In a world where economic gain often takes precedence, there have been moments when Canada, rather than prioritizing profits, chose to invest in its people. These decisions weren’t always easy or popular at the outset, but time and outcomes have shown their value. Here are 24 times Canada chose people over profits, and won.
Universal Healthcare

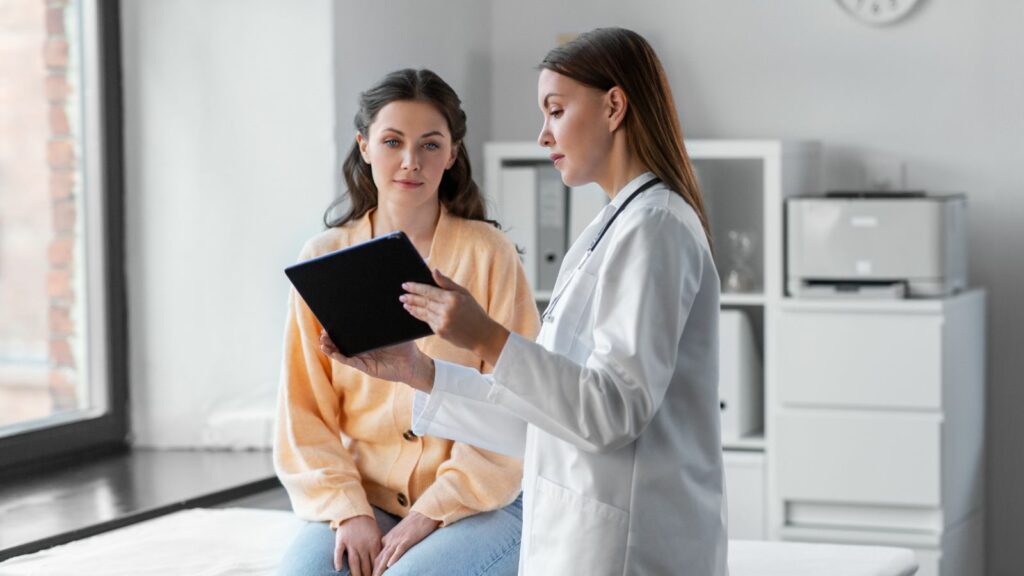
Instead of allowing a fragmented, for-profit system to take root, the government enacted universal healthcare in 1984 through the Canada Health Act. It wasn’t about efficiency metrics or insurance company returns; it was about ensuring no citizen would go bankrupt from a medical bill. Though initially costly and controversial, it has become one of the most cherished elements of Canadian identity. Long-term savings, healthier populations, and reduced administrative burden have proven that equitable access to healthcare is economically wise.
Legalization of Same-Sex Marriage
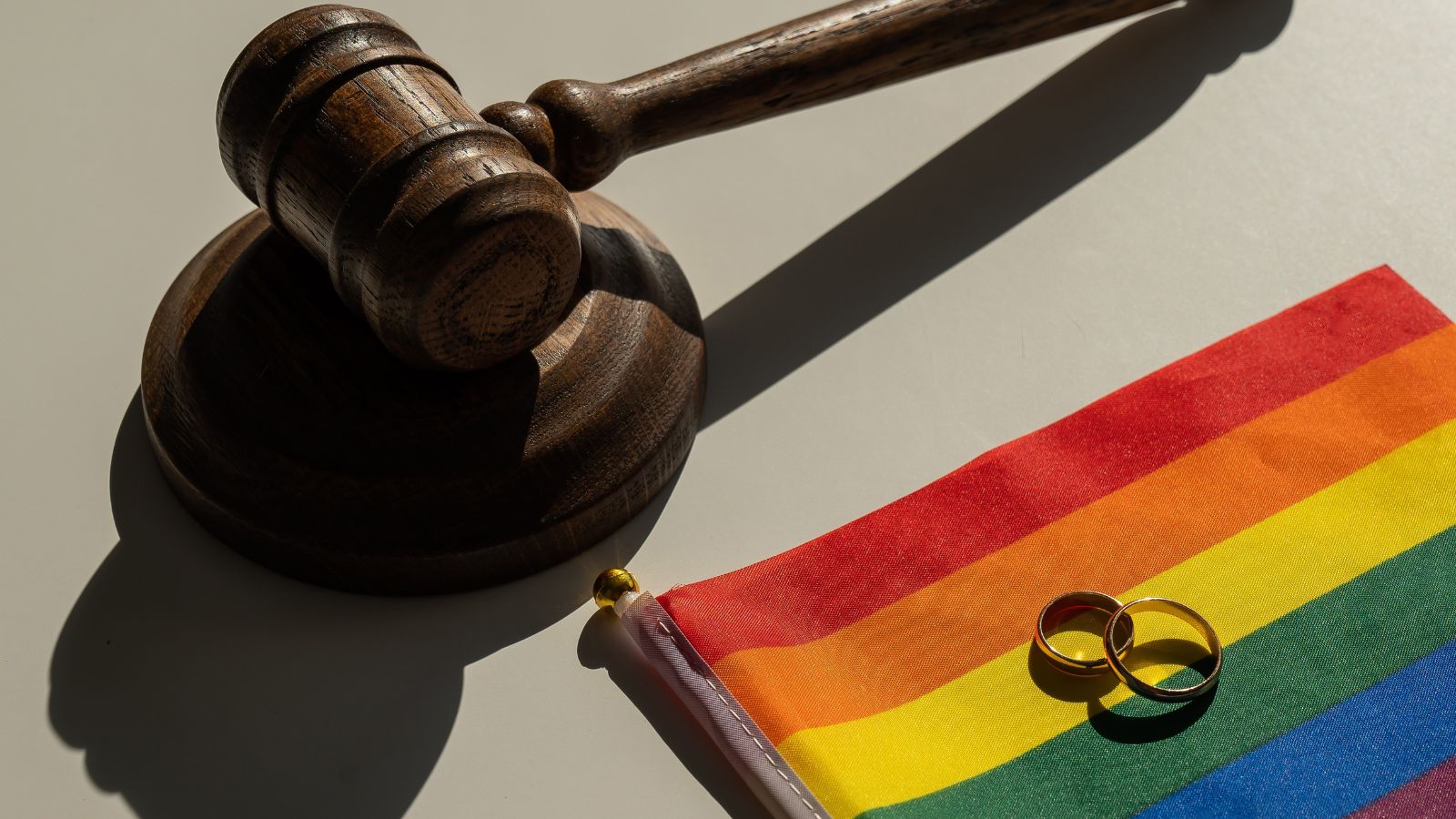

While other countries hesitated, Parliament passed legislation in 2005 granting equal marriage rights to same-sex couples. The debate stirred backlash from some sectors, including businesses worried about conservative clientele. But policymakers prioritized dignity, equality, and freedom over appeasing corporate interests. The outcome? Strengthened human rights, broader social inclusion, and international respect. Tourism and immigration from LGBTQ+ individuals seeking safety and equality also saw a boost, reaffirming that prioritizing human rights could coexist with long-term socio-economic gains.
Residential School Apology and Truth and Reconciliation Commission

Rather than ignore its colonial past to preserve national image or avoid costly reparations, the government issued a formal apology in 2008 and funded the Truth and Reconciliation Commission. The process brought painful truths to light but prioritized healing and accountability. Financially, it meant compensation packages, educational programming, and ongoing commitments. Yet, this investment helped rebuild trust with Indigenous communities, fostered national dialogue, and laid the groundwork for future cooperation.
Banning Asbestos
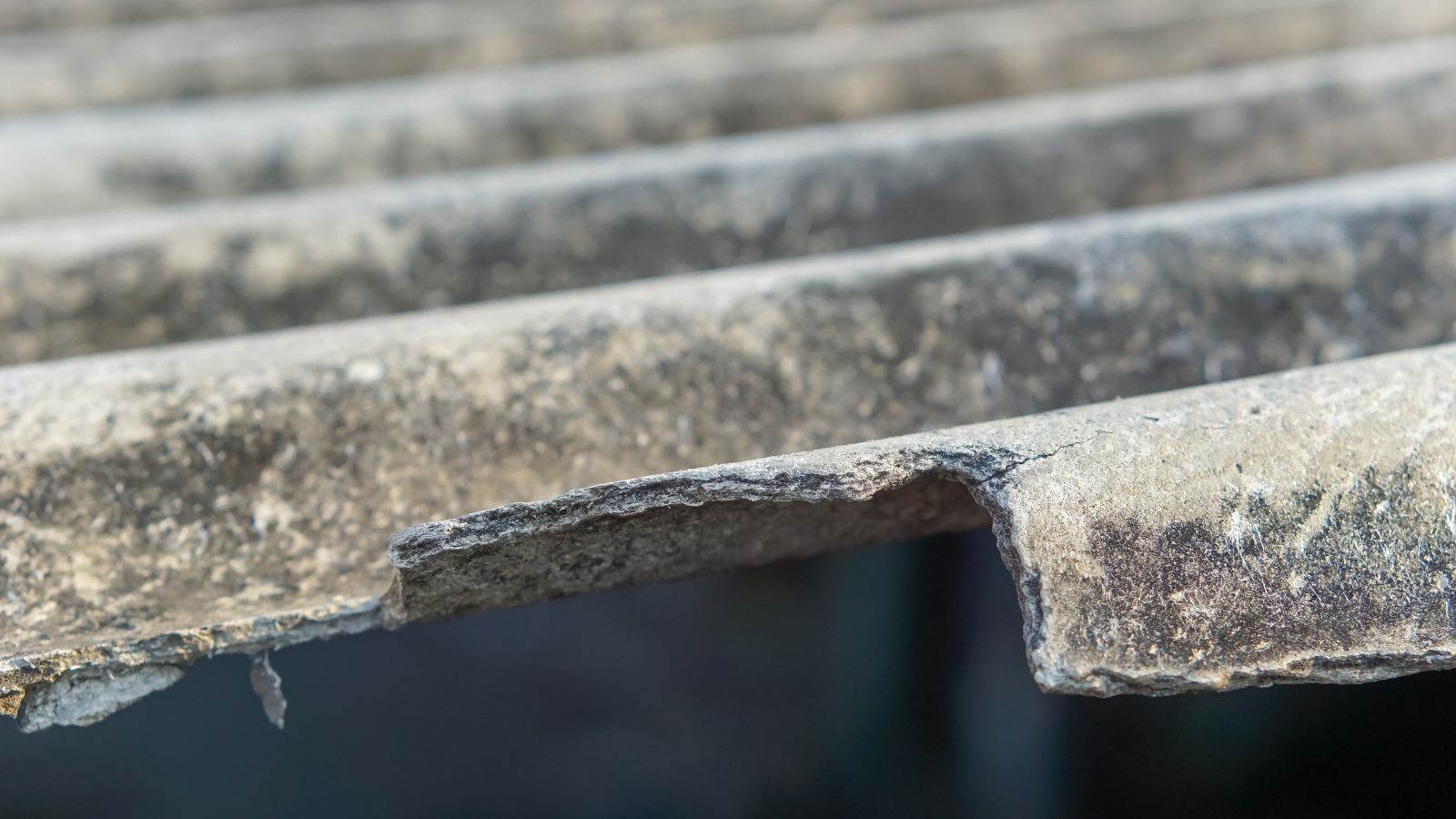

Despite its past economic significance, especially in Quebec, Canada banned asbestos in 2018. Health experts had long warned of its dangers, but industries resisted change due to profit risks. Choosing public health over industrial lobbying, the ban prioritized the lives of workers and communities exposed to carcinogenic materials. Transitioning affected regions toward safer industries required subsidies and strategic planning, but the decision is widely seen as a significant public health victory. It also improved Canada’s credibility in global occupational safety discourse.
Legalization of Cannabis

The decision to legalize cannabis in 2018 was rooted in harm reduction rather than revenue potential. Public opinion was divided, and there were fears of societal consequences. Yet the government pushed forward with regulations that focused on public safety, medical research, and decriminalization. Instead of enriching black markets or punishing non-violent offenders, the approach redirected resources to education and health. Over time, the legal framework has generated tax revenue and created jobs, but its core intent was to improve lives and reduce incarceration.
COVID-19 Emergency Response Benefits (CERB)
When the pandemic upended the workforce, the federal government launched CERB, a $2,000/month relief program for those who lost income. Critics warned about fiscal blowback and disincentivizing work. But the focus remained on keeping people housed, fed, and stable during the crisis. The measure protected millions from economic collapse, stabilized consumer demand, and maintained a semblance of national morale. It may have been expensive upfront, but its long-term benefits included faster economic recovery and reduced strain on social services.
Public Broadcasting with CBC/Radio-Canada

Rather than allowing the entire media landscape to be dictated by market forces or foreign ownership, Canada maintained a publicly funded broadcaster. This commitment ensures that even remote regions have access to news, culture, and language preservation, especially for francophone and Indigenous communities. While not consistently profitable, CBC/Radio-Canada remains a cultural pillar. Its educational programming, emergency communication capabilities, and local storytelling contribute to civic engagement and national unity.
Pharmacare Programs in Select Provinces
Although Canada has universal health coverage, prescription drug coverage remains patchy. Yet some provinces, like Ontario and British Columbia, introduced public pharmacare for youth, seniors, or low-income populations. These programs were implemented despite pressure from pharmaceutical interests and without immediate financial return. By reducing hospitalizations, improving chronic illness management, and enhancing productivity, these targeted initiatives demonstrated how choosing care over costs leads to broader societal savings.
Banning Single-Use Plastics

The federal ban on single-use plastics, beginning in 2021, was implemented despite pushback from manufacturers and retail lobbies. The environmental impact of plastic waste far outweighs the convenience or profitability of such products. The ban aimed to protect marine ecosystems, reduce landfill overflow, and promote sustainable alternatives. While businesses had to adapt, the shift catalyzed a growing green economy. Over time, consumers embraced reusable goods, validating the initial risk.
$10-a-Day Childcare Agreements
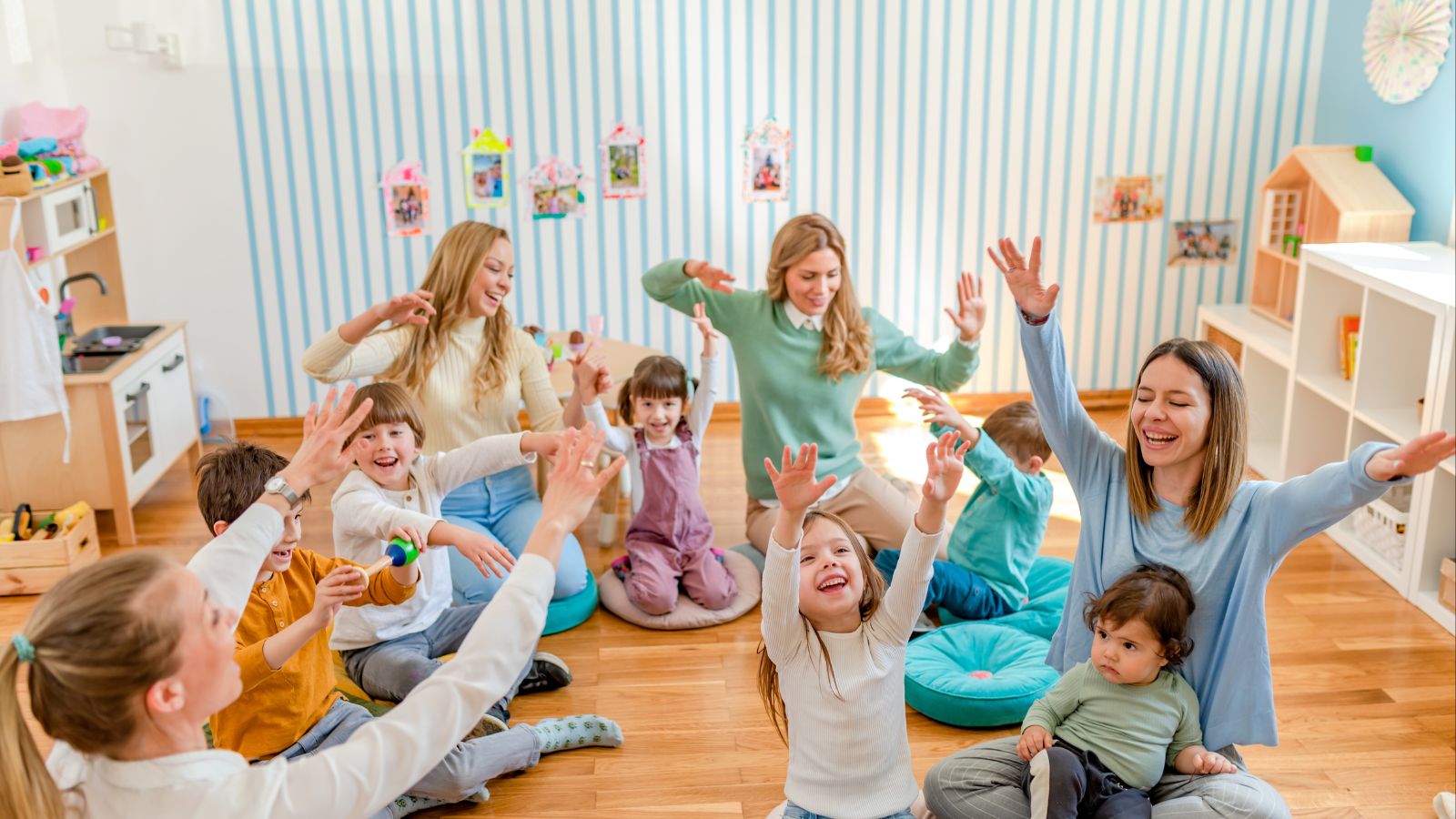

Collaborating with provinces and territories, the federal government launched a plan to lower childcare costs to $10/day. Although costly to implement and manage, the initiative aimed to make childcare accessible, especially for women re-entering the workforce. Rather than leave this sector to market pricing, the approach centered on equity and long-term development. Early results show higher participation in the workforce and improved early childhood outcomes, proving that social infrastructure can pay dividends.
Support for Ukrainian Refugees

Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Canada fast-tracked visas and offered support for displaced Ukrainians, including work permits and temporary housing. This decision prioritized humanitarian aid over logistical and fiscal concerns. The response was swift, generous, and coordinated with community groups. While not immediately profitable, this act of solidarity strengthened diplomatic alliances and enhanced Canada’s global reputation as a welcoming and principled nation.
Decriminalization of Suicide and Mental Health Investment

Past laws in Canada criminalized suicide attempts. Over the years, these statutes were removed, and investment in mental health services increased. This shift acknowledged mental illness as a public health issue, not a criminal one. Governments allocated funding for helplines, youth programs, and psychiatric care. The focus moved from punishment to prevention. These reforms led to broader awareness, destigmatization, and reduced suicide rates in several demographics, illustrating the effectiveness of prioritizing care over condemnation.
Ban on Conversion Therapy

Despite lobbying from certain religious and ideological groups, the federal government passed legislation banning conversion therapy practices in 2021. The decision followed years of advocacy from survivors and mental health professionals. The law sends a clear message that identity is not a disorder. It was less about legislative popularity and more about protecting vulnerable communities. The policy bolstered LGBTQ+ protections and encouraged a more inclusive, trauma-informed society.
Minimum Wage Increases in Multiple Provinces

Several provinces opted to increase minimum wage despite protests from business groups predicting job losses. These decisions were framed around lifting workers out of poverty and reducing income inequality. Though some sectors faced short-term adjustments, research indicates that increased earnings translated into better health, education, and stability for low-income families. In many cases, higher wages also stimulated local economies through increased consumer spending.
Banning Harmful Cosmetic Testing on Animals

In 2023, legislation was passed prohibiting animal testing for cosmetics. Companies were required to reformulate or adopt cruelty-free testing models. The move was widely supported by animal welfare groups but opposed by segments of the beauty industry, citing research delays and costs. However, consumer demand shifted toward ethical products, and many Canadian brands gained international recognition for cruelty-free practices. The law reaffirmed a moral stance that aligned public policy with evolving societal values.
Indigenous Protected and Conserved Areas (IPCAs)
Governments partnered with Indigenous communities to co-manage and protect large tracts of ecologically sensitive land. These agreements prioritized environmental stewardship and Indigenous sovereignty over resource extraction profits. They often required foregoing lucrative mining or development projects. The long-term benefits include biodiversity preservation, cultural revitalization, and climate resilience. By recognizing Indigenous rights and knowledge systems, Canada charted a path toward more sustainable conservation strategies.
Banning Trans Fats

Health Canada officially banned artificial trans fats in 2018, following decades of research linking them to increased risks of heart disease, stroke, and other chronic conditions. Despite resistance from parts of the food industry due to reformulation costs and shelf-life concerns, public health prevailed. The measure pushed food producers to adopt healthier ingredients and increased consumer awareness about nutrition. Since its implementation, the regulation has led to a decline in trans-fat-related health complications, reducing strain on the healthcare system and fostering a healthier national food supply.
Accessible Canada Act

The Accessible Canada Act, enacted in 2019, sought to make all federally regulated workplaces and services barrier-free by 2040. It introduced legal obligations for accessible employment, transportation, information technology, and built environments. Implementation required investment in infrastructure, training, and systemic redesigns. Although costly, it improved daily life for millions of Canadians with disabilities and spurred innovation in inclusive design. The legislation advanced civil rights and ensured broader participation in public life, reaffirming a national commitment to equity over convenience or immediate return on investment.
Creation of Public Pension Plans (CPP/QPP)

The Canada and Quebec Pension Plans, introduced in the 1960s, ensured working Canadians would have a reliable source of income upon retirement. Though controversial at inception due to required payroll contributions, the plans aimed to reduce senior poverty and ease reliance on family or welfare systems. Administered publicly and shielded from market volatility, CPP/QPP has become one of the most successful social safety nets in the country. It demonstrated that long-term planning focused on dignity and stability can outperform short-term market gains.
Banning Coal-Fired Power Plants
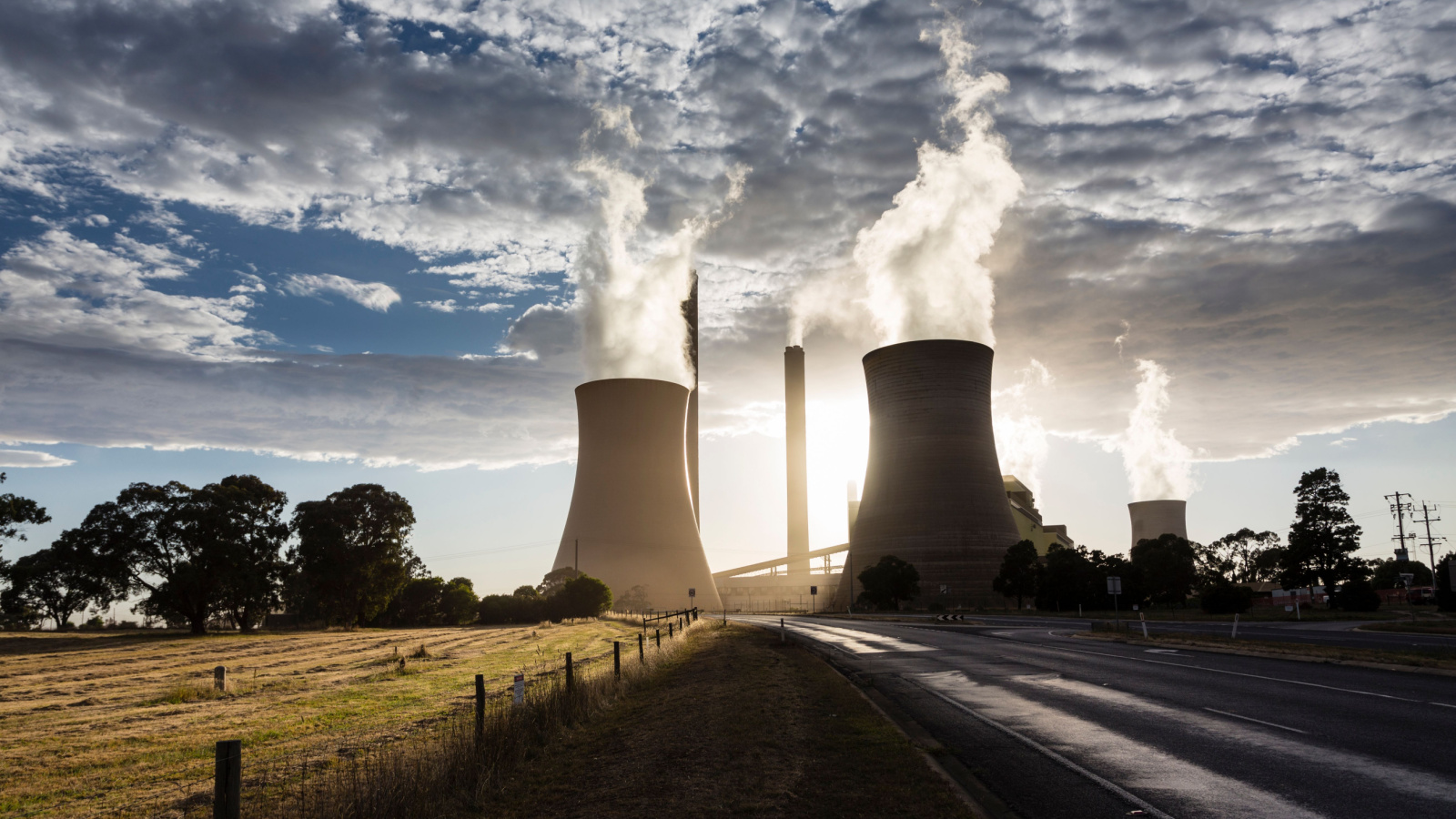

Coal once powered large swaths of Canadian industry and homes, particularly in Alberta and Ontario. Recognizing the environmental and public health costs, governments began phasing out coal plants, culminating in complete bans in key provinces. This shift involved economic sacrifices, retraining workers, and infrastructure investment. However, the result has been a marked improvement in air quality and emissions reduction. The transition also stimulated growth in the renewable energy sector, showing that prioritizing environmental health can generate economic and public health benefits.
Inclusive National Census Questions

In recent years, Statistics Canada updated the national census to collect data on gender identity, sexual orientation, and housing instability. These changes allowed for more accurate reflections of the country’s diversity, despite criticism from those who viewed the questions as unnecessary or invasive. The improved data helped tailor social programs, healthcare services, and housing initiatives to meet actual needs. This evidence-based policymaking model fostered inclusion, allowed for better resource allocation, and supported communities often left invisible in traditional surveys.
Safe Supply Programs for Opioid Users

Facing an opioid crisis with record overdose deaths, some provinces launched safe supply initiatives, offering controlled, pharmaceutical alternatives to toxic street drugs. The controversial strategy focused on harm reduction rather than criminalization. Despite initial skepticism, pilot programs showed decreased mortality rates, fewer emergency room visits, and improved stability for users. These programs reshaped addiction treatment by treating it as a health issue, not a criminal one.
Anti-Scab Labour Legislation

Several provinces enacted anti-scab laws to protect the integrity of labour strikes by prohibiting employers from hiring replacement workers during legal labour disputes. While some businesses feared disruptions, the legislation balanced employer-employee power dynamics and encouraged genuine negotiation. It reduced the frequency and length of conflicts by fostering respectful dialogue. These laws elevated labour rights, supported union strength, and promoted fair working conditions.
Free Public Libraries and Internet Access

Public libraries have evolved into community lifelines offering more than just books. With investments in free internet access, literacy programs, and inclusive public spaces, libraries serve newcomers, job seekers, and low-income families alike. Despite being non-revenue-generating institutions, municipalities continue to fund them, recognizing their social value. These services promote digital literacy, equal opportunity, and lifelong learning.
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit

If trade tensions escalate between Canada and the U.S., everyday essentials can suddenly disappear or skyrocket in price. Products like pantry basics and tech must-haves that depend on are deeply tied to cross-border supply chains and are likely to face various kinds of disruptions
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit

