Glittering new trends and fashions are always considered a sign of advancement and modernization. At the same time, we are neglecting one of the very important concerns of its negative environmental impact. It may seem fascinating, but the reality of it is very harsh. The rate at which it is affecting the environment is very dramatic. Shedding light on the key factors that are affected by these latest trends can be eye-opening for many. Below discussed are the facts that are most affected because of this fast fashion.
Water Consumption

The production of new fabrics requires a lot of water. The textile industry uses almost 1.5 trillion gallons of water every year. Water is a very sensitive issue in today’s world. Clean or no water is available in many parts of the world. The shortage of water supply is caused by factors such as deforestation, pollution, greenhouse effects, uncontrolled water use in industries, and many other reasons.
Emission of Greenhouse Gas

Greenhouse gas emissions are the main cause of global warming and drastic climate change. These gases are produced by automobiles, agriculture, textiles, and different industrial procedures. The fast fashion industry has a significant role in the production of these gases. Around 12.8% of greenhouse gases are produced during textile procedures, which exceeds the Carbon footprint of international flights.
Use of pesticides and insecticides

Fashion clothes production is challenging. It involves a series of steps. The production of cotton crops consists of the use of pesticides and insecticides on a large scale, which leads to environmental hazards. Therefore, it is important to keep an eye on this production. In this fast fashion, almost 24% of pesticides and 11% of insecticides are used, leading to air, water, and soil pollution.
Microplastic pollution
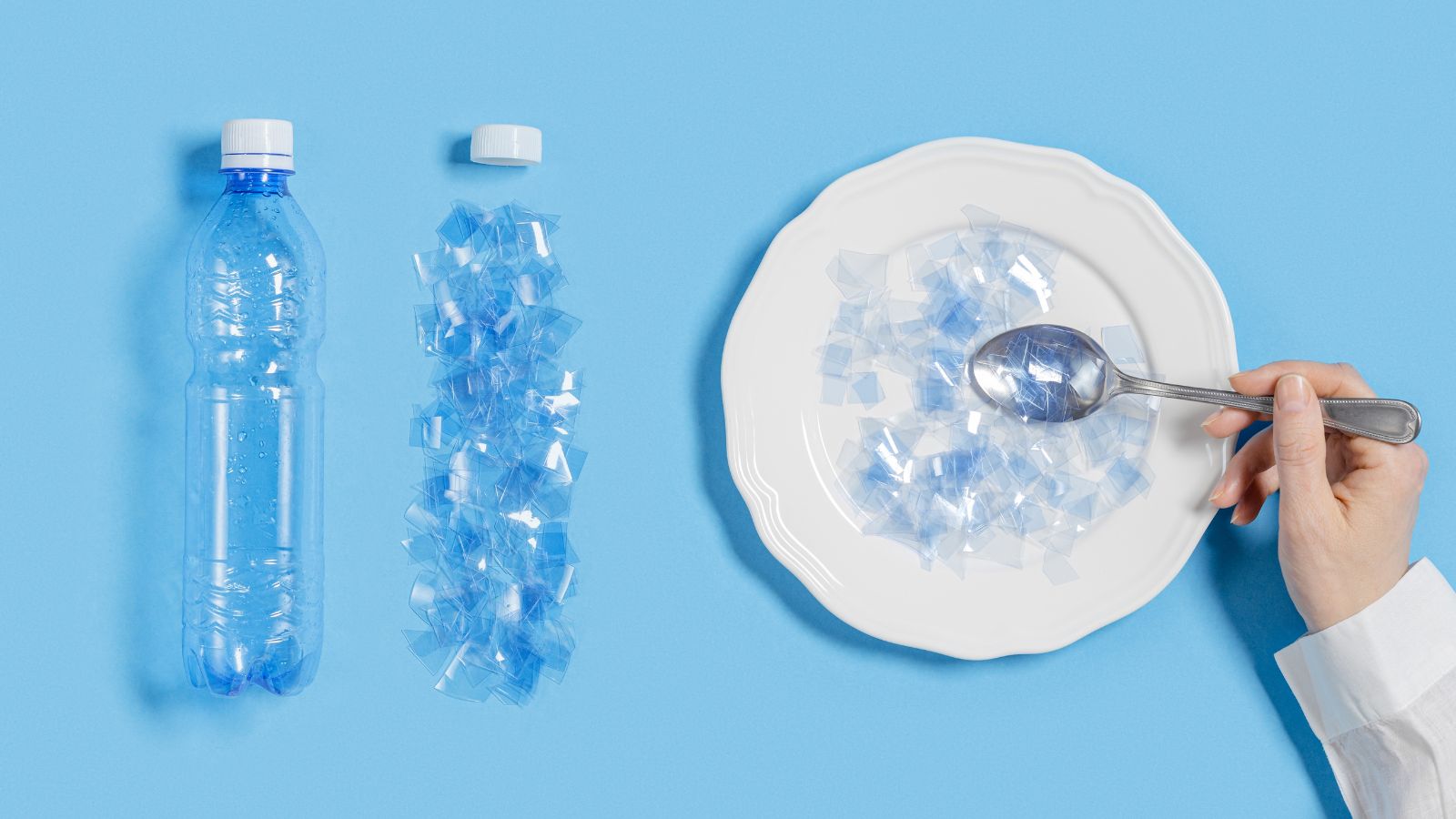

Synthetic fiber, especially polyester thread, which is made of recycled plastic, releases microplastic on every wash. Five hundred thousand tons of microplastic enter the oceans yearly, harming marine life.
Dye Pollution
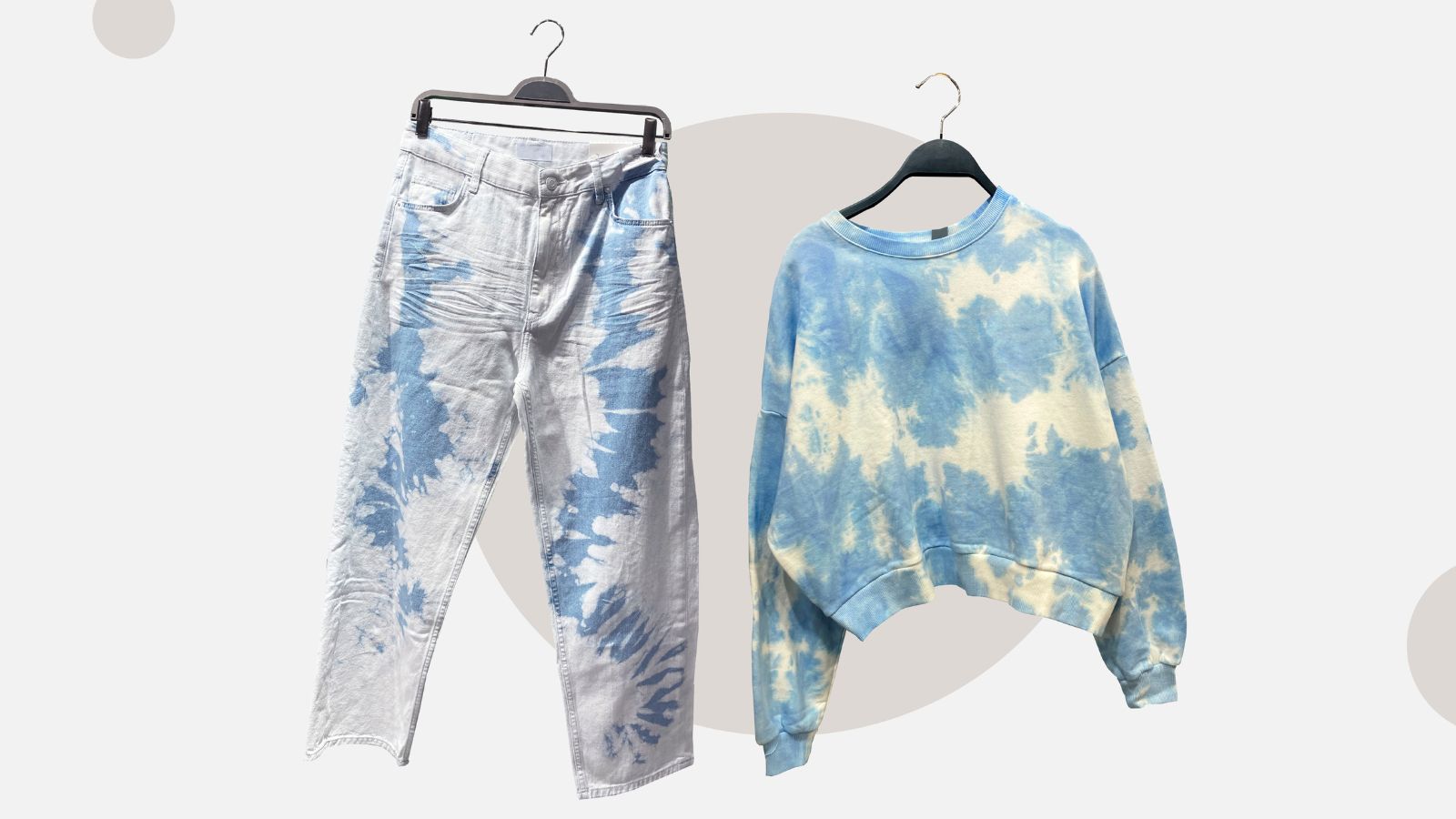

Trendy, colorful clothes may seem fascinating, but a large number of toxic dyes are used to achieve the desired colors. Most factories do not have the proper system in place to treat the contaminated water produced as a result of using these dyes, which are released directly into the rivers and oceans. Consequently, it is influencing our marine life and poses a threat to its survival.
Waste Generation
While technology and modernity may be present in today’s world, there is a lack of quality in everything. Everything wears out quickly. Lifetime guarantees or quality assurance are not a part of the equation. The lifespan of fast-fashion clothes is limited to seven years before they wear out and go out of style, which results in global waste. Textile waste amounts to approximately 92 million tons annually.
Improper Ways of Waste Management
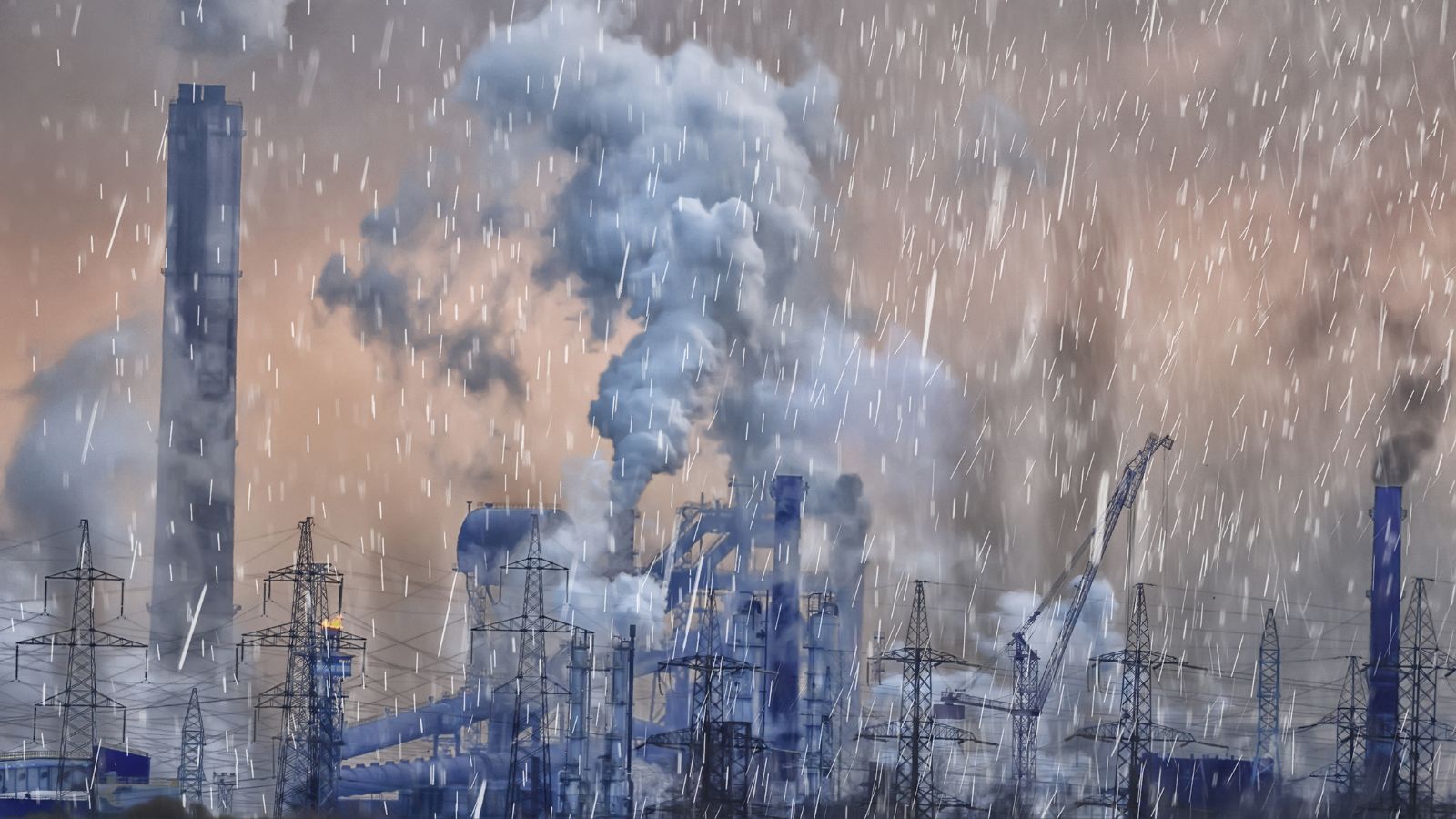

Most of these fast-fashion factories lack the proper waste management systems and strategies. These companies incinerate their unsold articles rather than donate them, which produces a lot of air pollution that damages the ecosystem.
Deforestation
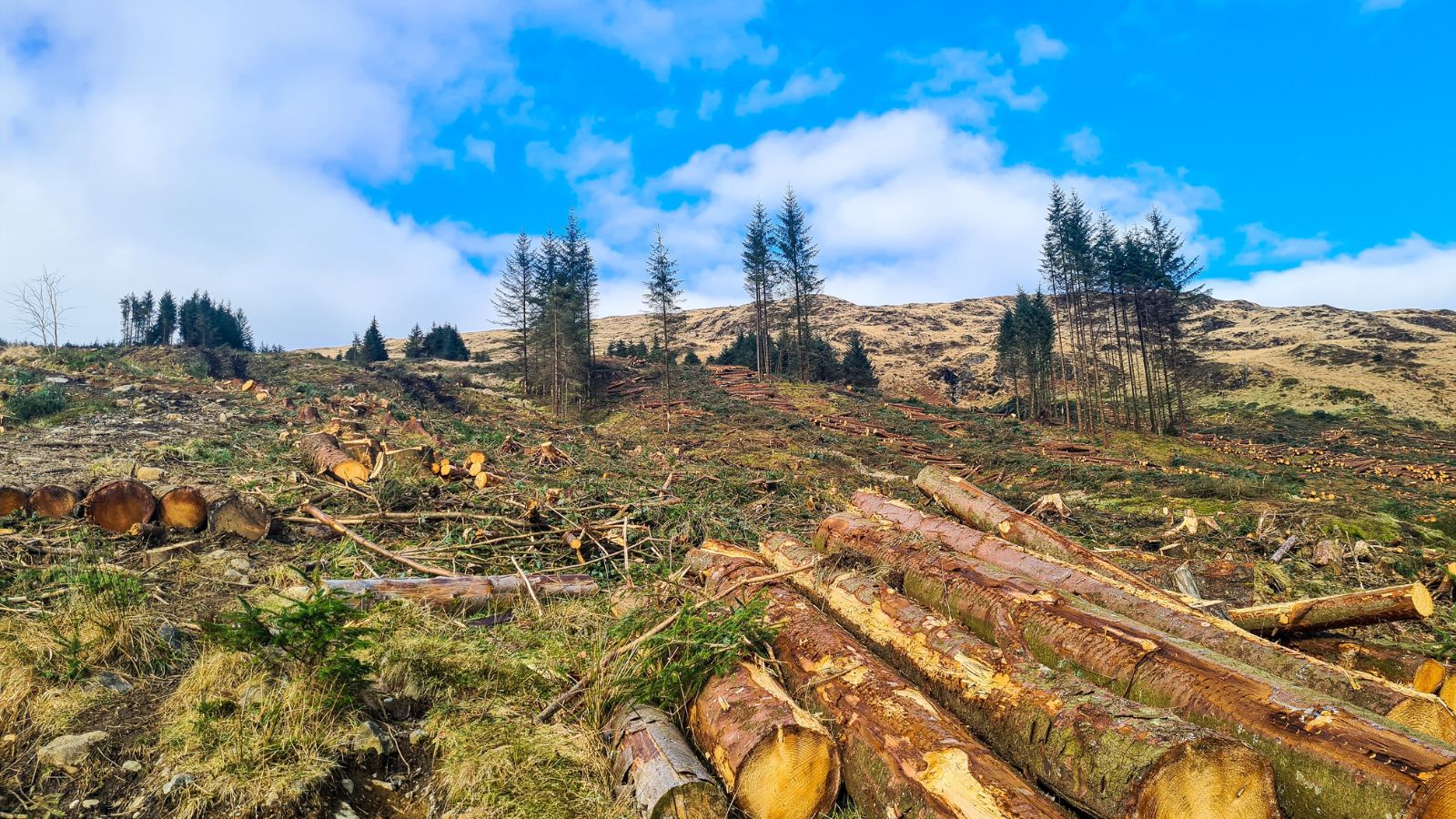

Rapid advancement and industrialization are the leading causes of deforestation, thus threatening our environment and biodiversity. Textile production, particularly cotton, is the leading culprit, therefore causing an everlasting effect on our environment and significantly affecting the climate.
Labor Exploration

The whole concept of fast, fashionable, cheap clothes is wrong. The use of a large number of toxins to produce cheap, low-quality clothes that are not durable and are available at low prices includes many steps that are not compatible with the environment and the system. In pursuit of this journey, factory owners rob the laborers of their basic rights, making them work for minimum wages, particularly in developing countries.
Landfill crisis

Recently, there has been a lot of awareness regarding waste management and protecting our earth from this ever-increasing pollution. Textile industries are a potential source of pollution; approximately 85% of it ends up in landfills. Decomposition may take hundreds of years, adding up to methane, the greenhouse gas in our environment.
Fast Production cycles

These trends change periodically, thus requiring a fast production system. This leads to an increase in production cycles that further damages the environment by increasing pollution and waste.
Global transportation Footprint

These fast-fashion models involving large supply chains often produce large amounts of global carbon emissions. Carbon emissions are the primary cause of the greenhouse effect and global warming, which leads to environmental destruction and ecosystem damage.
Limited Recycling

The rate at which new production has been carried out does not match the recycling rate. Recycling is an old concept that is still not being practiced properly. Only around 1% of the production is recycled, while 98% of clothes are wasted, thus adding to the pollution.
Chemical dyes

Many toxic chemicals, such as dyes and detergents, are used in the textile industries. These chemicals are directly released into the clean water of rivers and oceans without any wastewater treatment, harming marine life and causing lead contamination in the water.
Depletion of Resources

The production of trendy clothes mostly depends on non-renewable resources like coal and petroleum. The increase in production required for fast-changing trends leads to a significant depletion of resources. As a result, natural resources are depleted, and pollution levels increase.
Plastic Bags Waste

Awareness regarding the use of plastic bags is very common. Everyone knows about the drastic effects of these plastic bags on the environment, yet their use is in practice. These fast-fashion industries use 100 billion plastic bags.
Overconsumption

Trends change quickly, requiring overconsumption of resources for no good. Many resources, such as water, electricity, manpower, and fabric, are used just in the name of fast fashion, with no gain as a result. Better strategies and limited resources should be utilized properly.
Unsustainable Materials

The use of unstable materials in fast fashion is a significant factor in contributing to the damage. These unsustainable materials include virgin cotton, polyester, and nylon. Their non-renewable nature means that they cannot be reduced, leading to landfills and pollution.
Cotton Production
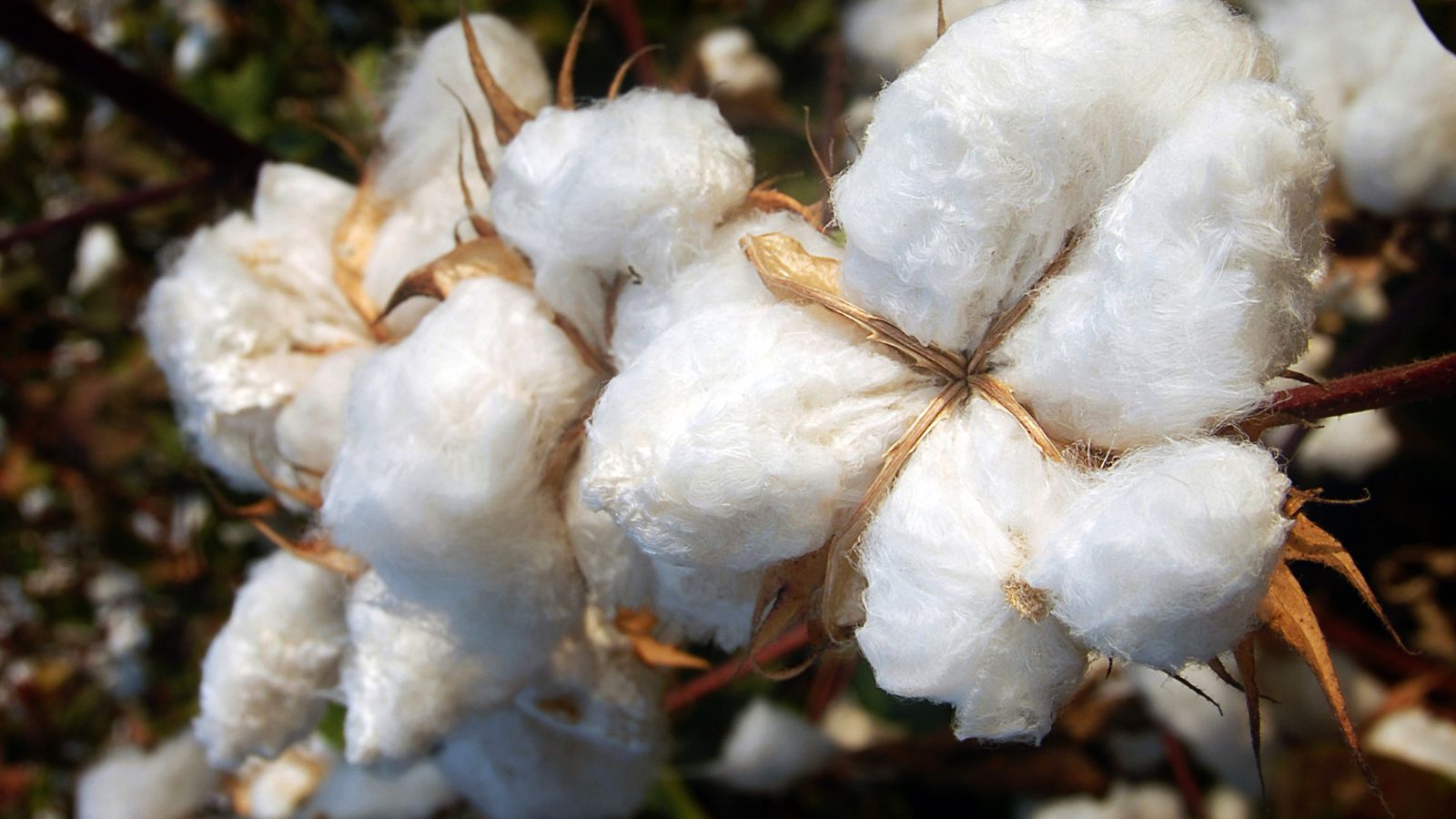

Cotton is the main raw material used for the production of fast-fashion clothes. This process requires a large number of pesticides, insecticides, and 25% fertilizers. The whole process contributes to pollution in the air, water, and land, affecting the ecosystem as a whole.
Soil Degradation

Fast-fashion clothes are produced using cotton as their main raw material. The cultivation of this cotton involves intensive farming methods. As a result, soil degradation occurs, which impacts the soil’s productivity and crop quality.
Conclusion

Trendy fast-fashion clothes can look like a sign of advancement and modernization, but they deprive our resources. All that glitters is not gold, as the above-mentioned points explain. We need to be more mindful while making such choices. Recycling and Thrift stores should be encouraged. Most clothes should be recycled or reused instead of dumped in landfills or incinerated. All this fashion at the cost of polluting our dear planet Earth is not worth it. A mature and mindful approach is required to fight back this crisis.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
