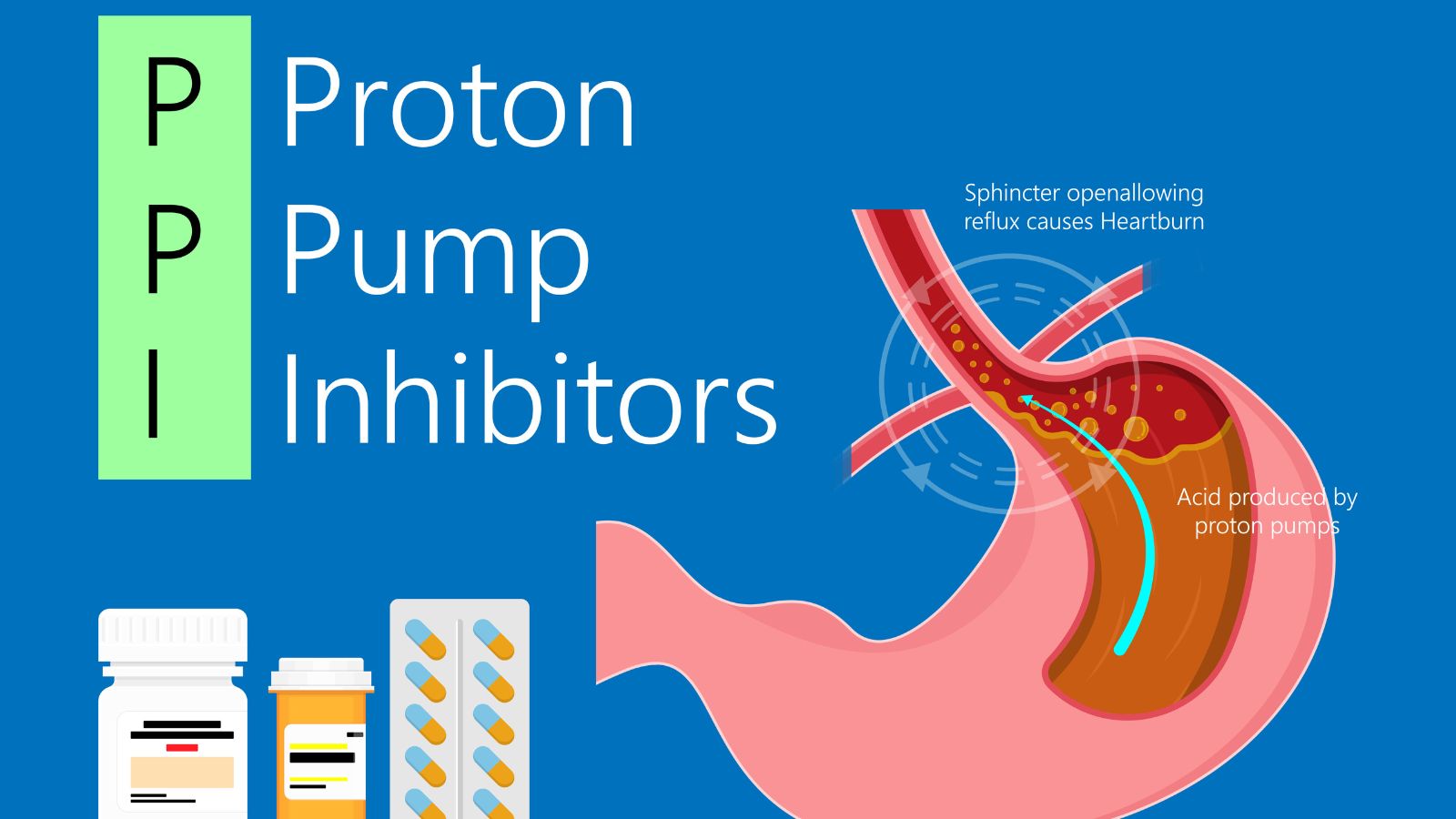
PPIs are commonly used to treat acid reflux and heartburn. Long-term use can lead to kidney disease, bone fractures, and vitamin deficiencies. It’s advisable to use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications, but long-term use can cause weight gain, high blood pressure, and increased risk of infections. They should be used under strict medical supervision.
Blood Thinners
Blood thinners are essential for preventing blood clots, which can lead to severe conditions like strokes and heart attacks. However, they come with the risk of increased bleeding and bruising. Regular blood tests and careful monitoring by a healthcare provider are crucial to ensure safe use. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and immediately report any unusual bleeding or bruising to your doctor.
Decongestants

Decongestants relieve nasal congestion by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages. However, overuse can lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate. It’s essential to use them sparingly and not exceed the recommended dosage. Prolonged use can also cause rebound congestion, where symptoms worsen once the medication is stopped. Always consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or if you have underlying health conditions that might be affected by decongestants.
Antihistamines

Antihistamines are effective in relieving allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. However, long-term use can cause side effects such as drowsiness, dry mouth, and urinary retention. Non-drowsy formulations are available, but it’s important to use them as directed. Consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent side effects or have underlying health conditions.
Opioids

Opioids are highly effective for pain relief but carry a high risk of addiction and overdose. They should be used only under strict medical supervision and for the shortest duration necessary. Common side effects include drowsiness, constipation, and nausea. Long-term use can lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses for the same effect, which increases the risk of dependency. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and discuss any concerns or side effects you experience.
Diabetes Medications

Diabetes medications help manage blood sugar levels but can come with side effects such as hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal issues. It’s crucial to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. Some medications may require dietary adjustments or specific timing for optimal effectiveness. Always discuss any side effects or concerns with your healthcare provider to ensure the best diabetes management and overall health.
Beta-Blockers

Beta-blockers are prescribed commonly for heart conditions, such as high blood pressure and arrhythmias. They work by slowing the heart rate and reducing blood pressure. However, they can cause side effects like fatigue, cold hands and feet, and depression. If you experience any adverse effects, consult your doctor to adjust the dosage or explore alternative treatments.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is used to alleviate symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and mood swings. However, it can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and certain cancers. It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider and to use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary.
Antipsychotics

Antipsychotics are used to treat mental health conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. While effective, long-term use can lead to significant side effects, including weight gain, diabetes, and movement disorders like tardive dyskinesia. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to manage these risks. It’s important to follow the prescribed dosage and report any adverse effects to your doctor promptly.
Diuretics

Diuretics, also known as water pills, help reduce fluid buildup in the body and are commonly used for conditions like high blood pressure and heart failure. However, they can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, dizziness, and headaches. It’s important to follow the prescribed dosage and report any unusual symptoms to your doctor on time to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Over-the-counter (OTC) Medications

Over-the-counter (OTC) medications, like cough syrups and pain relievers, are easily accessible but can have serious side effects if misused. It’s important to read labels carefully and follow the recommended dosage. Overuse or combining multiple OTC drugs can lead to adverse effects such as liver damage, gastrointestinal issues, and increased blood pressure. Always consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns or if symptoms persist to ensure the safe and effective use of OTC medications.
Conclusion

While medications are vital in managing health conditions, it’s important to be aware of their potential risks. Always use medicines as directed and consult with a healthcare professional about any concerns or side effects you may experience. By staying informed, you can make better decisions for your health and well-being.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
