As the global population continues to age at an unprecedented rate, society is going through major changes that are affecting us all. As life expectancy increases and birth rates decline, the world’s population is experiencing impact healthcare, the economy, technology, and even social structures. We take a look at 20 worrying trends in the aging population.
The World’s Elderly Population is Growing Rapidly

By mid-century, the global population of seniors is expected to exceed 1.5 billion, demanding significant adjustments to healthcare, pensions, and workforce dynamics. To meet these challenges, governments must revise their strategies, and businesses must innovate their products and services.
Longer Life Expectancy is Redefining Retirement

Advancements in medical technology and healthier lifestyles have extended life expectancy significantly. People are now living decades beyond traditional retirement age, making the idea of retiring at 65 increasingly obsolete. Many seniors will need to remain in the workforce longer or find new ways to sustain themselves financially during extended retirement years.
The Shrinking Workforce and Economic Implications

With an increasing number of older individuals leaving the workforce and fewer younger workers entering, many countries face potential labor shortages. This disparity can impede economic expansion, put more strain on social security systems, and compel companies to automate jobs that were formerly performed by people.
Demand for Geriatric Care

The healthcare system is already feeling the strain of an aging population. With more people requiring long-term care, treatments for chronic illnesses, and specialized geriatric services, healthcare costs are skyrocketing. To avoid putting a financial burden on families and public health systems, governments and insurance companies will need to come up with creative methods to finance and handle these costs.
Growth of the Senior Housing Market

As people live longer, the demand for senior-friendly housing and assisted living facilities is growing. Developers are designing communities with accessibility, medical support, and social engagement in mind. Aging-in-place technology is also emerging as a popular solution, allowing seniors to remain in their homes safely for longer periods.
Increased Need for Caregivers

The rising elderly population has led to an increased demand for caregivers, both professional and familial. However, there is already a shortage of trained professionals in elder care, and family members often struggle to balance their own responsibilities with caregiving duties. This trend may lead to significant policy changes, such as financial support for family caregivers or increased recruitment efforts for healthcare workers.
Surge in Aging-Related Diseases

With a growing elderly population comes a rise in diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other neurodegenerative conditions. As healthcare systems must create better management and treatment plans to deal with the growing number of afflicted people, research and funding for these disorders will become a top priority.
The Silver Economy Will Boom

Older consumers have significant purchasing power, and industries are beginning to recognize this untapped market. Travel, fashion, fitness, and technology companies are developing products and services tailored to the needs of older adults, from senior-friendly gadgets to wellness programs that promote longevity.
Greater Dependence on Technology

Seniors are adopting technology at a growing rate, using smartphones, wearables, and AI-driven assistants to maintain their independence. Robotics, smart home technology, and telemedicine advancements will be essential to raising their standard of living while lowering medical expenses and the strain on caregivers.
The Rise of Multigenerational Households
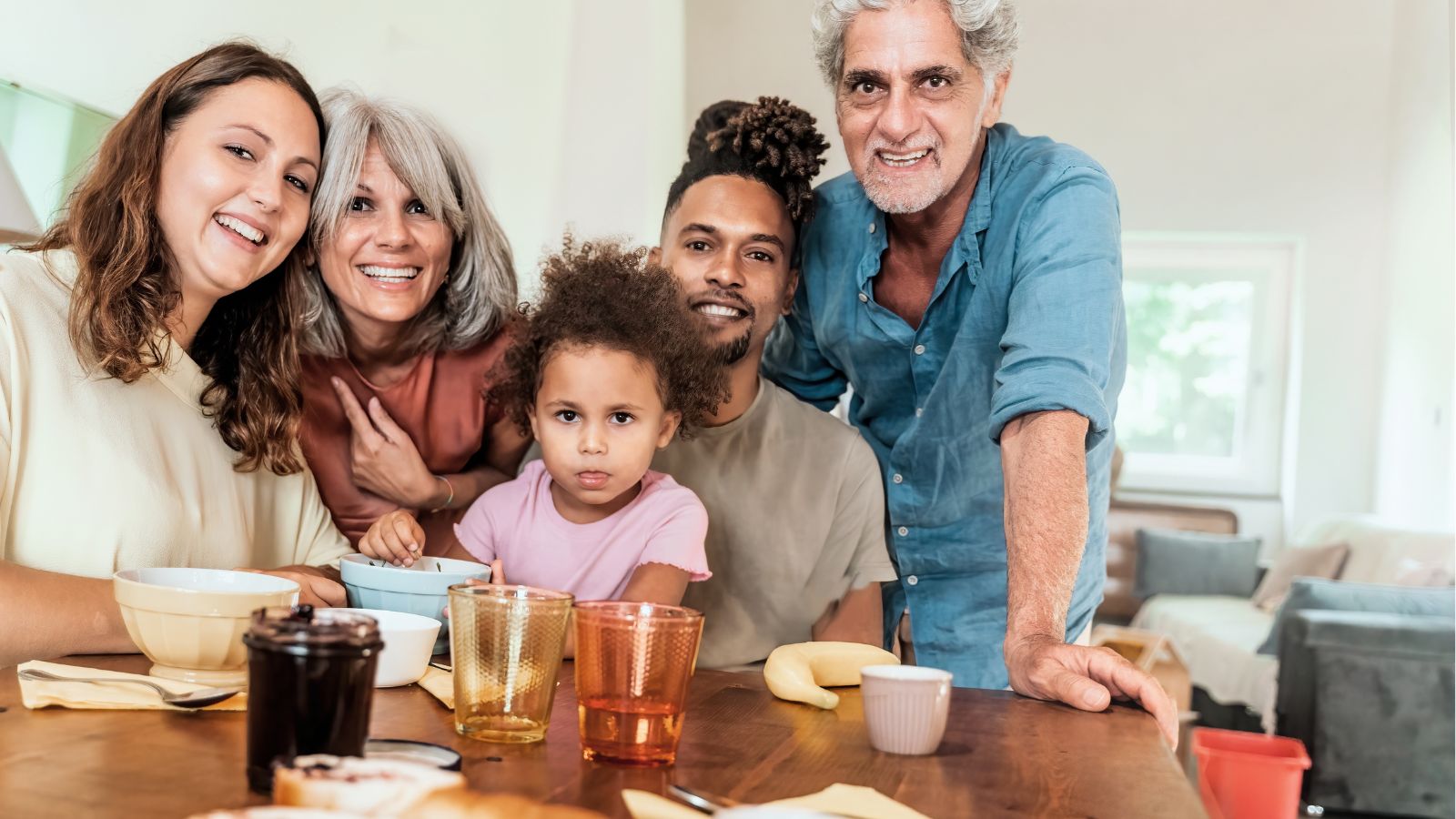

Economic pressures and longer life expectancies are leading to a rise in multigenerational living arrangements. Families are choosing to live together to support aging relatives, creating new dynamics that require adjustments in housing designs and family roles.
Shift in the Workforce: More Older Employees

Retirement is no longer a given at 65. Many seniors are continuing to work well into their 70s, either due to financial necessity or a desire to stay engaged. Employers are now adapting to an older workforce by offering flexible schedules, part-time roles, and ergonomic workplace adjustments.
Changing Social Norms Around Aging

Society’s perception of aging is evolving. Instead of viewing old age as a time of decline, more people see it as a phase for reinvention, learning, and new experiences. This shift is leading to increased demand for lifelong learning programs, senior entrepreneurship initiatives, and more inclusive policies in workplaces and social settings.
Delayed Parenthood Leading to Older Grandparents

With many people choosing to have children later in life, grandparents are also getting older. This shift affects family structures, as older grandparents may have different levels of involvement in childcare and support compared to previous generations.
Higher Divorce Rates Among Seniors

Divorce rates among older adults, known as “gray divorce,” are increasing. Many seniors are choosing to separate later in life to pursue new relationships or personal fulfillment, leading to financial and emotional challenges for older divorcees.
The Impact of Climate Change on Older Adults

Seniors are more vulnerable to extreme weather events, from heatwaves to hurricanes. As climate change intensifies, governments and communities must implement strategies to protect older adults from environmental hazards.
Increased Demand for Alternative Medicine

More seniors are turning to alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and holistic health approaches. This trend is influencing healthcare providers to incorporate integrative medicine options alongside conventional treatments.
Global Aging and Migration Patterns

Aging populations are reshaping global migration trends. Many countries are easing immigration policies to attract younger workers who can support an older demographic, while retirees are relocating to countries with lower living costs and better healthcare options.
Financial Struggles in Retirement

Many seniors are unprepared for the financial realities of extended retirement. Insufficient savings, rising healthcare costs, and pension instability are leading to an increased reliance on social security and government aid.
Ethical Dilemmas in Aging

Advances in medical technology raise ethical questions about end-of-life decisions. Assisted dying laws, prolonged life support, and quality-of-life considerations are discussions being made in healthcare and policy-making.
Increased Political Influence of Older Adults
Older adults are becoming a powerful voting bloc, influencing policies on healthcare, social security, and retirement benefits. As their numbers grow, political parties and governments will need to address their specific needs to secure electoral support.
25 Countries Predicted to Become Economic Superpowers in the Next 20 Years

The strength of an economy plays a crucial role in various international policies about trade and relations. Certain factors determine the strength of an economy, including population growth, availability of resources, and development and advancement. Here are 25 countries predicted to become economic superpowers in the next 20 years
25 Countries Predicted to Become Economic Superpowers in the Next 20 Years
