Social media has become an integral part of many of our daily lives, influencing how we think and interact with the world. But, while social media connects people across the world, it’s also having a significant impact on our brain function in ways we may not fully realize. We take a look at 19 alarming ways social media can rewire your brain.
Decreasing Attention Span

Social media platforms thrive on rapid content consumption, encouraging users to scroll endlessly through bite-sized information. Studies suggest that the average attention span has dramatically reduced due to the constant bombardment of short-form content, making it harder to focus on long-term tasks like reading or maintaining deep conversations.
Addiction to Dopamine Hits

Every like, comment, or share on social media triggers the release of dopamine, the brain’s “feel-good” neurotransmitter. This creates a reward loop similar to gambling, making people compulsively check their notifications and conditioning the brain to seek instant gratification.
Increased Anxiety and Depression

Constant exposure to curated, idealized versions of others’ lives can lead to feelings of inadequacy and depression. Research shows that excessive social media use correlates with higher anxiety levels, especially among teenagers as they compare themselves to influencers or peers.
Reduced Empathy

The lack of face-to-face interaction in social media conversations leads to a decline in empathy as online interactions often lack emotional cues like body language and tone of voice. This type of conversation makes it easier to misunderstand others and can contribute to cyberbullying and insensitive online behavior, especially in young people.
Rewiring of Reward Processing

Social media hijacks the brain’s reward system by associating external validation (likes and comments) with self-worth. This causes people to start valuing themselves more on the basis of digital approbation than on their own accomplishments, which changes intrinsic motivation to extrinsic validation.
Memory Distortions and False Memories

People often recall events inaccurately due to the way social media presents selective memories. When algorithms highlight past posts, they reinforce specific narratives while suppressing others, which can lead to false memories, where people reconstruct past events.
Increased Multitasking

Social media encourages constant multitasking, encouraging people to switch between different platforms, respond to messages, and watch videos simultaneously. While multitasking feels productive, research shows that it can reduce efficiency and lead to some tasks being incomplete.
Negatively Affecting Sleep Patterns
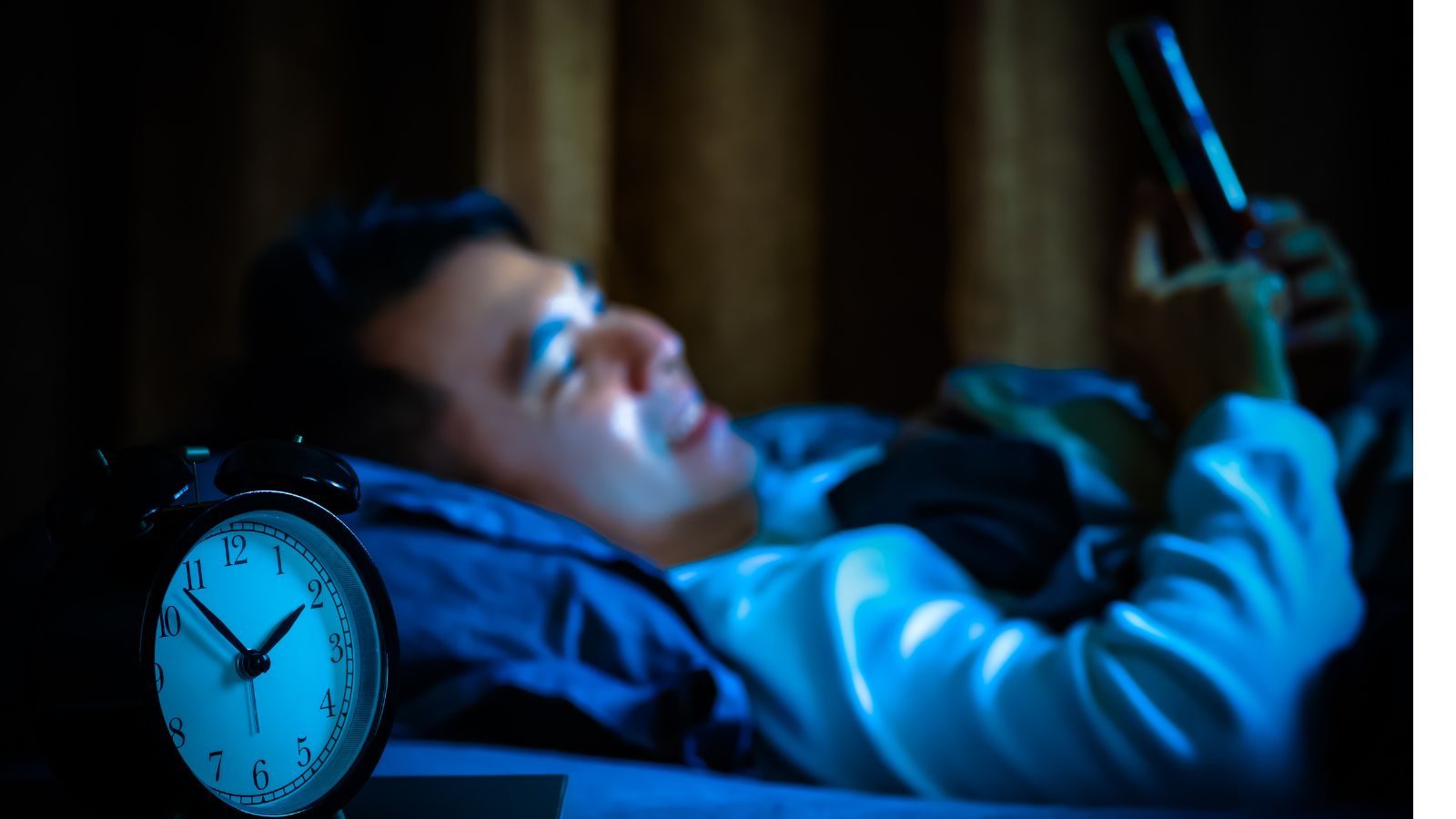

The blue light from screens interferes with melatonin production, disrupting sleep cycles. Social media can also stimulate us too much, particularly when switching between multiple apps, which increases the risk of insomnia and poor sleep quality.
Encouraging Echo Chambers

Social media algorithms curate content based on past interactions, reinforcing existing beliefs and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Echo chambers fuel confirmation bias, where people become more consumed in their views and less open to opposing opinions.
Weakening Face-to-Face Communication Skills

As digital conversations replace in-person interactions, people struggle with non-verbal communication skills. Building genuine connections requires eye contact, attentive listening, and real-time replies; however, social media downplays these qualities, making in-person conversations more uncomfortable and stressful.
Altering Risk-Taking Behavior

Research indicates that social media encourages impulsive decision-making, often making teenagers take part in viral trends and risky online challenges. Poor impulse control can also lead people to post controversial content, whcih can cause offense to others.
Decreasing Deep Thinking and Creativity

The fast-paced nature of social media discourages deep thought and contemplation. Rather than encouraging critical thinking and complex discussions, users are overwhelmed with oversimplified information, diminishing their capacity for creative problem-solving and intellectual engagement.
Normalizing Superficial Relationships

Social media fosters connections based on likes, comments, and follows rather than meaningful interactions. People often prioritize maintaining a digital presence over deepening real-world relationships, leading to a decline in genuine friendships and emotional bonds.
Promoting Narcissistic Tendencies

The pressure to curate a perfect online image encourages narcissistic traits, such as excessive self-promotion and vanity. Social media platforms reward those who constantly showcase their lifestyles, reinforcing a culture of self-obsession over humility and authenticity.
Increasing Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)

Constant updates on friends’ activities can lead to a psychological phenomenon known as FOMO. Seeing others enjoying vacations, parties, or milestones can create anxiety, making people feel they are missing out on life, leading to stress and dissatisfaction.
Encouraging Passive Consumption Over Active Participation

Social media often turns users into passive consumers rather than active participants. Instead of engaging in real-world activities like reading, exercising, or socializing, people spend hours scrolling through content, reducing their overall life engagement and productivity.
Affecting Political and Social Perceptions
Misinformation spreads rapidly on social media, shaping political and social views based on sensationalized or biased content. Fake news and misleading narratives exploit cognitive biases, influencing public opinions and sometimes even real-world actions.
Triggering Stress Responses Similar to Physical Danger

Notifications, online conflicts, and social comparison can trigger the brain’s fight-or-flight response. This stress response, when frequently activated, increases cortisol levels, leading to chronic anxiety, burnout, and even physical health issues.
Encouraging a Culture of Superficial Validation

Social media fosters an environment where worth is measured in likes and followers rather than accomplishments and character. This shifts societal values toward superficial approval rather than genuine self-worth, affecting mental health and identity formation.
25 Countries Predicted to Become Economic Superpowers in the Next 20 Years

The strength of an economy plays a crucial role in various international policies about trade and relations. Certain factors determine the strength of an economy, including population growth, availability of resources, and development and advancement. Here are 25 countries predicted to become economic superpowers in the next 20 years
25 Countries Predicted to Become Economic Superpowers in the Next 20 Years
