The gig economy offers workers flexibility and the chance to earn extra cash. But, despite the flexibility that gig work brings, it can also lead to career instability, as we explore in these 21 examples:
A Freelancing Boom

More people are choosing freelancing over typical 9–5 jobs as a result of the gig economy. The independence freelancing brings is not to be denied but it can lead to a lack of security as people constantly wonder where the next gig is coming from.
Platform-Driven Work

Digital platforms, such as Uber and DoorDash are big players in the gig economy, offering workers opportunities to find clients quickly. Digital platforms do provide convenience for gig workers but they take a significant portion of fees from workers’ earnings.
Dependence on Multiple Jobs

Gig workers often struggle to secure enough hours to cover their bills so will often rely on multiple jobs to make ends meet. Juggling several jobs means you can’t always predict how much income you will bring in each month, making it difficult to budget and save for the future.
Lack of Employer-Provided Benefits

Traditional employees usually receive benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid sick leave but this isn’t usually the case for gig workers. With no safety net, gig workers will often have to work when they’re ill and may struggle to take time off work, which means there’s little downtime.
Increased Competition Among Workers

The gig economy has created a highly competitive environment where workers have to prove their worth in order to win repeat custom. Millions of people now compete for the same chances because of digital platforms that allow worldwide involvement, which frequently results in lower earnings for many.
Unpredictable Earnings

One of the most worrying aspects of the gig economy is the lack of predictable earnings, due to fluctuating demand for their services. Not knowing how much money you will make each month can be stressful and unpredictability can lead to missing payments on important household bills.
Reliance on Ratings

Gig platforms often rely on ratings and reviews to match workers with clients and a single negative review can significantly impact a worker’s opportunities. The pressure to meet customer expectations can lead to a loss of motivation as well as earning, both causing long-term stress.
No Long-Term Job Security

Many jobs in the gig economy are short-term or task-specific, which means there’s no job security for workers. Without the security of long-term employment, workers are constantly in search of the next opportunity, often without success which means money becomes tight.
On-Demand Working

On-demand work, such as food delivery or ride-sharing, is a key feature of the gig economy. While these jobs offer flexibility and the potential to earn money, they don’t offer much in the way of career growth, leaving workers in a constant state of financial instability.
Difficulty in Accessing Credit

Gig workers often struggle to access credit or loans due to their irregular income as banks favor applicants with stable jobs and predictable earnings. A poor credit rating makes it harder for gig workers to qualify for mortgages, car loans, or other financial services.
Changes in Worker Classification and Rights

Most gig workers are classified as independent contractors rather than employees, often limiting their rights to minimum wage protections, unemployment benefits, and workers’ compensation.
Reliance on Personal Resources

Gig workers often have to use their own cars, laptops, and tools to perform their jobs, which is an added cost. Workers may need to go into debt to buy resources and then there’s the cost of maintaining and replacing damaged items, all of which adds up over the year.
Lack of Retirement Planning

Without employer-sponsored retirement plans, many gig workers struggle to save for their future. Without consistent income and long-term job security, many gig workers are worried about how they will fund their retirement as they don’t get a chance to put money into a pension or savings account.
Algorithmic Control

Gig platforms use algorithms to determine how work is assigned and how much workers are paid, often leaving workers in the dark about how their performance is evaluated. If employers aren’t up front about how algorithms work, gig workers won’t always understand why their earnings fluctuate.
Outsourcing

The gig economy means employers can outsource tasks to workers worldwide, often as a cost-cutting exercise. While globalization provides opportunities for remote workers, it also drives down wages due to increased competition from regions with lower labor costs.
Burnout

The lack of boundaries between work and personal life in the gig economy often leads to burnout. Gig workers frequently take on excessive workloads to compensate for low pay or inconsistent opportunities, sacrificing their home life well-being in the process.
Side Hustles

Traditional employees are turning to the gig economy for side hustles, supplementing their income to cope with rising living costs. The ability to take on a side hustle is great for when people need money but it highlights the financial problems many households are facing.
Economic Downturns

Gig workers are particularly vulnerable to economic downturns, especially when there’s periods of low demand. Unlike traditional employees, gig workers rarely qualify for unemployment benefits or other safety nets, adding to the financial strain of managing a monthly budget.
Gender and Racial Inequalities

Studies show that women and minority groups are overrepresented in lower-paying gig jobs, such as domestic work or ride-sharing. Gender and race inequalities highlight the financial instability faced by already vulnerable populations.
Regulatory Uncertainty

The gig economy operates in a legal gray area, leaving millions of workers vulnerable to exploitation. A lot of gig workers are classified as independent contractors, which means they can’t rely on the same legal protections as traditional employees.
Worker Advocacy Movements
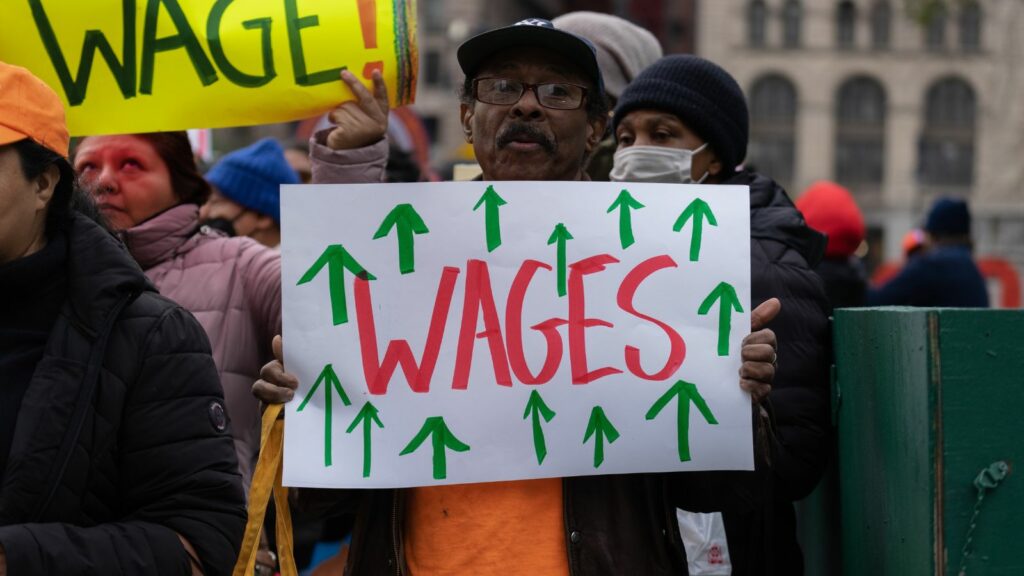
In response to the instability and inequities of the gig economy, worker advocacy movements have gained momentum. Unionization and campaigns for fair compensation are focusing on how we can make things better for gig but there’s a long way to go to improve job stability.
20 Reasons Why Wealthy Investors Are Looking At The Caribbean

The Caribbean has long been known for its stunning landscapes and vibrant culture, but in recent years, it has also become an attractive destination for wealthy investors. The region offers numerous financial, economic, and lifestyle advantages that appeal to high-net-worth individuals seeking opportunities. Here are 20 reasons why the Caribbean has captured the attention of the global investment community.
20 Reasons Why Wealthy Investors Are Looking At The Caribbean
