Public transportation systems are vital for urban mobility, yet many face unprecedented challenges in 2024. Despite their potential to reduce traffic congestion and promote sustainability, these systems are struggling to meet the needs of commuters. Factors such as insufficient funding, outdated infrastructure, and a lack of accessibility contribute to the decline in ridership and effectiveness. In this article, we will explore 19 shocking reasons why public transportation is failing, highlighting the critical issues that must be addressed to revitalize these essential services for communities everywhere.
Poor Urban Planning

Urban sprawl and ineffective city design have hindered public transport’s ability to reach many areas efficiently. When a city expands without considering transit accessibility, public transportation systems become overstretched or irrelevant in specific neighborhoods. As a result, residents often resort to private cars for their commuting needs, exacerbating traffic congestion and undermining the goals of sustainable urban mobility.
Underfunding and Budget Constraints

Underfunding and budget constraints are significant factors contributing to the failure of public transportation systems in 2024. Many transit agencies struggle to secure adequate financial resources, leading to service cuts, delayed maintenance, and outdated infrastructure. As budgets tighten, essential projects often go unfunded, resulting in deteriorating vehicle and facility conditions.
Technological Setbacks

Where automation and smart technologies were seen to bring about a revolution in the public transport system, implementing the said systems was slower and far more problematic than anybody could have anticipated. From uninteresting ticketing apps to malfunctioning automated buses, technological glitches have often left commuters stranded.
Aging Infrastructure

Many cities rely on earlier infrastructures that were developed decades ago. Aging railway tracks, buses, and subways, which have not received proper maintenance and new technologies, break down often. These are certainly not reliable for commuters.
Increasing Cost of Operations

Rising fuel prices, labor costs, and maintenance expenses put immense pressure on transit agencies. Public transit operators cannot balance their budgets without a large fare increase or service cut, further accelerating ridership decline and lowering public support.
Environmental Pollution and Degradation

Ironically, many public transportation systems contribute to environmental degradation. Most buses and trains continue to run on diesel, resulting in significant greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. While there is hope for a transition to cleaner energy sources, this shift has been painfully slow, undermining the very sustainability goals that public transit aims to promote.
Competition from Ride-Sharing Services

Ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft have dramatically reshaped the public transit landscape. Many commuters now prefer ride-hailing due to its convenience and comfort compared to traditional public transportation. Although ride-hailing is generally more expensive, its appeal has led to significant ridership and revenue decline for public transportation systems. This shift poses a major challenge for transit agencies, as they must find ways to compete with the flexibility and accessibility offered by these services.
Political Mismanagement

Another strong issue has been mismanagement at the government level. Most politicians use public transport merely as bargaining chip currency for their politicized gain instead of addressing the main problems in the system. Corruption and inefficiency have led to stalled projects, poor service, and a lack of long-term vision in improving transit.
Safety and Crime Concerns

Safety concerns and rising crime rates in urban areas have deterred many individuals from using public transportation. Inadequate security measures at transit stations and a lack of personnel have heightened fears among commuters. Additionally, increasing incidents of harassment and theft further erode public confidence in these systems, making potential riders hesitant to rely on public transit for their daily needs.
Inadequate Accessibility for Disabled People

Accessibility is yet another problem; in most public transport systems, it has not been adequately addressed. As of 2024, reports indicate that many transit systems are still not fully accessible for persons with disabilities. This lack of accommodation excludes this population, contradicting basic principles of equity and inclusion.
Overcrowding

Public transportation is often overcrowded in large cities, especially during rush hours. When trains and buses are filled, commutes can become undesirable experiences, discouraging potential riders from using the service regularly.
Unaffordable Price of Tolls

The operating cost of public transport in some cities has become very high, mainly because of the need to save on costs. As fares become unbearable, the poor commuter, the one dependent entirely on public transport, cannot afford to resort to alternatives, which are less time-effective most of the time.
Inaccurate Service Timetables

Irregular service schedules can make public transport impractical for most users. Commuters lose confidence in the system when buses and trains do not arrive on time or operate at inconsistent intervals. They will likely choose more reliable options, such as cars or bicycles.
Shockwaves from a Global Pandemic

The COVID-19 pandemic brought public transport services worldwide to a grinding halt, and the after-effects continue to be felt in 2024. As these services gradually recover, fears of overcrowding and potential virus exposure keep many commuters from returning.
Climate Change and Natural Disasters
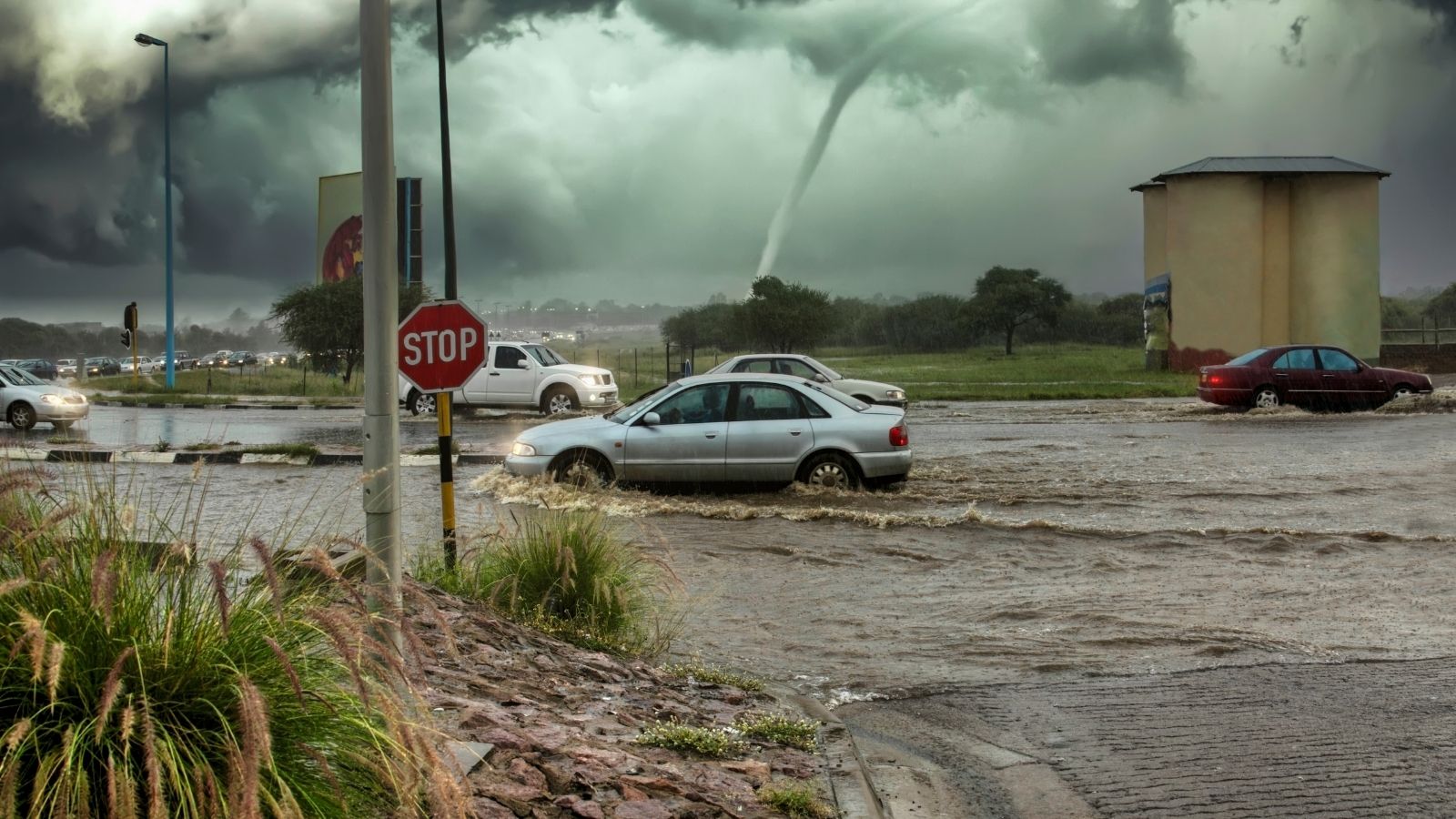

Public transport systems are increasingly vulnerable to disruptions caused by climate change. Severe weather events, such as flooding that affects subway lines, snowstorms that trap buses, and hurricanes or earthquakes that damage infrastructure, undermine the reliability of transit services.
Lack of Public Trust

Public transportation systems face a significant challenge in overcoming negative public perception and a profound lack of trust. Years of unreliable service, safety concerns, and political mismanagement have eroded confidence in these systems. As a result, many people are hesitant to use public transit, making it essential for authorities to address these issues and rebuild public trust to encourage ridership and improve the overall reputation of their services.
Slow Adoption of Renewable Energy
Years are passing with a message towards sustainability; however, much of public transportation continues to lag in transitioning to greener alternatives, such as electric buses or hydrogen trains. The inability to invest in sustainable energy solutions continues to cause environmental issues and means that transit systems are not as clean as they should be.
Insufficient Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles

While electric buses and trains are promoted as solutions to air pollution and rising fuel costs, the infrastructure needed to support electric vehicles—such as charging stations and updated power grids—remains inadequate in many cities. This lack of essential infrastructure makes the effective implementation of green technology challenging.
Lack of Integration Between Different Modes of Transport

Most public transportation systems operate in silos, with limited coordination between buses, trains, and trams. As a result, transfers can be time-consuming and overly complicated. Commuters often find themselves in limbo, as these systems are not interconnected and interact poorly. This lack of integration causes passengers to lose their most valuable assets: time and money.
Conclusion

The failure of public transport systems in 2024 is multifaceted, stemming from economic, technological, social, and political factors. Issues such as underfunding, poor infrastructure, safety concerns, and the rise of ride-sharing applications must be addressed urgently. Without intervention, public transportation risks fading away in an era that demands more efficient mobility solutions. Furthermore, creating livable cities is increasingly challenging in the face of environmental issues. By investing in modern infrastructure, ensuring accessibility for all, and prioritizing sustainability, governments and businesses can collaborate with communities to reshape and enhance public transportation for the future of urban mobility.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
