Canada has long lived in the shadow of its southern neighbor, shaped economically, politically, and culturally by U.S. influence. But in an increasingly multipolar world, it’s becoming evident that Canada has the infrastructure, talent, and independence to chart its course. From healthcare innovation to clean energy leadership, Canada is more than capable of thriving without leaning heavily on American models or markets. Here are 24 distinct areas where Canada succeeds without U.S. influence.
Strong Public Healthcare System
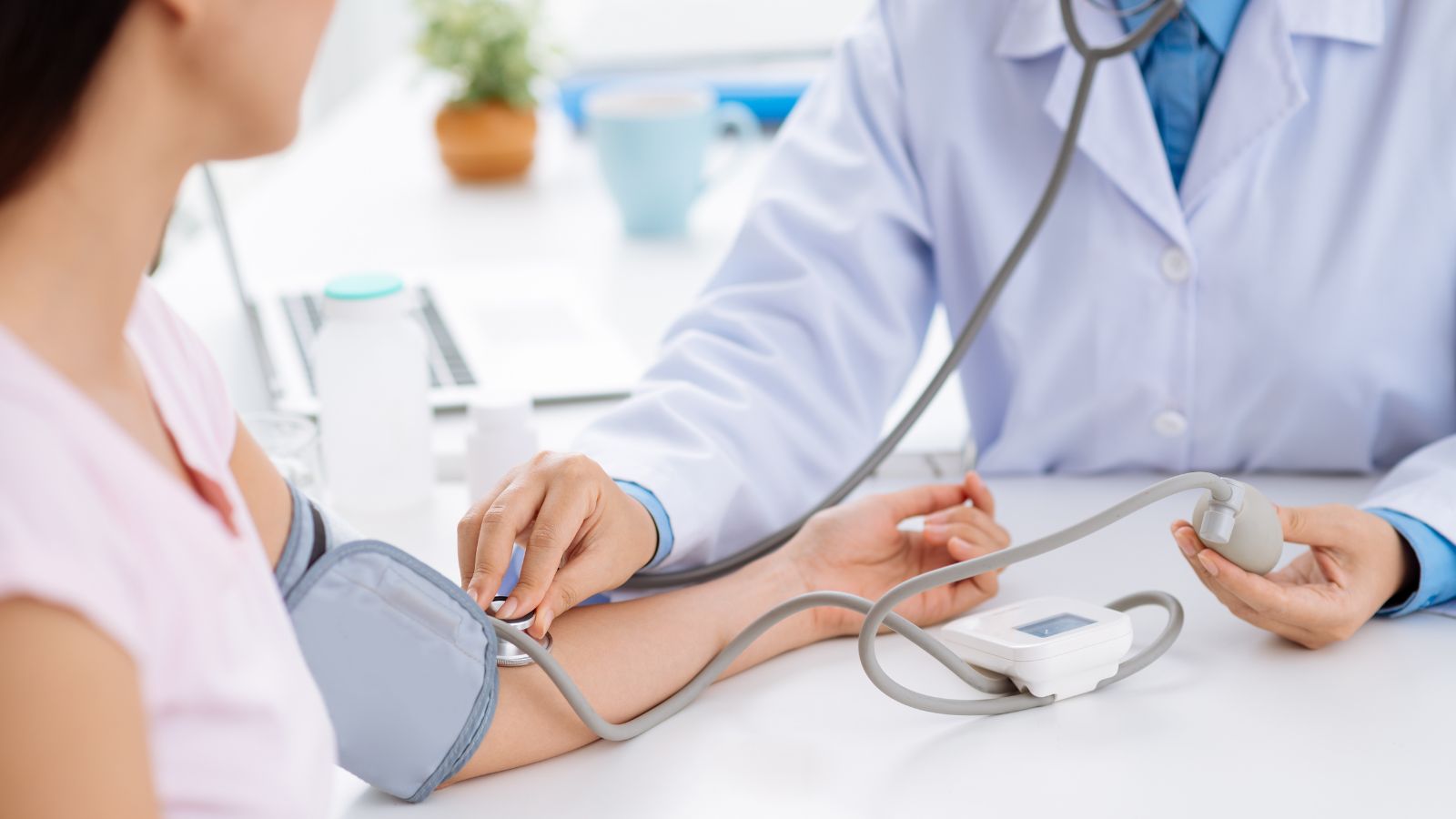
Canada’s universal healthcare model continues to function effectively without adopting the privatized framework prevalent in the U.S. By focusing on preventive care, reducing administrative costs, and ensuring equitable access, the country has created a system that supports long-term public health outcomes. The strength of Canadian Medicare enables it to operate independently of U.S. influence, demonstrating how publicly funded systems can effectively serve a modern population. The World Health Organization and OECD rankings also consistently recognize Canada’s healthcare achievements.
Economic Trade Diversification

Over the past two decades, Canada has strategically expanded trade relationships beyond the U.S. market. Agreements like CETA (with the EU), CPTPP (Asia-Pacific), and bilateral deals with countries such as South Korea and Chile have reduced reliance on the American economy. This diversification strategy has paid off during times of U.S. volatility, like the 2008 recession or recent tariff disputes. The Canadian Trade Commissioner Service actively promotes global partnerships, and Canadian exporters are now more likely to enter European or Asian markets than ever before.
Independent Immigration Policy

Canada’s immigration model prioritizes skilled migration and multicultural integration, setting it apart from the often-polarized immigration debates in the U.S. The Express Entry system and Provincial Nominee Programs are domestically controlled and tuned to labor market demands. Canada also has a higher per-capita intake of refugees than the U.S., reflecting a distinct humanitarian stance. Public support for immigration in Canada remains relatively high, and the economic contributions of immigrants are well-documented in various sectors, including technology, healthcare, and construction.
Stable Banking and Financial Sector

The banking sector in Canada is considered one of the most stable globally, a status it earned during the 2008 financial crisis when Canadian banks remained resilient as U.S. institutions collapsed. This strength stems from conservative lending practices, strong oversight by the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions, and a regulatory framework rooted in risk aversion. Canada’s Big Five banks —RBC, TD, Scotiabank, BMO, and CIBC —are globally respected and operate with substantial autonomy. Their influence in international markets shows that a prudent, Canadian-crafted approach to finance can flourish without adopting the high-risk culture often associated with Wall Street.
Sovereign Cultural Identity

Canada has maintained a distinct cultural identity through government support for the arts, strong public broadcasting (such as CBC/Radio-Canada), and content regulations that protect Canadian voices in the media. Institutions like Telefilm Canada and the Canada Council for the Arts ensure Canadian stories are told and exported globally. Unlike the U.S., where private studios dominate, Canada’s cultural sector thrives through public investment and multicultural policies. Canadian artists, from authors like Margaret Atwood to musicians like Drake, succeed internationally without compromising their Canadian identity.
Clean Energy Leadership

Canada is a global leader in clean energy, with over 80% of its electricity generated from non-emitting sources, primarily hydroelectricity. Provinces like Quebec and British Columbia power entire regions through renewable sources, reducing the need for imported fossil fuels. Investments in wind, solar, and hydrogen energy further showcase Canada’s homegrown transition to sustainability. Government initiatives such as the Net-Zero Emissions Accountability Act are developed independently of U.S. climate politics. While the U.S. continues to grapple with energy policy divides, Canada’s consistent focus on clean energy illustrates its capacity to lead in environmental matters.
Global Peacekeeping Reputation

The country has a longstanding reputation as a peacekeeping nation, often taking roles in UN missions and international mediation efforts. Unlike the U.S., which is more inclined toward military intervention, Canada often adopts a diplomatic approach rooted in multilateralism. From Rwanda to Cyprus, Canadian peacekeepers have been involved in conflict resolution efforts worldwide. This foreign policy strategy has earned Canada trust in international circles and contributes to its influence in global affairs.
Robust Public Education System

The public education system in Canada consistently ranks among the best in the world. Provinces have authority over education policy, resulting in regionally tailored curricula that reflect local needs and priorities. Programs promoting bilingualism, Indigenous education, and STEM excellence are examples of homegrown innovation. Canadian universities, such as McGill, UBC, and the University of Toronto, attract global talent without needing to emulate American Ivy League models. With high literacy rates, well-compensated teachers, and a focus on inclusion, Canada’s education system demonstrates that public investment can yield results, enabling the country to thrive without mimicking U.S. education structures.
Nationalized Resource Management

Canada’s natural resources are controlled mainly through provincial and federal policies that prioritize long-term sustainability and public benefit. Institutions like the Alberta Energy Regulator and Crown corporations like Hydro-Québec manage these resources domestically. These frameworks help ensure that profits are reinvested locally and environmental standards are enforced. Unlike the U.S., where resource extraction is often heavily privatized, Canada emphasizes regulatory oversight and public ownership.
World-Class Tech Ecosystems

Cities like Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, and Waterloo have emerged as global tech hubs, attracting investments from companies like Google, Microsoft, and Shopify. Thanks to institutions like the Vector Institute and investments in AI, clean tech, and biotech, Canada has become a magnet for innovation. Government grants, startup incentives, and visa programs for tech workers further bolster this ecosystem. While American influence is present through global corporations, the infrastructure, policies, and talent behind these hubs are distinctly Canadian.
Strong Labor Protections

Canada enforces comprehensive labor laws that ensure fair wages, safety, and job security. Policies such as paid parental leave, universal healthcare coverage for workers, and public pensions show a commitment to worker welfare that is often more generous than in the U.S. Union density, though declining, remains stronger than in many American sectors, and there’s wider public support for labor rights. Provincial governments regularly update labor codes in consultation with local unions and employers, creating a dynamic yet stable labor market.
Indigenous Reconciliation Framework

While progress is ongoing, Canada has taken structured steps toward Indigenous reconciliation through the Truth and Reconciliation Commission, land acknowledgements, and investment in Indigenous education and health services. The United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP) has been incorporated into the laws of multiple Canadian jurisdictions. These actions, though imperfect, demonstrate a willingness to confront historical injustices and promote self-determination. Additionally, the emphasis on nation-to-nation relationships with Indigenous communities is an approach shaped internally, rather than modeled on American policy.
Homegrown Food Security Policies

The country has invested in agricultural innovation, local food systems, and farm subsidies that reflect its geography and economy. Programs under Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada support small and medium-sized farms, climate resilience, and supply chain security. Initiatives like supply management in dairy, poultry, and eggs help stabilize markets and support rural livelihoods. These policies are tailored to meet Canadian needs and have been developed without external influence from U.S. agricultural lobbying.
Resilient Public Infrastructure Investment

Canada’s infrastructure investments are largely domestically funded and focused on long-term sustainability. From transit expansions in major cities to broadband connectivity in rural communities, the focus is on inclusive growth. Infrastructure Canada and the Canada Infrastructure Bank provide billions in funding without relying on American contractors or investment vehicles. Projects like the REM transit system in Montreal and the Gordie Howe International Bridge demonstrate Canada’s ability to conceive, fund, and build large-scale infrastructure initiatives.
Autonomous Judicial System

The judicial system in Canada is independently structured, with the Supreme Court of Canada as its highest court of appeal. Judges are appointed based on merit and legal experience, and the judiciary is largely insulated from political interference. Legal principles such as proportional sentencing, restorative justice, and constitutional protections under the Charter of Rights and Freedoms are distinctly Canadian. And, unlike the politicized appointment processes in the U.S., Canada’s system emphasizes impartiality and judicial independence.
Made-in-Canada Environmental Policy

Canada has developed its environmental standards, including the Canadian Environmental Protection Act and carbon pricing systems, such as British Columbia’s carbon tax. The federal government’s climate policies, including bans on single-use plastics and large-scale reforestation commitments, are enacted based on domestic science and public consultations. While the U.S. has had erratic environmental leadership, Canada’s approach has generally followed a more stable and scientifically grounded trajectory. These frameworks, supported by both public demand and legislative action, reinforce Canada’s capacity to safeguard its environment without looking to Washington for direction.
Advanced Public Transit Strategies

Urban transit in Canada is shaped by federal funding, provincial infrastructure planning, and municipal coordination. Systems like the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC), Vancouver’s SkyTrain, and Montreal’s Metro are funded and operated independently of one another. Canada’s green infrastructure funds are targeted at electrifying fleets, expanding services, and reducing emissions. American transit systems often rely on patchy funding and lag in modernization, while Canadian cities are increasingly building for accessibility and sustainability.
Francophone and Bilingual Policy Framework

Canada’s commitment to bilingualism is enshrined in the Official Languages Act. Federal services, parliamentary proceedings, and public communications are delivered in both English and French. Quebec, as a majority French-speaking province, has substantial autonomy in preserving its linguistic culture. This framework doesn’t mirror American language policy, which has no official language at the federal level. Canada’s investment in bilingual education, translation services, and multicultural integration shows how a nation can preserve linguistic duality without relying on external models. It helps reinforce a uniquely Canadian cultural and administrative identity.
Independent Global Diplomacy

Canada conducts foreign relations guided by its values of multilateralism, diplomacy, and human rights. From hosting G7 summits to contributing to global health and development through organizations such as GAVI and the WHO, Canada remains a leading global player. Unlike the U.S., which often takes unilateral positions, Canada emphasizes alliances, such as with the Commonwealth, Francophonie, and Arctic Council. Canada’s diplomatic service is highly regarded and functions independently of American interests. This enables Canada to establish global partnerships and resolve international conflicts with an identity grounded in cooperation and consensus.
Independent Monetary Policy

The Bank of Canada sets interest rates and manages inflation targets based on domestic economic conditions, rather than decisions made by the U.S. Federal Reserve. While North American economies are interlinked, the Bank of Canada has consistently demonstrated its autonomy by adjusting monetary policy to Canadian needs. Its dual mandate, to preserve purchasing power and promote economic stability, is fulfilled through evidence-based models and consultations with Canadian economic stakeholders.
Unique Legal and Constitutional Traditions

Canada’s legal foundation is rooted in both British common law and civil law in Quebec. It’s a constitutional monarchy, the Charter of Rights and Freedoms, and a parliamentary democracy form a political identity separate from the U.S. model. The constitutional amending formula ensures that major changes require broad provincial consensus, promoting unity and caution. Unlike the U.S., which operates under a presidential system, Canada’s governance structure emphasizes collective cabinet responsibility and legislative discipline. These differences result in a more pragmatic and less partisan approach to policymaking and national governance.
Arctic Sovereignty and Strategy

Canada’s Arctic strategy focuses on Indigenous partnerships, environmental protection, and a military presence through the Canadian Rangers. While the U.S. often views the Arctic through a security lens, Canada views it as a region that requires collaborative stewardship. Investment in icebreaker fleets, remote satellite communication, and Indigenous-led development initiatives highlights a strategy built on sovereignty, sustainability, and northern community resilience.
Resilient Small Business Ecosystem

Canada supports its small businesses through organizations like the Business Development Bank of Canada (BDC), federal loan programs, and localized economic development agencies. These enterprises, which make up over 98% of all Canadian businesses, are embedded in diverse regional economies. Unlike the U.S., where venture capital and Wall Street dynamics dominate entrepreneurship, Canada’s model is focused on sustainability and long-term growth. Policies on fair taxation, export development, and rural economic strategies help small businesses thrive independently.
High Social Cohesion and Trust

Canadian society benefits from high levels of social trust, public confidence in institutions, and civic engagement. These elements contribute to social stability and effective governance. The Canadian model emphasizes inclusivity, reconciliation, and social safety nets, fostering a collective approach to national challenges. Public institutions like Elections Canada and the CBC are trusted sources of democratic information, unlike in the U.S., where polarization undermines such confidence.
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit

If trade tensions escalate between Canada and the U.S., everyday essentials can suddenly disappear or skyrocket in price. Products like pantry basics and tech must-haves that depend on are deeply tied to cross-border supply chains and are likely to face various kinds of disruptions
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit
