Several long-standing challenges were addressed early and decisively in Canada, often becoming examples that other countries later studied or adopted. These solutions were not just symbolic adjustments but measurable improvements supported by clear policy decisions, scientific planning, and nationwide coordination. Here are 21 problems Canada solved before anyone else.
Eliminating Leaded Gasoline Early

The phaseout of leaded gasoline began earlier here than in many industrial nations. Scientific evidence on lead exposure was taken seriously in the 1970s, leading to mandatory reductions starting in 1973 and a full ban by 1990. This timeline placed the country ahead of several large economies that continued using leaded fuel into the 2000s. The early removal reduced childhood lead levels, improved air quality, and lowered long-term public health costs. By acting quickly, regulators created a precedent that later became a benchmark for other governments evaluating the connection between auto emissions and neurological health outcomes in children.
Universal Healthcare Based on Need, Not Income
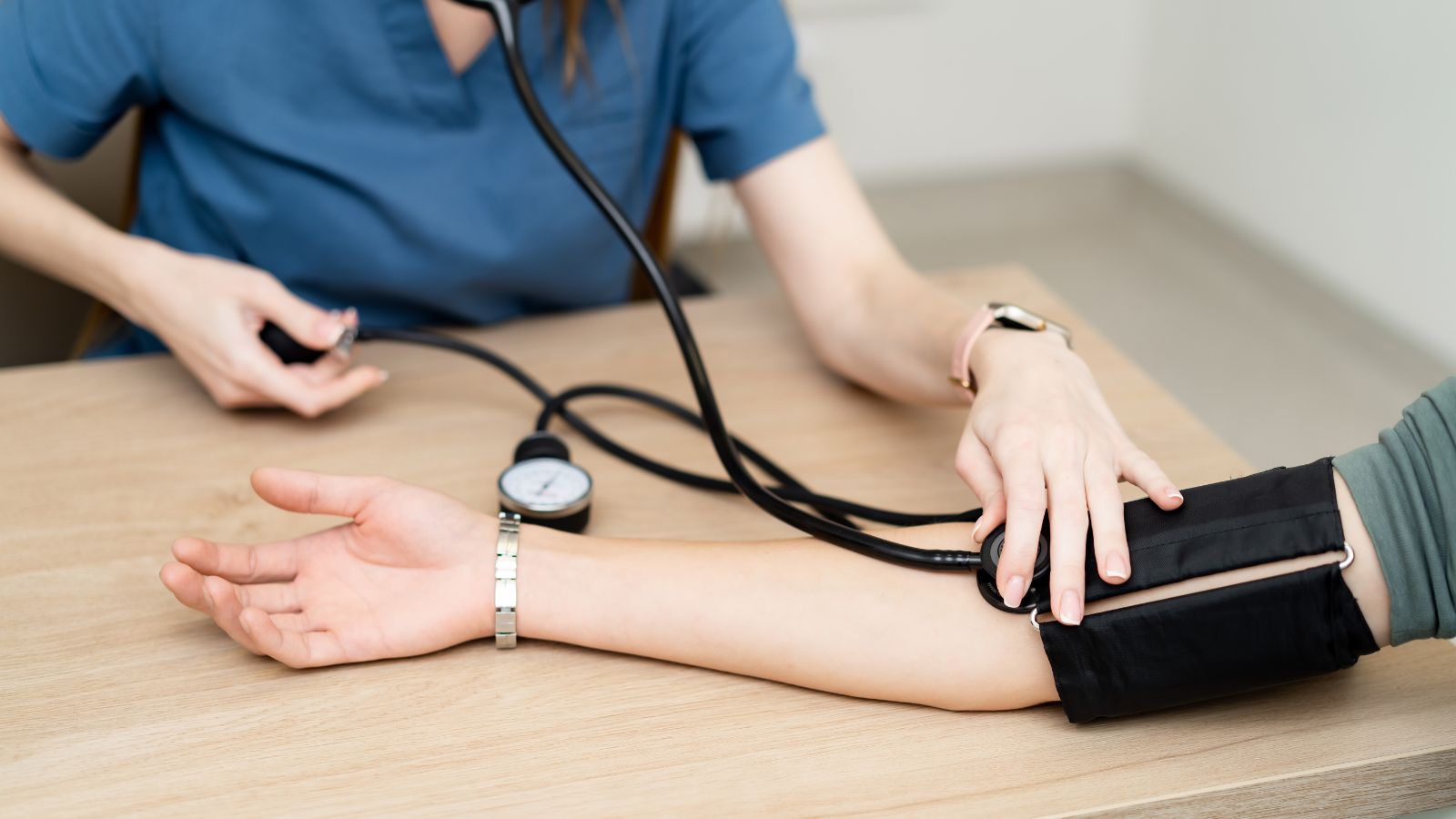
A publicly funded healthcare model based on medical need instead of personal finances was introduced decades before many nations adopted similar approaches. Saskatchewan’s provincial plan in 1962 and the national model in 1966 demonstrated that a universal system could operate efficiently, reduce catastrophic medical expenses, and maintain strong health outcomes. Countries examining growing inequalities or insurance gaps later used this framework as a reference. The shift helped stabilize access to primary care, encouraged earlier diagnosis of chronic conditions, and lowered overall administrative costs. It also proved that coordinated provincial and federal participation in healthcare delivery could function effectively and sustainably.
Early Adoption of Vehicle Seat Belt Laws

Ontario became one of the first jurisdictions worldwide to create mandatory seat belt laws in 1976. The decision followed detailed accident research showing that restraints significantly reduced injuries and fatalities. Other provinces followed, and national enforcement grew quickly afterward. Many countries implemented similar rules years later, often citing Canadian studies as part of their justification. Insurance data showed consistent declines in injury severity after enforcement improved, reinforcing the value of early legislation. The move also encouraged automakers to prioritize safety features, influencing broader industry standards. The early transition demonstrated that strong road safety policies could be implemented with clear results.
Standardized Food Nutrition Labels Before They Were Global

Nutrition labels listing calories, fats, and key nutrients became mandatory in Canada before several major economies introduced similar requirements. The system took effect in 2003 after nearly a decade of research and public consultation. The goal was to allow consumers to compare items accurately, reduce hidden unhealthy ingredients, and encourage reformulation. Other countries later adopted comparable label formats, and the World Health Organization referenced this model during global guideline discussions. The early introduction improved transparency in grocery stores and helped set expectations for accurate product information. Manufacturers also shifted to clearer packaging and more consistent ingredient disclosures following the update.
Early Nationwide Wireless Spectrum Auctions

Long before digital access became a top global priority, Canada implemented competitive spectrum auctions in the late 1980s and early 1990s. These auctions replaced discretionary licensing processes with transparent, revenue-generating systems that encouraged fair competition among telecom operators. Several nations later adopted similar auction frameworks once mobile demand expanded. The approach accelerated wireless expansion, improved rural access, and created predictable timelines for technological upgrades. It also encouraged carriers to invest earlier in infrastructure because spectrum ownership carried clear obligations. The benefits helped shape a communications environment in which consumers gained earlier access to emerging mobile technologies and better coverage.
Smoke-Free Indoor Public Spaces: Before Global Norms

Provincial bans on indoor smoking started appearing in the late 1990s, before many countries had national smoke-free laws. Research on secondhand smoke prompted early restrictions in workplaces, restaurants, and public buildings, which contributed to significant reductions in smoking-related illnesses. Other nations implemented their own bans years later, often referencing Canadian public health data to support policy changes. The early shift normalized smoke-free environments and encouraged businesses to adopt cleaner air standards. It also provided consistent protections for workers in service industries. These early measures became international examples of how coordinated enforcement can reshape public health behavior.
Early Action on Acid Rain Through Cross-Border Agreements

During the 1970s and 1980s, acid rain was damaging lakes, forests, and soil. Canada pushed early for binding emission reduction agreements, eventually securing the 1991 Air Quality Agreement with the United States. This commitment required both sides to lower sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions. The effort started before several other industrialized countries had formal programs in place. Environmental data later showed significant recovery of freshwater ecosystems. The approach demonstrated that cross-border pollution required joint governance, influencing later agreements in Europe and Asia. Early recognition and action helped restore vulnerable regions and maintain biodiversity in affected areas.
Implementing Early DNA Forensic Databases

A national DNA databank was established in 2000, earlier than similar systems in several other countries. It included profiles from serious offenders and crime scene samples, creating a standardized approach for forensic investigations. The structure balanced privacy protections with investigative efficiency, which later informed other jurisdictions building their own frameworks. Police agencies gained new capabilities to solve cold cases, identify repeat offenders, and clear suspects more quickly. The databank also set uniform guidelines for handling and analyzing samples, improving reliability in court. Its early rollout demonstrated how structured forensic technology could support public safety without compromising civil rights principles.
Early Ban on Microbeads in Personal Care Products

Microbeads used in face scrubs and body products were recognized as a growing environmental threat in the early 2010s. These plastic particles accumulated in waterways and affected aquatic life. Canada introduced a ban that took full effect in 2018, ahead of several major markets that adopted similar rules later. The decision followed scientific reviews showing that wastewater treatment systems could not effectively filter microbeads. Manufacturers shifted formulations quickly, and consumers gained access to safer alternatives. The early response demonstrated that preventative action on emerging pollutants could occur before contamination reached irreversible levels, setting a precedent for future environmental safeguards.
Reducing Trans Fats Before Many International Markets

Partially hydrogenated oils, a major dietary source of trans fats, were recognized as harmful early. After years of health research, Canada moved toward eliminating industrial trans fats and introduced a full ban in 2018. This occurred before similar measures in several countries that later referenced Canadian risk assessments. The early phaseout reduced cardiovascular disease risk and pushed food manufacturers to reformulate products with healthier fats. Restaurants and packaged food companies adjusted menus quickly. The transition also encouraged more transparent nutrition reporting. With measurable improvements in diet quality, the early initiative demonstrated how strict nutritional standards could yield broad public health benefits.
Early Legal Recognition of Same Sex Marriage

In 2005, Canada became one of the first nations to legalize same sex marriage nationwide. Years of court decisions and provincial rulings created momentum for federal legislation. The step provided full legal equality for marriage rights, influencing policy debates in other regions that had not yet addressed discrimination in family law. The legislation protected spousal benefits, adoption rights, and immigration processes for same sex couples. As other countries moved toward similar recognition over the following decade, many referenced Canada’s early implementation as evidence that inclusive laws could function effectively without disruption to existing systems. The decision helped reshape global human rights discussions.
Creating a National Parks System Early in the 20th Century

Banff National Park became one of the earliest national parks worldwide in 1885, and the system expanded quickly through the early 20th century. These designations occurred long before environmental tourism gained global attention. By preserving natural regions early, ecosystems remained intact even as surrounding areas developed. Other countries later used similar models when establishing their own national park networks. The early emphasis on conservation created protected habitats for wildlife, supported scientific research, and contributed to tourism economies. It also set standards for sustainable land management practices and long-term ecological planning, demonstrating the value of proactive environmental protection.
Early Mandatory Bicycle Helmet Laws in Several Provinces

Some provinces introduced mandatory helmet laws for cyclists in the 1990s, years before many international jurisdictions created similar rules. The legislation applied particularly to children and youth, addressing the rising number of bicycle-related head injuries. Medical data later confirmed significant reductions in hospitalizations where these laws were enforced. Other countries examined these early outcomes when evaluating their own cycling safety strategies. The rules also encouraged manufacturers to improve helmet quality and design. By treating cycling safety as a public health issue rather than an individual choice, the early regulations demonstrated how targeted legislation could create measurable improvements quickly.
Early Move to Chip and PIN Banking Cards

Banks transitioned from magnetic stripe cards to chip and PIN technology years ahead of many global markets. Widespread adoption began in the mid-2000s and reduced fraud by replacing signature verification with encrypted authentication. This upgrade occurred before several major economies implemented similar transitions. Retailers and payment processors adjusted quickly, supported by a coordinated national rollout. Fraud statistics showed consistent declines in card skimming incidents after the shift. The early move established a more secure financial environment for consumers and businesses. It also positioned the country to adopt further digital payment innovations as technologies and security standards continued to evolve.
Early Ban on Advertising Vaping Products to Youth

Concerns about rising youth vaping prompted early legislative action. Restrictions on marketing to minors were introduced before many global jurisdictions created comparable rules. These measures limited packaging designs, flavor promotions, and social media advertising targeted at younger audiences. Public health agencies monitored usage trends and used early data to guide further interventions. Countries facing similar increases in youth vaping later referenced the Canadian approach when building their own regulations. The early restrictions helped slow the growth of youth exposure to nicotine products and encouraged manufacturers to adjust their marketing strategies. The move demonstrated the importance of immediate action on emerging health risks.
Implementing a Carbon Pricing System Before Most Economies

A nationwide carbon pricing framework was implemented in 2019, becoming one of the earliest comprehensive systems among large economies. The structure required provinces to meet minimum pricing standards while allowing flexibility in implementation. This approach reduced uncertainty for businesses while establishing clear emissions reduction incentives. International organizations studied the system when advising other countries developing similar strategies. Early results showed shifts toward cleaner energy investments and more efficient industrial operations. The policy also encouraged technological innovation in emissions reduction. By addressing climate change with a market-based mechanism early, the system provided a functional example for jurisdictions evaluating similar solutions.
Early Development of the Electronic Medical Record Network

Efforts to digitize medical records began in the early 2000s, ahead of several health systems that relied on paper files until much later. Federal and provincial investments supported uniform data standards, allowing patient history to be accessed quickly across care settings. This improved coordination among practitioners and reduced duplication in testing. Countries considering similar modernization later referenced the Canadian experience. The shift also facilitated earlier adoption of telemedicine services. By prioritizing secure digital infrastructure early, the healthcare system strengthened continuity of care and demonstrated how integrated record keeping could support long-term efficiency and improved patient outcomes.
Restrictions on Single-Use Plastics Before Global Pressure Intensified
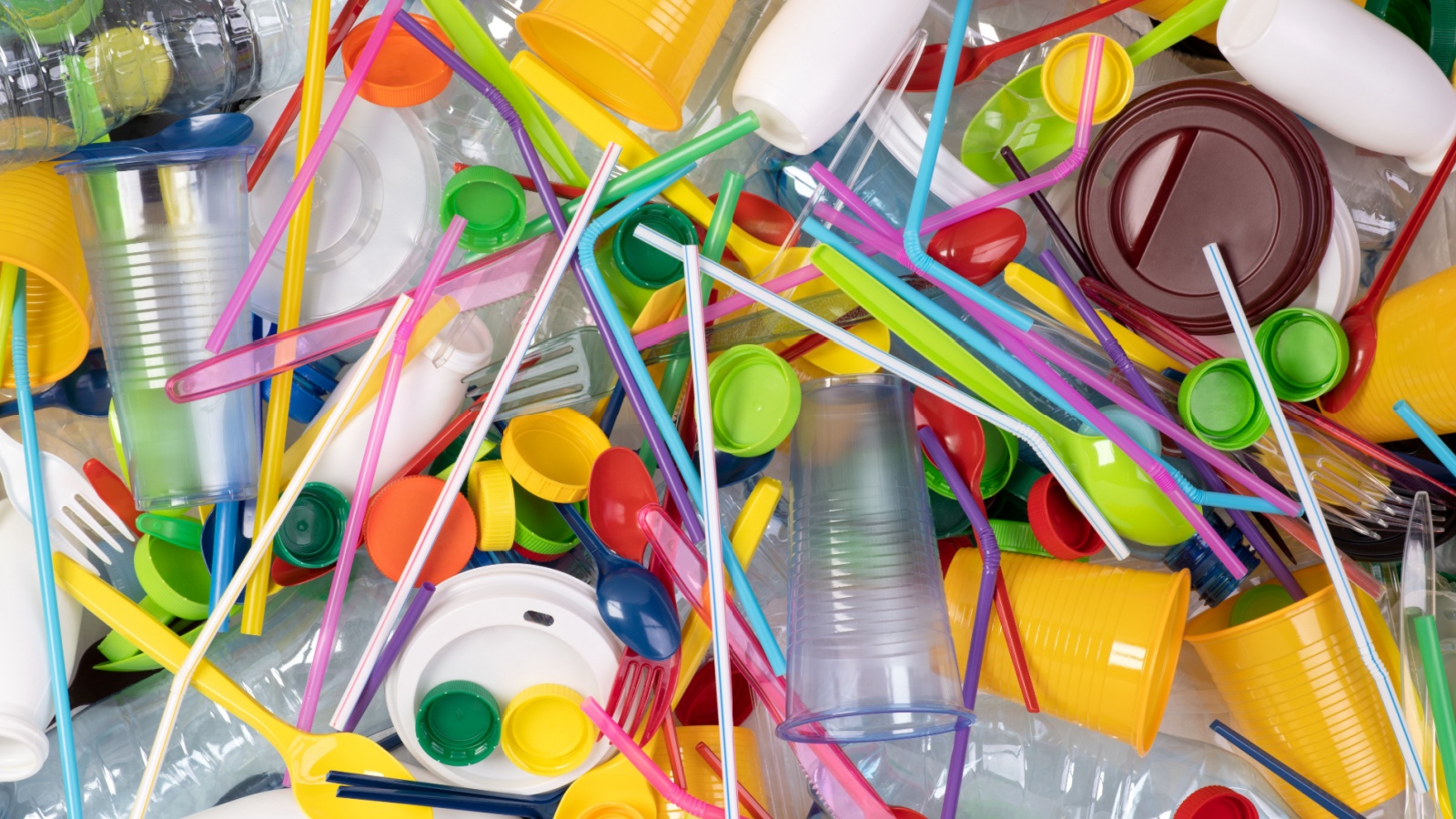

Efforts to address disposable plastic waste widened significantly with regulations introduced ahead of many international markets. The plan targeted items such as checkout bags, straws, and cutlery, supported by scientific assessments of environmental impact. These measures provided clarity for manufacturers on packaging changes and encouraged early investment in alternatives. Several countries later created comparable restrictions after observing public support and waste reduction patterns. The early pivot also helped standardize expectations for businesses in the retail and food service sectors. By addressing single-use plastics before global urgency peaked, the policy demonstrated how anticipatory regulation could reduce long-term environmental damage.
Strengthening Indigenous Language Protection Early

Legislation and federal funding aimed at revitalizing Indigenous languages were introduced early compared to many nations confronting similar cultural loss. The Indigenous Languages Act of 2019 recognized the right to preserve and promote traditional languages and provided structured support for community-based programs. This move occurred before several countries created comparable national strategies. The policy supported language education, documentation, and training for new educators. It also established partnerships between governments and Indigenous communities. By acting early, the country demonstrated how formal recognition and funding could strengthen cultural preservation and help reverse declining fluency rates in historically marginalized populations.
Creating a National Do Not Call Registry Early

Unwanted telemarketing was recognized as a growing consumer concern, leading to the launch of a national Do Not Call Registry in 2008. This initiative came before several large markets implemented equivalent systems. The registry allowed individuals to block most unsolicited commercial calls and introduced penalties for violations. Over time, complaints declined and enforcement improved. Other countries referenced the design when building their own anti-nuisance frameworks. Telecom companies adjusted internal policies to comply with the system, and consumers gained greater control over personal privacy. By addressing telemarketing early, the initiative set expectations for respectful communication standards in commercial outreach.
Early Recognition of Electronic Waste Recycling Needs
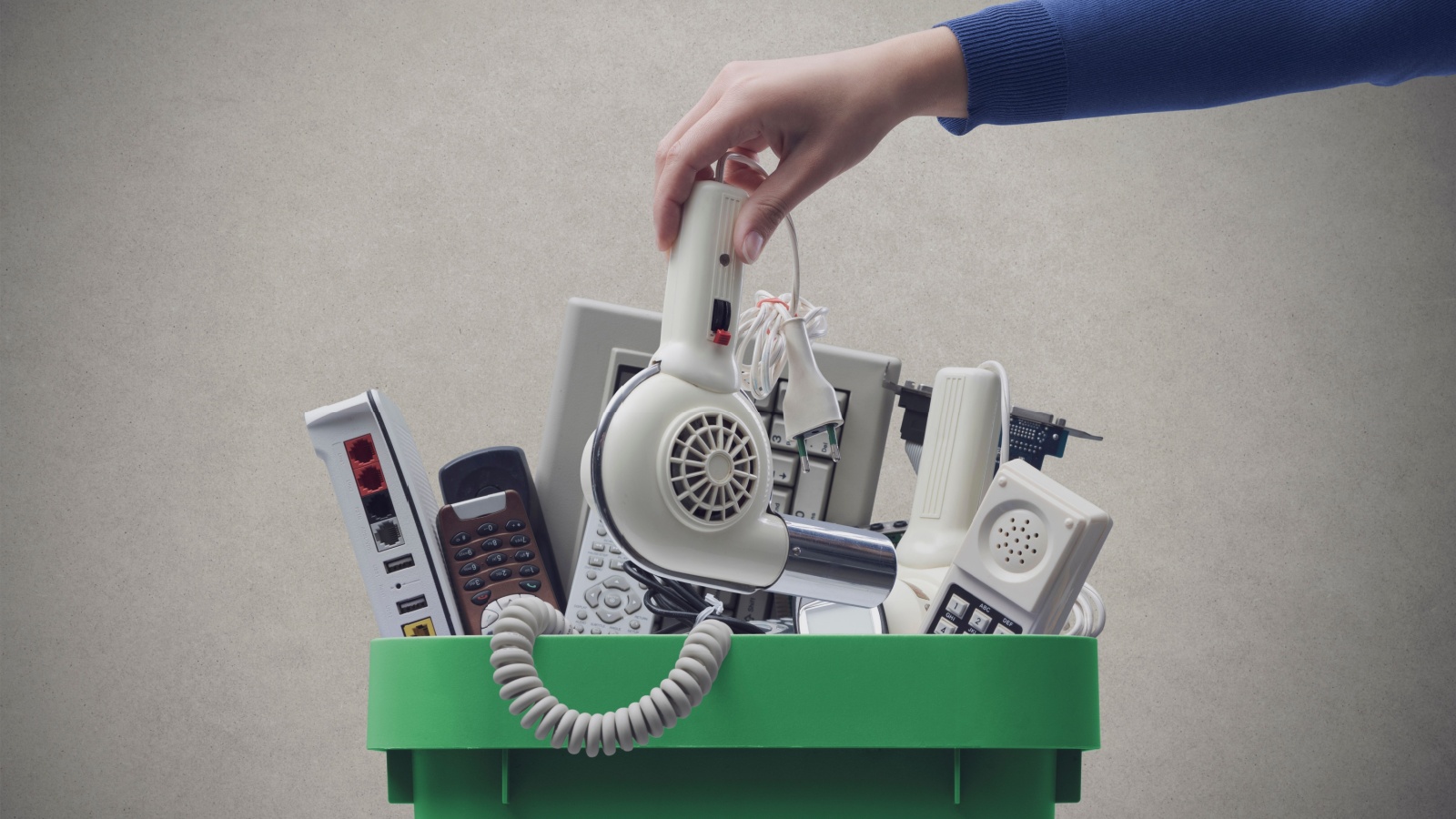

Electronics recycling programs were introduced in several provinces starting in the mid-2000s, earlier than many regions that handled e-waste through general waste streams. These programs required retailers and manufacturers to support the safe collection and recycling of devices such as computers, televisions, and phones. The approach reduced landfill contamination and recovered valuable materials. Other jurisdictions later implemented similar extended producer responsibility systems. The early shift highlighted the environmental and economic value of structured recycling networks. The programs also improved public awareness of safe disposal practices and contributed to steady growth in recycling infrastructure across the country.
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit

If trade tensions escalate between Canada and the U.S., everyday essentials can suddenly disappear or skyrocket in price. Products like pantry basics and tech must-haves that depend on are deeply tied to cross-border supply chains and are likely to face various kinds of disruptions
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit
