As the demand for sustainable living grows, many modern homes are being designed with eco-friendly features in mind. However, despite these intentions, some homes are becoming less sustainable due to inefficient energy use, over-reliance on non-renewable resources, and poor building practices. This article explores 19 surprising ways modern homes inadvertently contribute to environmental decline. These insights highlight the hidden challenges of achieving true sustainability in today’s housing market, from excessive material consumption to overlooked energy inefficiencies.
Bigger Homes, Bigger Problems

Have you observed the increasing size of homes? In many places, the average home size has risen over the previous few decades. Despite their seeming luxury, larger homes use more energy for maintenance, heating, and cooling. More space requires more resources, such as steel, concrete, and wood, which have significant negative environmental effects.
Over-reliance on Energy-Intensive Appliances

Modern homes often feature high-tech appliances like ovens, HVAC systems, and smart refrigerators, which, while convenient, consume a significant amount of energy. Despite being labeled “energy-efficient,” the combined power usage of these devices can still lead to high energy consumption, especially when multiple appliances are running simultaneously.
The Hidden Impact of Smart Home Technology

Do you use apps or voice commands to operate your house? The energy and resources needed to create and maintain these gadgets are something we hardly ever think about, despite the popularity of smart homes. The technology that powers your “smart” house, from servers to sensors, has its carbon footprint.
Short-Lived Building Materials

Speed and value are sometimes given precedence above resilience in modern buildings. Although they could save money upfront, cheap materials don’t last long. Synthetic finishes, vinyl siding, and particleboard decay rapidly, necessitating regular replacements and repairs and wasting money.
Glass Everywhere Isn’t So Green

Despite their beautiful appearance, floor-to-ceiling windows are not necessarily energy-efficient. Homes with large glass surfaces become greenhouses in the summer and let heat escape in the winter, increasing carbon emissions and energy costs.
Energy-Efficient Appliances That Still Waste Energy

Here’s a paradox: many modern appliances are labeled “energy-efficient,” yet they still encourage overuse. For instance, dishwashers with eco-modes might save water, but what’s the point if you run them half-empty? The same goes for washing machines and dryers.
Excessive Water Consumption
Luxurious bathrooms are common in modern homes; imagine rainfall showers, enormous bathtubs, and two sinks. While these features are fashionable, they drastically raise water consumption, particularly in areas where water shortage is already a problem.
Fast Furniture and Disposable Decor

Do you know what “fast fashion” is? Home décor is following the same trend. Mass-produced, low-cost furnishings and décor are made to be changed rapidly. These things usually end up in garbage dumps, adding to trash and pollution.
Rising Energy Demand for Home Offices

Many of us use computers, lighting, and heating or cooling systems around the clock as remote work becomes more common. Although there are benefits to working from home, it also sometimes results in higher household energy use than we expect.
The Environmental Cost of Modern Landscaping

Exotic plants and well-kept lawns look fantastic but can be expensive. Excessive amounts of water, fertilizer, and pesticides are needed to maintain lush greenery, which is bad for the environment and other ecosystems.
Excessive Use of Plastic in Construction

Modern homes rely heavily on plastic-based materials, from insulation to plumbing. While plastic is cheap and versatile, it’s not biodegradable and adds to the growing problem of plastic waste.
More Electronics, More E-Waste

Consider the number of gadgets you own, including game consoles, tablets, TVs, and smart devices. These devices rapidly become outdated as technology develops, creating mountains of e-waste that are difficult and often dangerous to recycle.
Poor Indoor Air Quality

To increase energy efficiency, modern housing is designed to be airtight. The catch is that indoor air quality may deteriorate without adequate ventilation. Dangerous chemicals are released into the air when synthetic materials, paints, and furniture are off-gas.
The Carbon Footprint of Renovations
H

ome renovation is more popular than ever due to home improvement shows and social media trends. However, removing walls, putting in new finishes, and changing out fixtures requires a lot of energy and produces a lot of waste.
Solar Panels Aren’t Always a Silver Bullet

Solar panels seem like the most environmentally friendly option, don’t they? Although they lower energy costs, their manufacturing method isn’t environmentally friendly. The emissions and rare metals needed for manufacturing outweigh some of the advantages of panels.
Modern Homes Overlook Passive Design

Passive design strategies, such as placing windows for natural light and circulation, were commonly utilized in traditional homes. However, modern homes miss out on the possibility of naturally lowering energy consumption since they rely largely on artificial lighting and HVAC equipment.
Construction Waste Is Through the Roof

Did you know that one of the biggest sources of garbage in the world is the construction sector? With their quick fixes and speedy construction, modern homes produce mountains of waste, most of which isn’t recycled.
The Problem of Over-Insulation
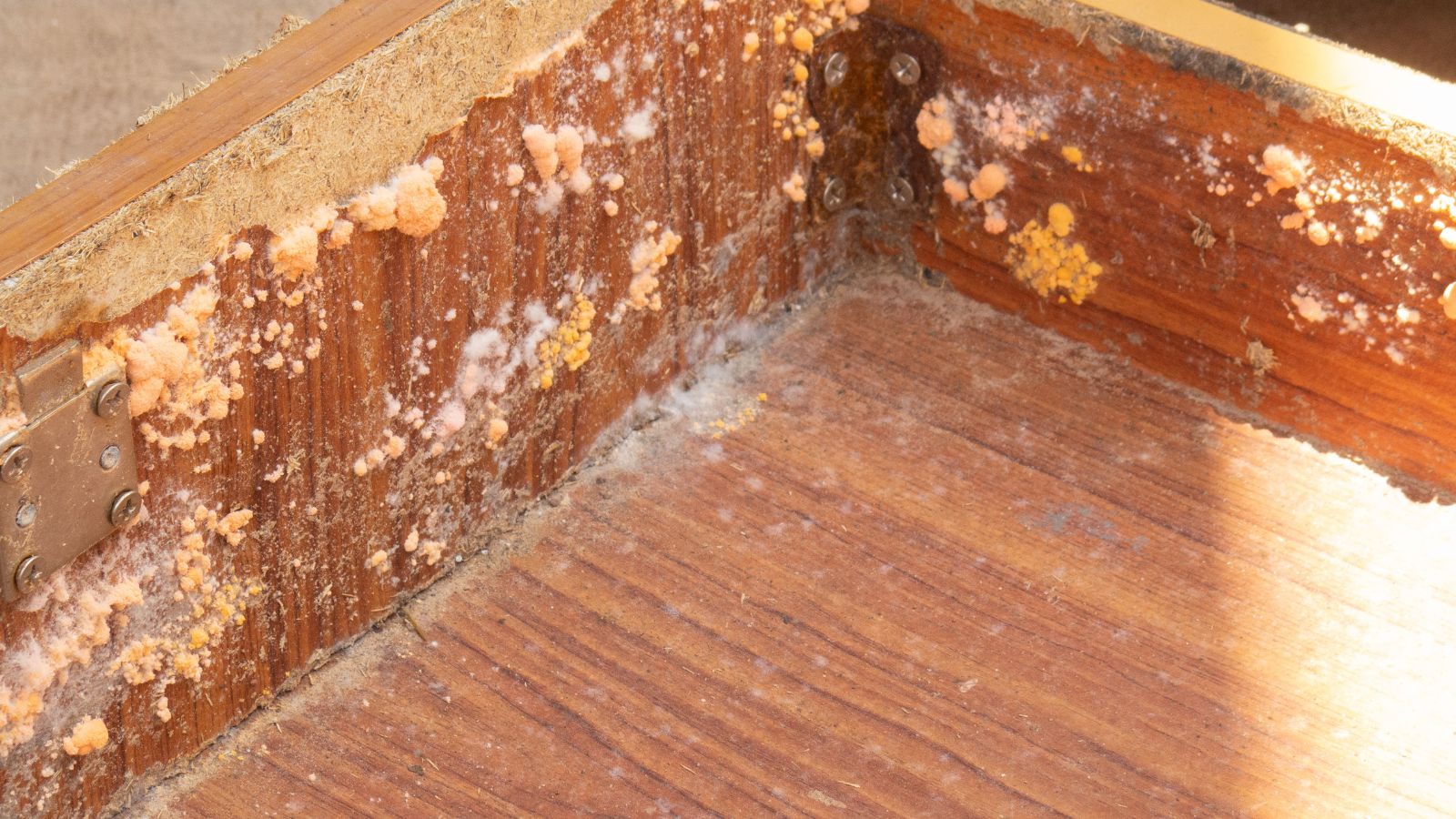

Although insulation is a terrific way to save energy, too much of it might work against you. Homes with excessive insulation may retain moisture, which can result in mold growth and necessitate the use of energy-intensive dehumidifiers.
Ignoring Local Materials

Modern buildings often rely on imported materials that travel thousands of kilometers to reach your home. While imported stone or exotic wood may look stunning, the carbon emissions from transportation make them far from sustainable.
Conclusion

As you read this, you might be wondering: Is it possible to make modern homes sustainable? The answer is yes. Achieving sustainability requires a balance between creativity and mindfulness. Long-term sustainability should be prioritized over fleeting trends. For instance, better designs for smaller homes can make a significant difference. Embracing passive techniques, like increasing natural light and ventilation, helps reduce energy consumption. Choosing durable, locally sourced materials lessens environmental impact while ensuring longevity. Modern homes can be eco-friendly, stylish, and functional with some effort. So, the next time you consider remodeling or building, ask yourself: Is this sustainable? After all, our homes are not just where we live; they are where we shape the planet’s future.
25 Countries Predicted to Become Economic Superpowers in the Next 20 Years

The strength of an economy plays a crucial role in various international policies about trade and relations. Certain factors determine the strength of an economy, including population growth, availability of resources, and development and advancement. Here are 25 countries predicted to become economic superpowers in the next 20 years
25 Countries Predicted to Become Economic Superpowers in the Next 20 Years
