Global supply chains are some of the most important pillars in international trade and commerce, connecting suppliers directly to producers and consumers further down the chain. Contemporary global supply chains have been marred by increased complexity and, even more lately, the COVID-19 pandemic, tense geopolitics, and climatic conflicts. Risks in the chain have increased since disruptions in industries worldwide have been severe, leaving most with new vulnerabilities that have never been seen before. Here are 20 startling new risks emerging from global supply chain disruptions.
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars

Geopolitical tensions between stronger economies such as the United States and China created trade wars with increasing sanctions and tariffs, which made it very difficult to have harmonious global supply chains. Political drivers encourage companies to revisit their supply chain strategies for sourcing products, potentially increasing costs and time spent during manufacturing.
Pandemic-Induced Production Shutdowns

The COVID-19 pandemic has proven how quickly production facilities can be shut down due to serious health concerns. Such events, pandemics, or health crises can happen again, and the just-in-time production model will become significantly riskier and unsustainable.
Raw Material Shortages
Global supply chain disruptions have led to a worldwide shortage of essential raw materials, such as semiconductors, rare earth metals, and lithium, which is impeding production in the electronics, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. Due to the shortage, prices have increased, and the resources are competitively acquired.
Increased Freight and Shipping Costs

Shipping costs have risen significantly over time due to shortages of containers, higher fuel prices, and disruptions at major ports. This increase translates into higher prices for consumers, directly contributing to inflation and diminishing the purchasing power of most consumers.
Port Congestion and Delays

Major global ports are now at full capacity, and congestion has become a very common occurrence, resulting in unreasonable delays. These bottlenecks are created largely due to labor shortages, environmental regulations, and excessive demand, creating unpredictable factors that disrupt shipping schedules.
Environmental Regulations and Carbon Footprints

Climate change has dramatically received international attention and scrutiny, leading to more stringent environmental regulations. This also increases the pressure on companies to reduce their carbon footprint while increasing the cost of operations and, subsequently, altering strategies for supply chain development.
Political instability in important regions

Political instability may be possible in countries critical to the global supply chain, such as Southeast Asia, Africa, or Latin America. This will lead to unsystematic and unforeseen disruptions in sourcing and manufacturing.
Natural Disasters and Climate Change
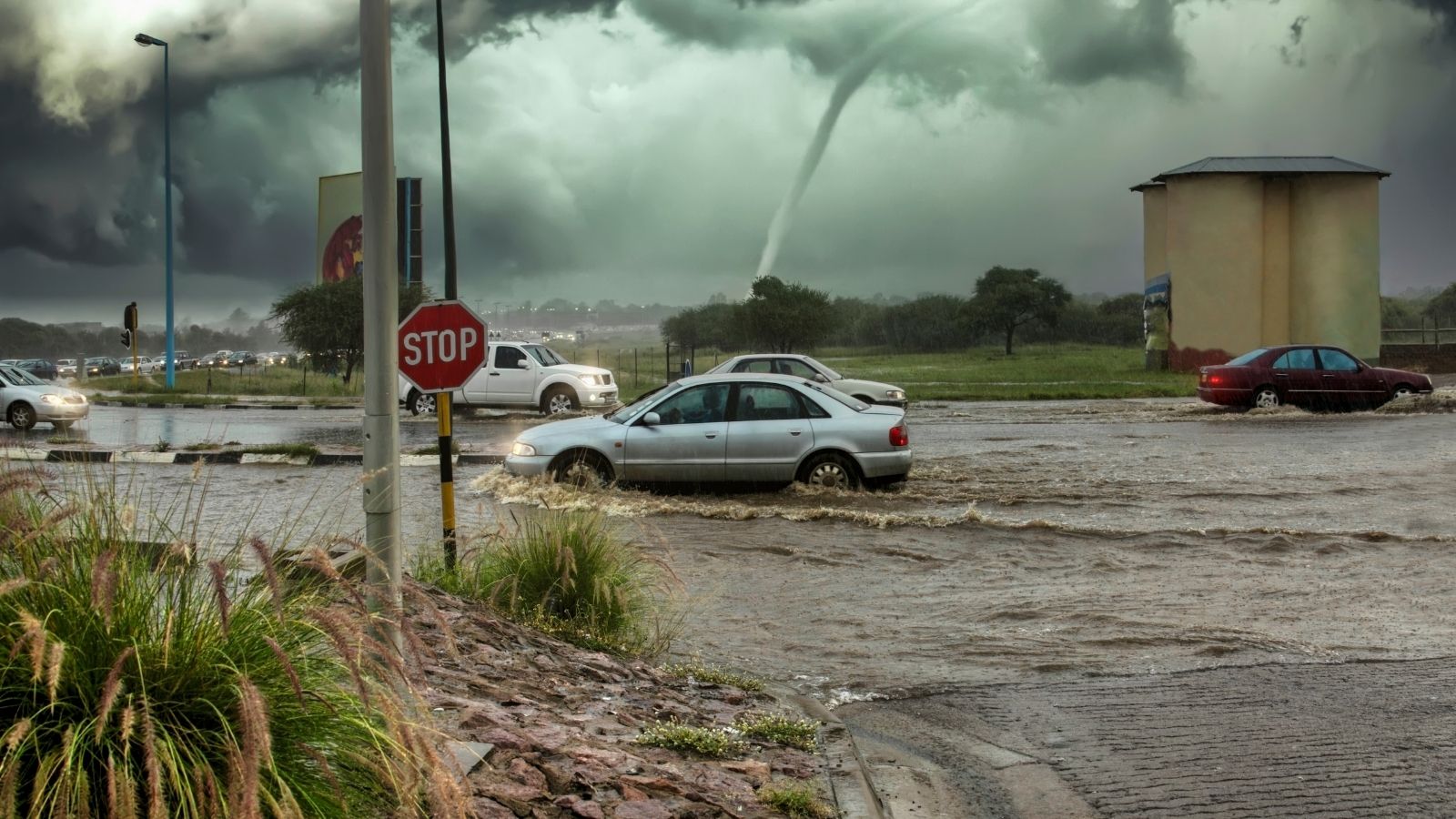

Hurricanes, flooding, and wildfires are more intense and frequent due to climate change. Such phenomena generally disrupt transportation routes, damage the infrastructure, and lead to a shortage of raw materials, further dealing a heavy blow to the existing global supply chains.
Labour Shortages

The skills shortage in the global labor market, especially in logistics and transportation, as well as manufacturing sectors, is at an all-time high. Shortages usually force production schedules to be delayed, deliveries to slow, and operational costs to increase.
Cyber Threats

Digitalization has made supply chains more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ransomware attacks, data breaches, and system shutdowns can create immunity for supply chain operations, while financial losses and reputational damages impact the bottom line.
Increased Compliance and Regulatory Requirements

Global supply chains are often subject to a more complicated network of regulatory requirements, such as labor laws, safety standards, and environmental guidelines. A flood of those regulations puts an administrative burden on them and heightens the risk of compliance failures.
Inflationary Differences in Currency Exchange Rates
Fluctuating currency exchange rates can almost directly impact the cost of imported items. Companies with global supply chains are typically more susceptible to changing circumstances, which may squeeze profit margins and make it difficult to establish the price.
Supplier Dependencies

Over-reliance on a single supplier or region can create significant risks for businesses. If a company depends heavily on one supplier, it becomes vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. Events such as natural disasters, political instability, or financial crises affecting that supplier can paralyze the entire supply chain, leading to delays and increased costs.
Change in Consumer Preferences

The pandemic indeed changed the very way in which people behave as consumers; this shifted demand. Thus, with all this immense development of e-commerce and unprecedented demand for certain products—thinking electronics and home goods—the new pressure on supply chains to accommodate all these changes in consumer expectations will require flexibility and an agile approach in these new ways of thinking.
Supplier Bankruptcy and Insolvency

Economic uncertainty and financial instability often lead to supplier bankruptcies. When a supplier fails, it can disrupt production processes and create significant challenges in the supply chain. This disruption may force businesses to seek alternative sources quickly to maintain operations and minimize losses.
Vulnerability in the Transportation Network

The global transportation network, particularly in ocean freight, is highly susceptible to disruption. Incidents like the blockage of the Suez Canal highlight how a single point of failure can have far-reaching consequences for global trade routes, causing delays and ripple effects throughout the supply chain.
Disruptions in Energy Supply

Global energy markets are becoming more volatile. Disruptions in the activities of the oil, gas, and electricity supply chains were affecting manufacturing and transportation. Shortages or price increases in energy could slow down production lines and raise the cost of operations.
Reputational Risks
Consumers hold companies responsible for their supply chain practices, especially in terms of labor conditions, the environment, and ethical sourcing. A scandal or misstep can destroy the reputation of a brand, and it can lose customers.
Changes in Trade Agreements

Since governments start altering or discontinuing trade treaties, businesses must change supply chain strategies to accommodate new tariffs, new trade barriers, and new import/export restrictions with which they may have to contend.
Technological Advancements and Automation Risks

It is not to say that automation and AI-driven processes are not efficient. They come with new risk concerns: over-reliance without proper systems in place may result in spectacular failures when systems fail or are cyberattacked.
Conclusion

The global supply chain is more complex and interconnected than ever, introducing a range of risks. From geopolitical tensions and natural disasters to cybersecurity breaches and labor shortages, these threats signal a new wave of disruption that could reshape how businesses operate. To navigate this challenging landscape, companies should proactively diversify their supply chains, adopt new technologies, and strengthen their resilience against future shocks. By understanding and responding to these emerging risks, businesses can better address the challenges of the modern international supply chain and continue to thrive in an increasingly unpredictable world.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
