The impact of social media on youth culture is undeniable and ever-growing. Over the past decade, social media platforms have transformed how young people connect, learn, entertain themselves, and perceive the world. While there are undeniable benefits, such as increased connectivity and access to information, the darker side of social media has sparked concern among parents, educators, and mental health experts. Here are 18 alarming ways social media is reshaping youth culture and influencing the lives of young people.
The Surge in Screen Time

The average teenager now spends around 7-9 hours per day using screens, with a large chunk of that time devoted to social media. This marked increase in screen time has led to more sedentary lifestyles among youth, contributing to physical health issues like obesity and posture problems. The digital world has become a primary source of entertainment, often at the expense of outdoor activities and physical play.
Promoting Unrealistic Beauty Standards

Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat are filled with images of seemingly perfect bodies, flawless skin, and luxurious lifestyles. For young people, exposure to these unrealistic beauty standards can result in negative body image and self-esteem. Filters and editing tools make it difficult to differentiate between reality and digital enhancements, perpetuating a distorted view of beauty and contributing to mental health issues, including eating disorders.
The Rise of Cyberbullying

Bullying has transcended the schoolyard and found a more pervasive and insidious platform online. About one in three young people report having been a victim of cyberbullying. Social media’s anonymity can embolden bullies, leading to more severe and long-lasting emotional harm. Victims may experience anxiety, depression, and, in extreme cases, suicidal thoughts.
Worsening Mental Health
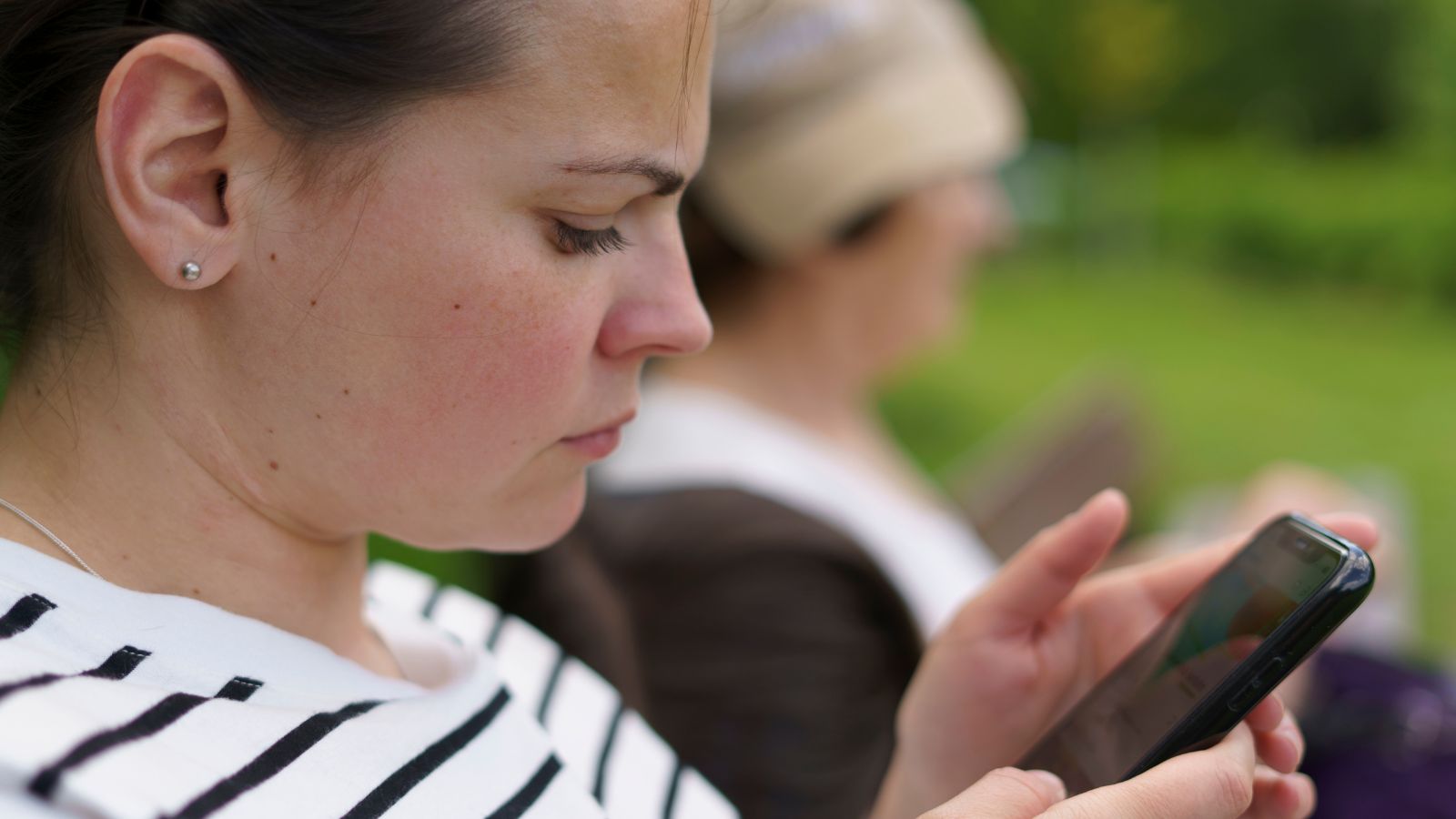

Heavy social media use is closely linked to a rise in anxiety, depression, and feelings of loneliness among teens. The curated highlight reels of friends and influencers create a false impression of constant happiness and success, making users compare themselves unfavorably. The pressure to present a “perfect” life can be overwhelming, especially for young people still developing their identity.
Sleep Disruption
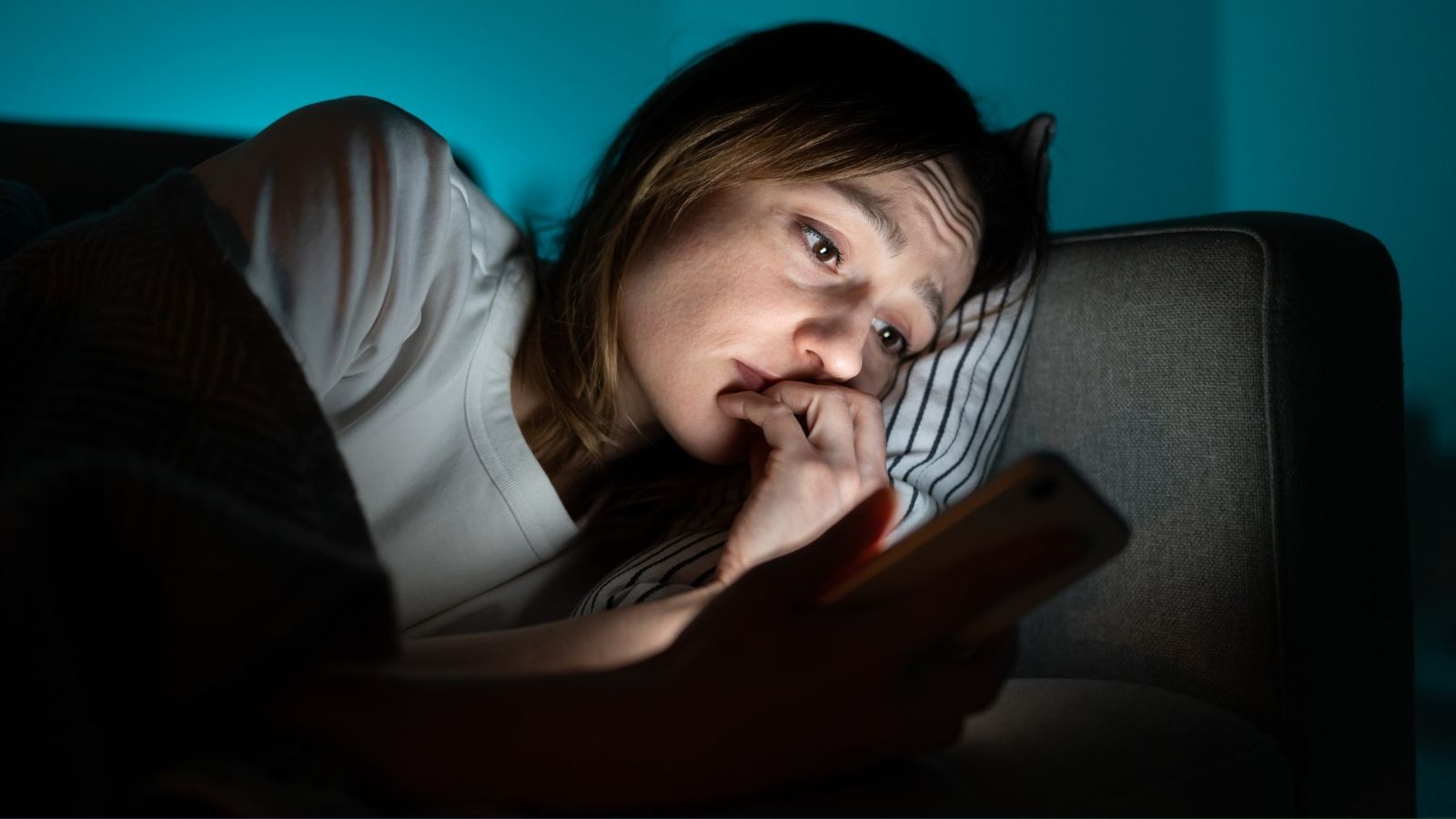

Social media’s “always-on” nature means that notifications can arrive at any hour, prompting teens to stay up late or wake up at night to check their devices. The blue light emitted by screens further disrupts sleep patterns by interfering with the production of melatonin (a hormone that regulates sleep). Inadequate sleep negatively affects concentration, academic performance, and overall well-being.
The Decline of Attention Spans
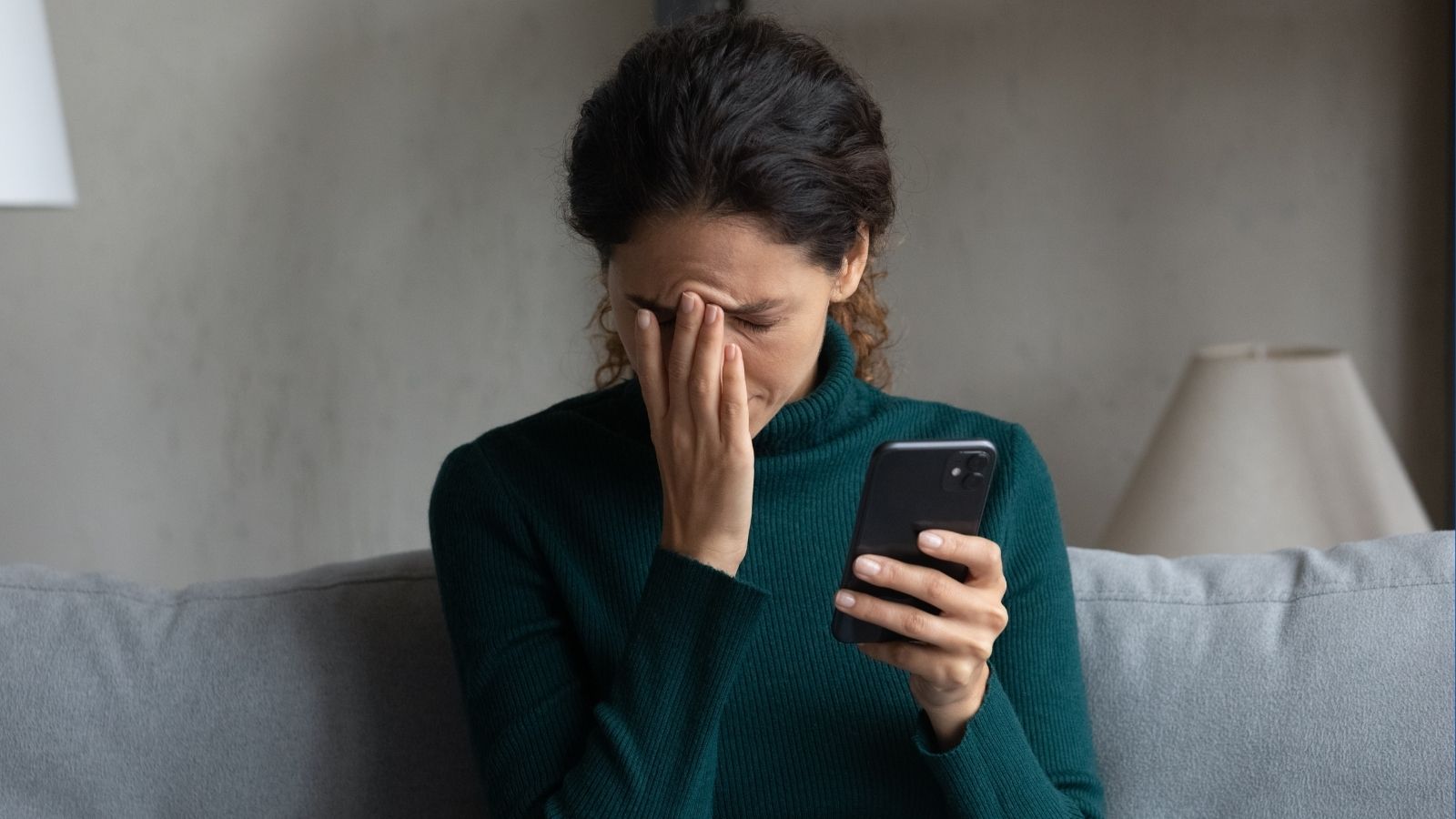

The quick, bite-sized content typical of social media, like short videos and rapid scrolling, has conditioned young people to expect immediate gratification. As a result, attention spans are shrinking, making it harder for teens to engage in prolonged tasks such as reading, studying, or even having in-depth conversations.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
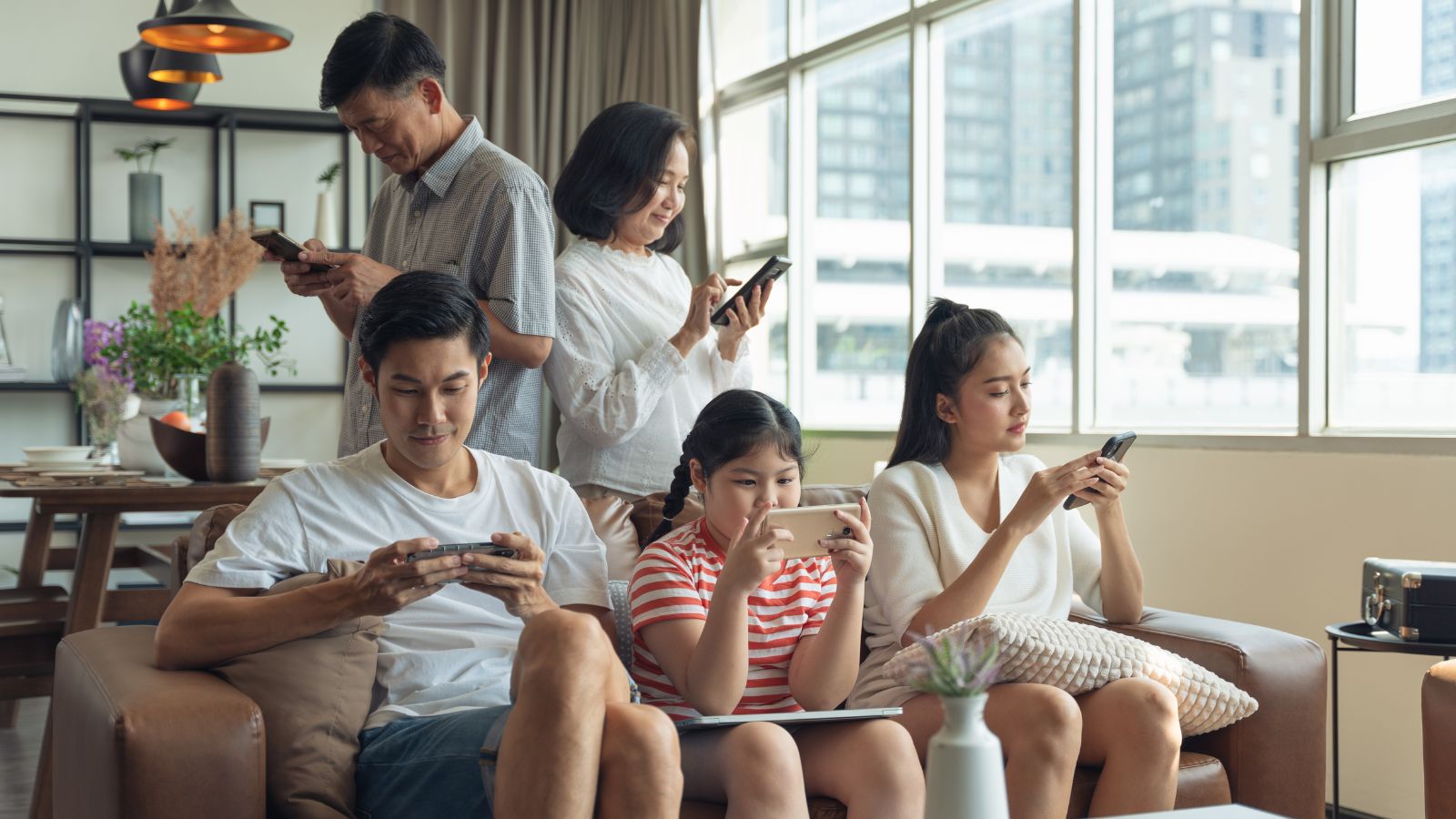

The fear of missing out has become more prominent in youth culture, as social media provides constant updates showcasing friends’ activities, events, and achievements. Seeing others engage in enjoyable experiences can evoke feelings of exclusion, inadequacy, and envy, leading to social anxiety and a compulsive need to stay connected.
Amplified Peer Pressure

Social media amplifies traditional peer pressure by constantly exposing young people to their peers’ behaviors and lifestyles. From fashion choices and prevalent challenges to more risky behaviors like substance use and sexting, teens may feel pressured to conform to gain acceptance or avoid being ostracized. This digital peer pressure can push young people towards choices they wouldn’t otherwise make.
Signs of Social Media Addiction

Many young users exhibit behaviors consistent with addiction, such as compulsive checking and distress when they are unable to access their accounts. The reward system created by likes, comments, and shares can lead to a dependency on social media for dopamine hits, causing withdrawal symptoms similar to those of other behavioral addictions.
Living in Echo Chambers

The algorithms that power social media are designed to show users content that aligns with their interests and beliefs. While this might enhance the user experience, it also reinforces confirmation bias and limits exposure to diverse perspectives. Youth increasingly consume content that mirrors their views, potentially fostering intolerance and limiting critical thinking.
Self-Worth Tied to Online Approval

The quest for likes, followers, and comments can lead young people to equate their self-worth with their social media presence. The pressure to maintain a curated and appealing online identity can negatively impact mental health, causing feelings of inadequacy when posts don’t receive the expected level of engagement.
Exposure to Inappropriate Content
Despite age restrictions on most platforms, young people can easily access explicit or harmful content, ranging from violent videos to graphic imagery. This exposure can have a desensitizing effect, potentially skewing young people’s understanding of reality, morality, and acceptable behavior.
Declining Face-to-Face Social Skills
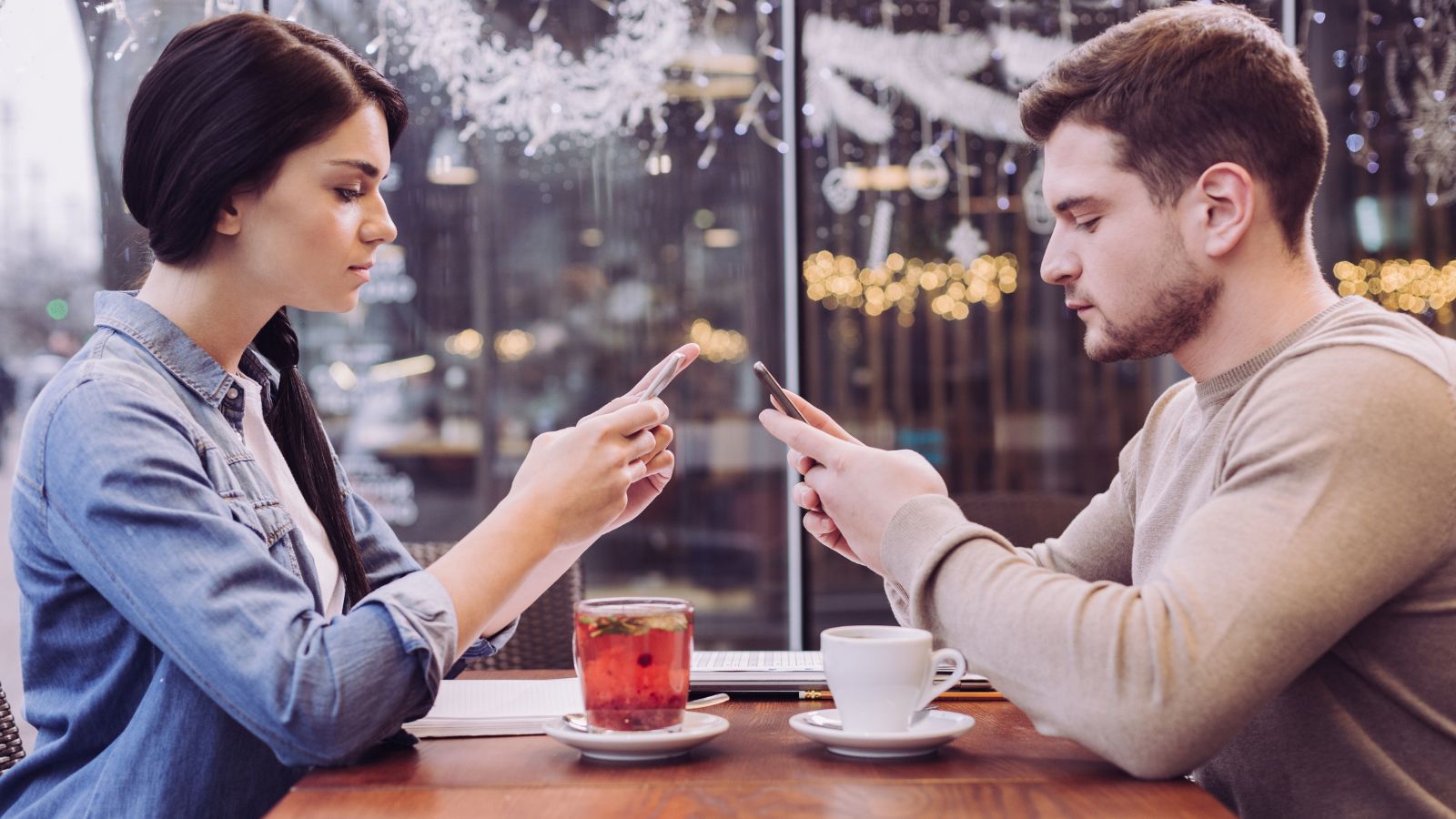

With so much online communication, some young people struggle to engage in meaningful face-to-face interactions. Overreliance on digital communication may impair the development of essential social skills, such as interpreting body language, understanding tone, and developing empathy in real-world settings.
Dopamine Dependency
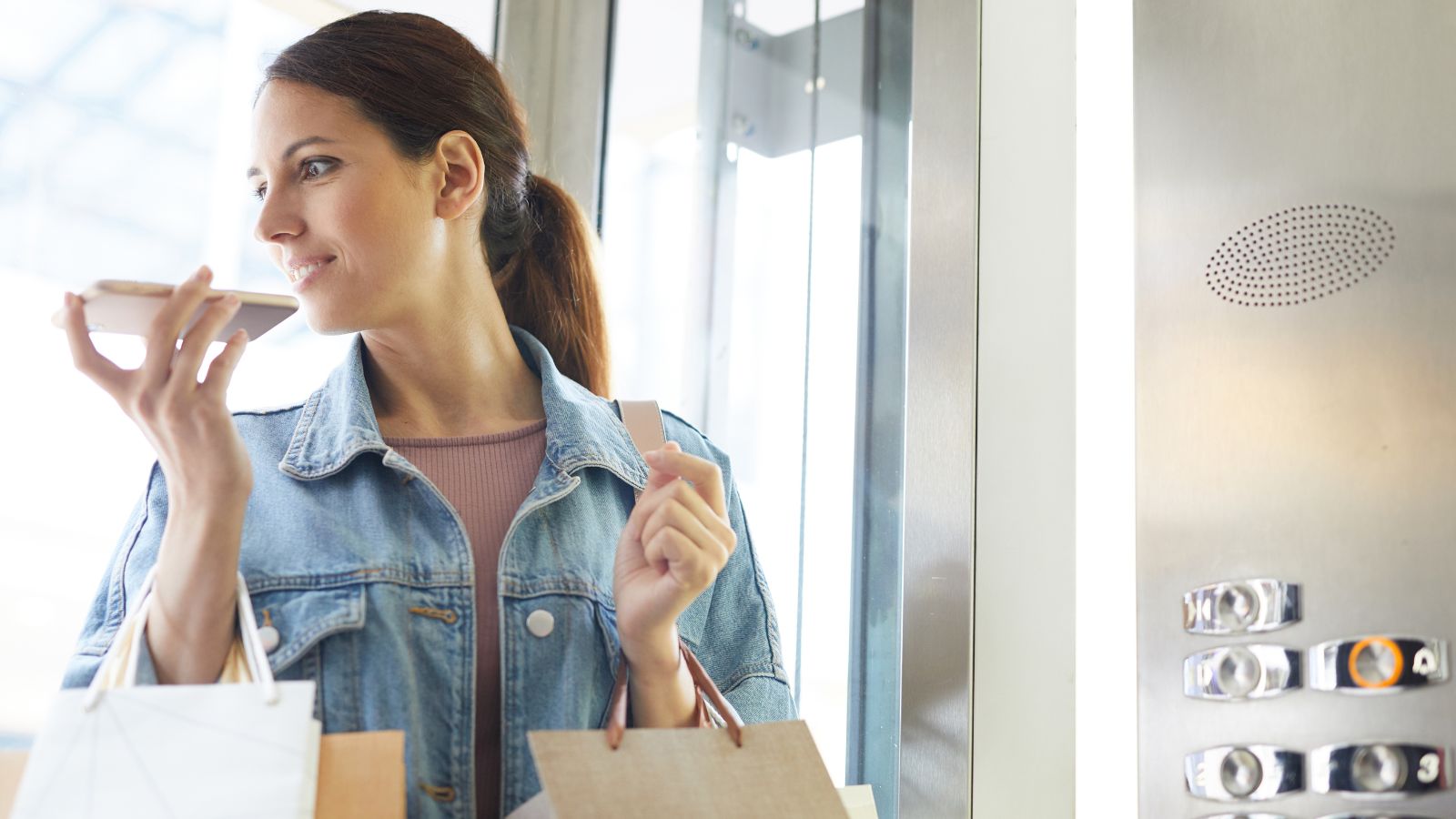

The instant gratification provided by social media notifications triggers dopamine release, leading to a cycle of reward-seeking behavior. This dependency on dopamine hits from likes and comments can reduce motivation for other, more fulfilling activities, such as sports, hobbies, or spending time with family and friends.
Increasing Political Polarization
Social media’s role in promoting sensationalist or divisive content contributes to heightened political polarization. Algorithms often prioritize content that provokes strong emotional reactions, making it easier for young people to become entrenched in their views and more difficult for them to engage in constructive political discussions.
Influence of the Influencer Culture
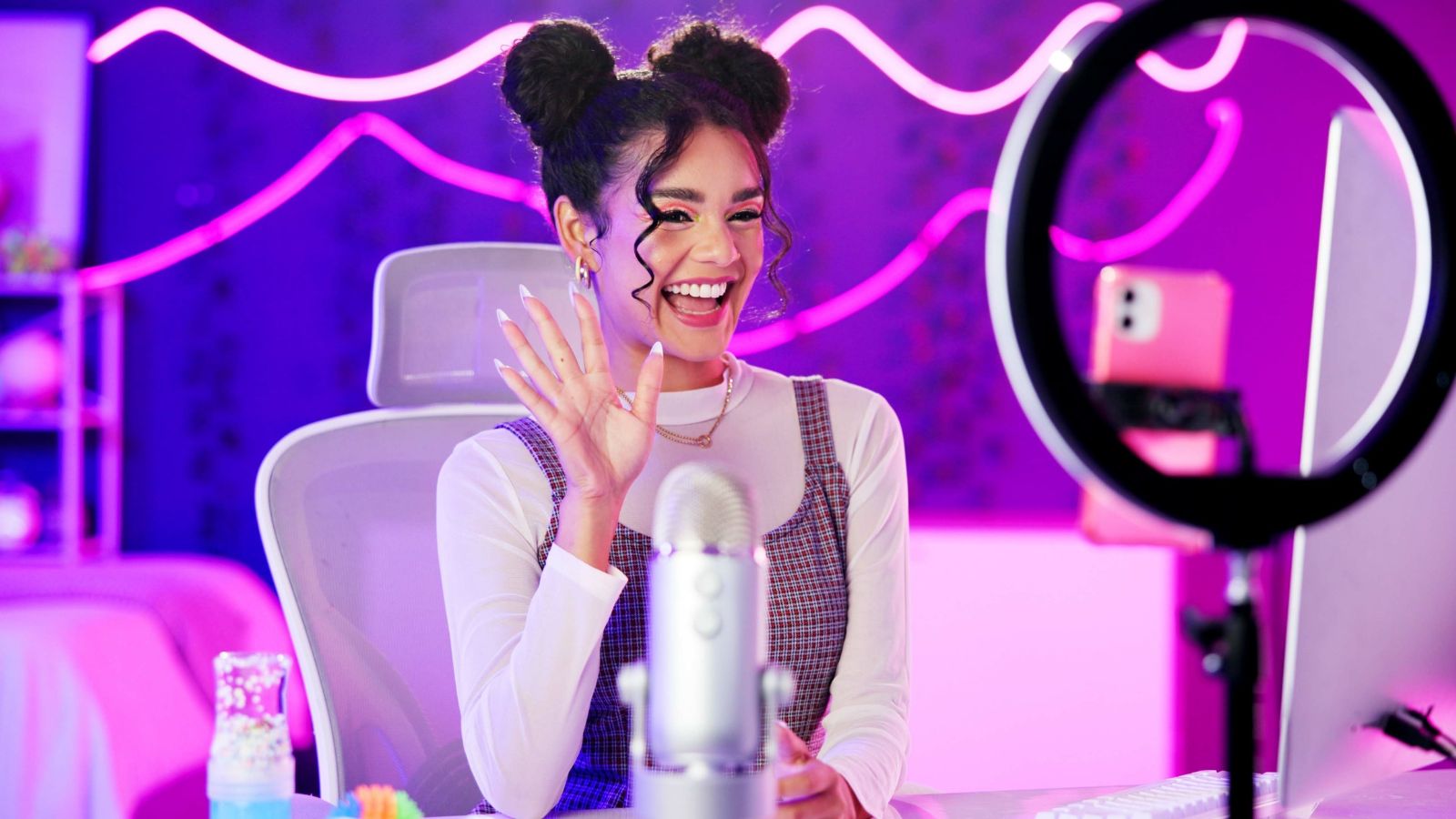

Influencers are modern-day role models with significant power over young people’s tastes, habits, and behaviors. Their unattainable lifestyles can create unrealistic expectations for material success or body image. Additionally, the constant promotion of products can encourage materialism and overconsumption among impressionable youth.
Risks of Online Predators

The anonymous nature of social media also makes it a dangerous space for young users who may unknowingly engage with online predators. Although platforms have safety measures in place, many teens are still susceptible to grooming and exploitation due to a lack of awareness about online safety.
Oversharing and Privacy Concerns

The culture of sharing every aspect of life online can lead young people to reveal personal information without understanding the risks. Once something is shared online, it can be difficult, if not impossible, to remove it altogether, which can have long-term implications for privacy, reputation, and even future employment.
Conclusion

Social media is a double-edged sword, offering unprecedented opportunities for learning, expression, and connection while presenting numerous risks that must be carefully managed. By understanding these 18 alarming facts, we can work towards mitigating the adverse effects of social media on youth and ensure that it serves as a tool for positive growth rather than a source of harm.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
