Headlines often emphasize downturns, deficits, or debt, but behind the noise lies a sturdier picture of Canada’s financial future. From robust trade agreements and growing industries to demographic advantages and responsible governance, many indicators show the economy is not as fragile as critics suggest. Here are 23 reasons why Canada’s financial future is stronger than the headlines might make you believe.
Strong Banking System

Canada’s banking sector is widely regarded as one of the most stable in the world, consistently ranking high in global safety indexes. Unlike in many countries, Canadian banks follow conservative lending practices, maintain robust capital requirements, and have close regulatory oversight. This has historically shielded households and businesses from severe banking crises. The resilience of banks ensures credit availability remains stable even during global downturns. Furthermore, consolidation within the sector means fewer but stronger institutions, making systemic risks less likely.
Trade Diversification Efforts

While the United States remains Canada’s largest trading partner, significant efforts have been made to diversify exports. Agreements such as the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) with the European Union and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) open access to new markets. These deals reduce reliance on a single economy and create opportunities for industries ranging from agriculture to advanced manufacturing. Trade diversification also enhances resilience during U.S. downturns, allowing Canadian firms to maintain revenue streams abroad.
Energy Transition Leadership

Canada is among the top producers of oil and gas, but it is also investing heavily in clean energy technologies. Federal and provincial policies have boosted wind, solar, and hydroelectric projects while providing incentives for green innovation. By leveraging its resource wealth to fund a transition toward low-carbon energy, Canada ensures long-term competitiveness in a world shifting toward sustainability. The growth of renewable energy jobs also diversifies employment opportunities in regions historically dependent on fossil fuels.
Immigration-Driven Workforce Growth

Population growth through immigration is one of Canada’s most significant economic advantages. At a time when many advanced economies face shrinking workforces, Canada continues to welcome skilled newcomers. Immigration policies are designed to attract workers in healthcare, technology, and skilled trades, areas with critical labour shortages. A growing population bolsters housing demand, consumer spending, and tax revenues, all of which contribute to fiscal strength. Additionally, young immigrants help balance an aging population by contributing to pension systems and healthcare funding.
Natural Resource Wealth

From minerals and forestry to freshwater and fertile farmland, Canada possesses abundant natural resources. Global demand for critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, key components in electric vehicle batteries, creates new opportunities for Canadian mining. Agricultural exports also play an essential role in global food security, giving Canadian farmers steady demand for wheat, canola, and pulses. And, with resource prices often rising during global instability, Canada’s commodities serve as a natural buffer for economic downturns.
Advanced Technology Sector

The technology sector has emerged as a major contributor to Canada’s economic future. Cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal are recognized hubs for artificial intelligence, clean tech, and software development. Investments from multinational firms alongside homegrown startups have accelerated growth in innovation-driven industries. Government programs such as the Strategic Innovation Fund provide financial support for scaling companies, while universities supply talent pipelines. This ecosystem strengthens Canada’s global competitiveness and reduces dependence on resource-based industries.
Stable Political Institutions

Political stability is a key factor for attracting global investment, and Canada consistently scores high in this area. Its democratic institutions, transparent rule of law, and consistent fiscal frameworks create an environment of predictability that investors trust. Even when governments change, major economic policies tend to evolve gradually rather than through disruptive shifts. This stability contrasts with more volatile political climates elsewhere, giving Canada a comparative advantage. Global investors value predictability as much as growth potential, meaning Canada’s ability to provide both keeps capital flowing into infrastructure, technology, and natural resources.
Growing Pension Funds
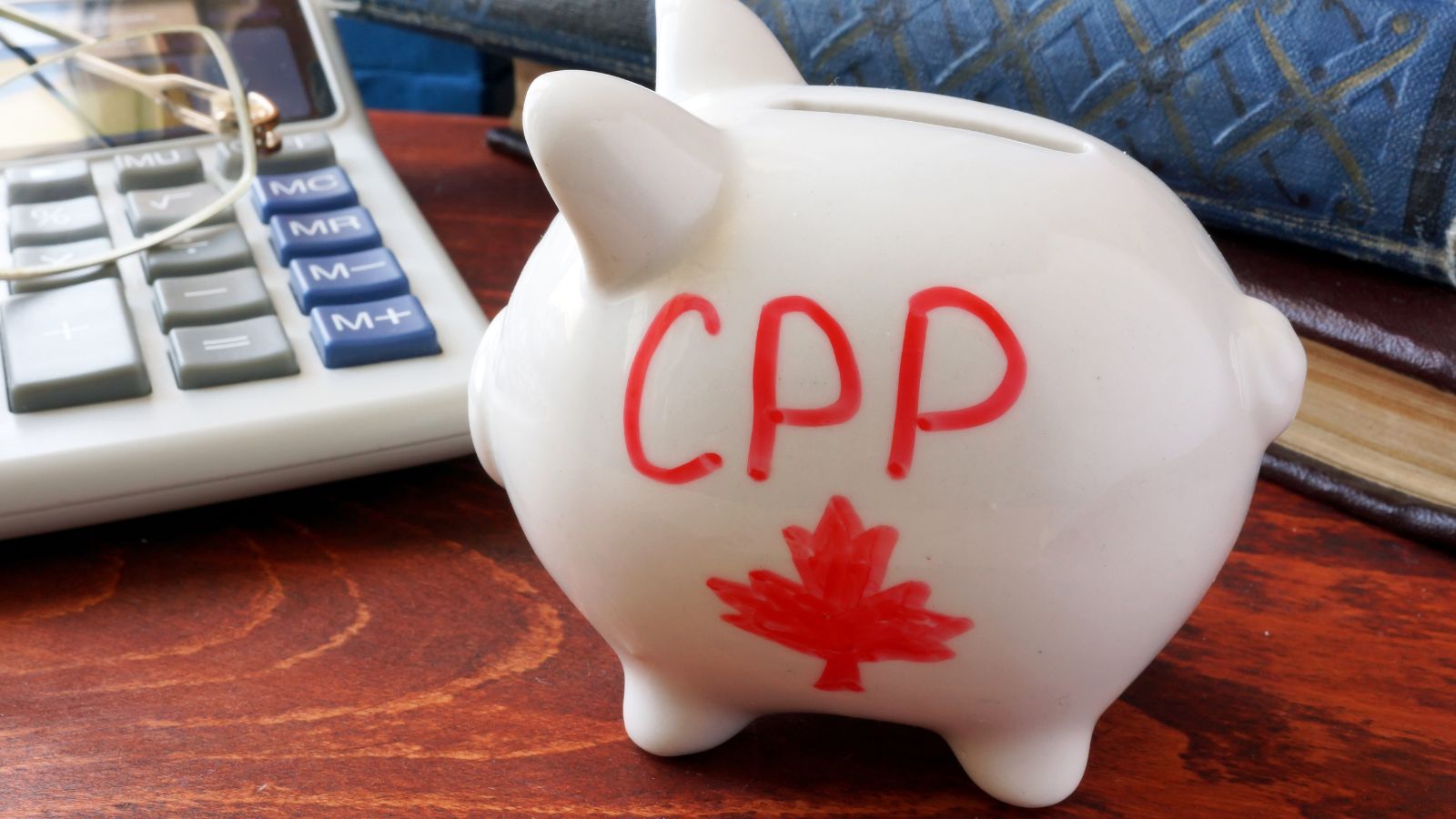

Canada’s pension system is considered one of the strongest globally, with the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) and major provincial plans managing significant assets. These funds invest strategically in global markets, real estate, and infrastructure, generating stable long-term returns. The health of pension funds ensures future retirees will have a steady income, reducing pressure on public finances. Moreover, pension funds act as major institutional investors, channeling capital into domestic projects that create jobs and stimulate growth.
Agricultural Export Strength

Canada consistently ranks among the top agricultural exporters, with products such as wheat, canola, pork, and pulses in high global demand. Food security concerns worldwide ensure steady markets for these goods. Canadian agriculture also benefits from large-scale mechanization, efficient logistics, and advanced research in crop science. Export earnings from agriculture provide stable revenues during commodity fluctuations, particularly since food demand remains relatively inelastic. Beyond exports, agriculture sustains rural communities and supports agri-tech innovation.
Urban Infrastructure Investments

Large-scale investments in urban infrastructure enhance both economic growth and quality of life. Federal and provincial governments continue to direct funds toward transit, roads, housing, and green infrastructure projects. These initiatives not only create jobs but also improve productivity by reducing congestion and modernizing systems. Infrastructure spending often has strong multiplier effects, supporting construction, technology adoption, and small businesses in local communities. Such projects also attract private sector investment and improve Canada’s long-term competitiveness in trade and tourism.
Healthcare System Resilience

While healthcare faces challenges, its universality provides long-term economic benefits. A publicly funded system ensures that medical costs do not cripple household finances, allowing consumers to maintain spending in other areas. From an employer’s perspective, universal healthcare reduces the cost burden of providing private insurance, keeping Canadian businesses more competitive globally. Additionally, investment in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare innovation is expanding, positioning Canada as a contributor to global medical solutions.
Fiscal Prudence in Public Debt

Compared to many developed nations, Canada maintains a relatively sustainable debt-to-GDP ratio. While spending increased during the pandemic, fiscal frameworks emphasize gradual deficit reduction and responsible borrowing. Independent oversight bodies regularly assess long-term sustainability, ensuring accountability. Importantly, Canada’s government borrowing costs remain manageable due to strong credit ratings. The approach to debt management balances short-term economic support with long-term fiscal responsibility. This credibility in global bond markets ensures access to financing even in turbulent times.
Strong Consumer Savings Base

Canadian households maintain significant savings, often supplemented through tax-advantaged accounts such as RRSPs and TFSAs. These savings act as buffers during economic downturns and provide capital for investment in retirement and housing. The pandemic accelerated household savings, leaving many with stronger balance sheets than before. A culture of long-term financial planning, supported by accessible financial institutions, ensures resilience against shocks. While debt levels are a concern, the existence of substantial assets and retirement accounts offsets some risks.
Education and Talent Development

Canada’s education system consistently ranks high internationally, producing skilled graduates across disciplines. Investments in research universities and vocational training ensure industries have access to the talent they require. Moreover, partnerships between academia and industry accelerate innovation in technology, healthcare, and engineering. International students further bolster the system, contributing tuition revenues while many transition into skilled workers through immigration pathways. By maintaining a highly educated population, Canada ensures workforce adaptability in rapidly changing industries.
Housing Market as a Capital Base

Despite affordability challenges, real estate remains a central pillar of household wealth. Rising property values provide families with significant equity, which in turn supports borrowing for education, entrepreneurship, and renovations. The housing sector also fuels construction jobs, material supply chains, and local services. While overheating poses risks, long-term demand driven by immigration and urbanization ensures the market remains a major store of wealth. Policymakers are gradually introducing measures to improve affordability while maintaining stability.
Expanding Renewable Resources Industry

Hydroelectricity has long been a Canadian strength, but recent investments in wind, solar, and biomass energy expand the renewable portfolio. Provinces like Quebec and British Columbia already export clean electricity to U.S. states, creating new revenue streams. Emerging industries such as hydrogen fuel production add further diversification. These sectors create jobs in engineering, manufacturing, and operations while aligning with global sustainability goals.
Tourism Recovery and Growth

Tourism has rebounded significantly following pandemic disruptions, contributing to job creation and service-sector revenues. Iconic destinations, from Banff to Niagara Falls, continue to draw millions of international visitors annually. Additionally, investments in cultural festivals, eco-tourism, and Indigenous-led tourism diversify offerings and expand regional economies. A lower Canadian dollar relative to the U.S. makes travel more affordable for foreign visitors, further boosting arrivals. Tourism spending supports hotels, restaurants, transportation, and local artisans, ensuring wide economic benefits.
Strong Legal and Regulatory Framework

Canada’s legal system is recognized for its transparency and predictability. Intellectual property protections, contract enforcement, and clear corporate governance rules create a favorable business environment. Regulatory bodies also ensure that industries such as banking, energy, and telecommunications operate responsibly. This framework reduces risks for investors and enhances consumer confidence. Stable legal protections also attract foreign companies seeking safe jurisdictions for long-term investments. By balancing oversight with flexibility, the regulatory environment sustains innovation while safeguarding financial stability.
Indigenous Economic Partnerships

Indigenous communities are increasingly becoming key players in Canada’s economic future. Equity partnerships in resource projects, renewable energy, and infrastructure developments are growing, creating shared prosperity. Indigenous-owned businesses are expanding across industries, contributing significantly to GDP. Government and private sector commitments to reconciliation are translating into new investments, workforce training, and market access. These partnerships not only generate economic activity but also build stronger communities and regional stability.
Innovation in Manufacturing

Canadian manufacturing is evolving beyond traditional models by incorporating automation, robotics, and advanced materials. Sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and pharmaceuticals have adopted high-value production methods that improve global competitiveness. Support from programs like the Innovation Superclusters Initiative fosters collaboration between firms and researchers, enhancing productivity. Export-oriented advanced manufacturing brings in stable revenues while creating skilled jobs domestically. Investments in electric vehicle assembly and battery production also signal long-term alignment with global trends.
Resilient Currency Position

The Canadian dollar benefits from the country’s resource wealth and stable institutions. While it fluctuates relative to the U.S. dollar, these movements often provide advantages, such as making exports more competitive when the dollar is weaker. Strong foreign exchange reserves and credible monetary policy from the Bank of Canada underpin confidence in the currency. A stable currency position encourages foreign direct investment, as businesses trust their returns will not be undermined by wild volatility. Currency resilience adds another layer of security to Canada’s financial system and global reputation.
Rising Global Investment Interest
Foreign investors continue to view Canada as a secure and profitable destination. Real estate, technology, and infrastructure consistently attract international capital. Canada’s membership in trade agreements, stable political climate, and resource wealth enhance its reputation as a reliable partner. Sovereign wealth funds and multinational corporations have expanded their Canadian presence, creating jobs and stimulating growth. Beyond investment dollars, these inflows bring new technologies and global expertise, further strengthening industries.
Climate Adaptation and Resilience Planning

Canada is actively investing in climate resilience, recognizing the economic costs of extreme weather. Infrastructure upgrades, disaster-preparedness programs, and green building standards reduce risks from floods, fires, and storms. These measures not only protect communities but also limit future financial liabilities. Businesses also benefit from government-supported adaptation programs that safeguard supply chains. By embedding climate resilience into planning, Canada reduces vulnerabilities that could otherwise destabilize finances.
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit

If trade tensions escalate between Canada and the U.S., everyday essentials can suddenly disappear or skyrocket in price. Products like pantry basics and tech must-haves that depend on are deeply tied to cross-border supply chains and are likely to face various kinds of disruptions
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit
