Multiple structural shifts are emerging across the country, and many of them have the potential to reshape long-term economic performance. These changes reflect new technologies, evolving resource strategies, workforce patterns, and growing global competition. They are not speculative ideas but measurable movements already influencing investment decisions, productivity strategies, and trade relationships. Here are 22 Canadian shifts that could redefine the economy.
Domestic battery manufacturing expansion
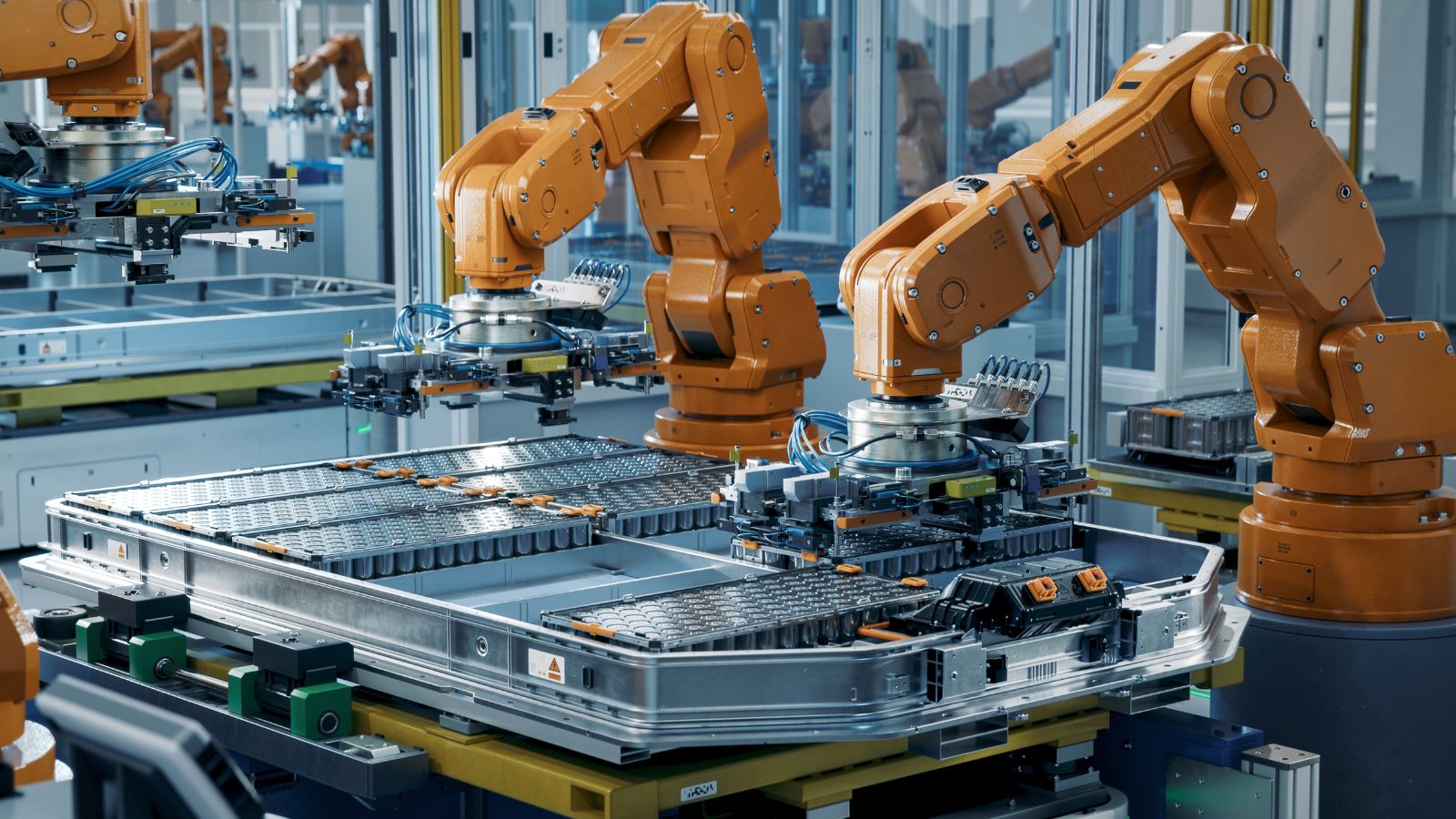
Several provinces are witnessing major investments in battery cell and component production. These plants support electric vehicle manufacturing but also supply energy storage companies building systems for utilities and commercial sites. The sector is attracting global companies that want stable policies, mineral access, and reliable power. New jobs in engineering, automation, testing, and chemical processing are emerging as construction progresses. The presence of large battery facilities helps shorten supply chains across North America and reduces reliance on imported cells. Over time, this shift raises national competitiveness in clean transportation and grid modernization, while strengthening advanced manufacturing capabilities across regions.
Growth in critical mineral refining and processing

A significant shift involves new refining and processing capabilities for lithium, nickel, graphite, and rare earth elements. Historically, raw minerals were exported to overseas refineries, but new federal incentives and private investment are keeping more value creation inside the country. Companies are building facilities in Ontario, Quebec, and the Prairies to meet rising global demand for clean technology materials. This development reduces exposure to international supply disruptions while supporting domestic battery and electronics supply chains. With stronger processing capacity, mining regions gain new long-term revenue streams and skilled employment opportunities. This shift strengthens trade leverage and builds strategic independence.
Rapid expansion of small modular reactor projects

Small modular reactor technology is progressing from planning to deployment, particularly in Ontario, Saskatchewan, and New Brunswick. Utilities view SMRs as a practical option for reliable baseload power with lower emissions. The projects are attracting engineering, construction, and nuclear research investment and positioning local firms to supply components for a future export market. SMRs could also support industrial regions that need consistent energy for manufacturing and resource development. As several provinces align policies around this technology, the shift strengthens energy security and creates long-term industry clusters. These reactors may eventually replace aging infrastructure and support broader electrification goals.
Surge in domestic clean hydrogen development

Clean hydrogen projects are expanding quickly as provinces pursue new energy export opportunities. Facilities in Alberta, Ontario, and Atlantic Canada are developing hydrogen derived from natural gas with carbon capture and from renewable-powered electrolysis. International partners, particularly in Europe and Asia, are showing interest in long-term supply agreements. This shift opens new pathways for decarbonizing steel production, heavy transport, and industrial heat. The growth of hydrogen infrastructure also attracts investment in pipelines, storage, and fuel cell technology. Over the next decade, these projects could create a diversified energy export market and broaden industrial manufacturing capacity.
Rebuilding of domestic pharmaceutical and bioscience capacity

The life sciences sector is seeing renewed investment in vaccine production, biomanufacturing, and pharmaceutical research facilities. This shift began after global supply disruptions exposed gaps in domestic manufacturing capacity. New plants in Quebec, Ontario, and British Columbia are producing vaccines, biologics, and specialized therapeutics. Research clusters near universities are attracting partnerships with multinational firms seeking stable regulatory environments. Strengthening domestic production reduces vulnerability during global emergencies and creates high-skilled employment. As bioscience companies scale, opportunities emerge in medical devices, diagnostics, and clinical research services. Combined, these investments support long-term innovation and diversify the broader healthcare economy.
Increased automation and robotics adoption in manufacturing

Manufacturing firms are adopting more robotics, automated inspection, and advanced production systems to address labour shortages and improve productivity. This shift is most visible in automotive plants, food processing facilities, and logistics centers, adapting to rising demand. Government programs supporting modernization are helping smaller manufacturers upgrade equipment and train workers. The transition encourages higher-skilled roles in programming, maintenance, and machine integration while reducing repetitive manual tasks. Greater automation strengthens global competitiveness and attracts new investment from companies looking for efficient and reliable production capacity. Over time, this movement helps stabilize exports and fortify advanced manufacturing sectors nationwide.
Acceleration of agri tech and controlled environment farming

Agricultural regions are seeing growth in vertical farming, greenhouse expansion, and robotics for crop monitoring and harvesting. These technologies reduce dependence on seasonal labour and improve reliability during extreme weather events. Regions such as Southwestern Ontario and Alberta are attracting agri-tech startups creating tools for soil analytics, precision irrigation, and livestock monitoring. Increased domestic production helps stabilize food supply and reduces import requirements for certain produce. This shift also encourages new research partnerships between universities and private firms focused on sustainability. As technology adoption spreads, agriculture becomes more resilient, productive, and capable of supporting long-term economic growth.
Expansion of carbon capture and storage infrastructure

Carbon capture and storage projects are advancing rapidly, particularly in Alberta and Saskatchewan, where geology supports long-term storage. Energy companies are integrating large-scale capture systems into existing facilities to meet emerging emissions targets. New pipelines designed to transport captured carbon to storage sites are under development, creating engineering and construction jobs. The technology also supports industrial sectors like cement and chemicals that require new strategies to reduce emissions. As CCUS infrastructure expands, the region strengthens its position as a hub for low-carbon energy development. Over time, this shift attracts global investment seeking stable carbon management solutions.
Growth in digital services exports and remote skilled work

Digital services such as software development, cybersecurity, data analytics, and cloud consulting are becoming a larger share of exports. Remote work has enabled companies to serve global clients without relocating talent. Mid-sized cities are also benefiting as skilled workers move for affordability while keeping international clients. Government programs supporting broadband expansion are accelerating this shift by improving connectivity in non-metropolitan regions. As more global firms outsource digital work, competitive labour costs and a strong education system attract long-term contracts. This movement strengthens the knowledge economy and reduces reliance on traditional goods-based exports in several provinces.
The rise of Indigenous led economic development projects

Indigenous communities are leading major investments in energy, infrastructure, tourism, and natural resource development. New ownership models allow communities to hold equity stakes in pipelines, renewable power projects, and mining operations. These arrangements ensure revenue flows remain local and support long-term community development. Enhanced participation also improves regulatory certainty by aligning interests between project developers and Indigenous governments. Training programs in engineering, environmental monitoring, and skilled trades strengthen workforce capacity. As more communities gain direct economic influence, regional economies diversify and strengthen. This shift supports reconciliation through practical economic frameworks that create stable growth opportunities.
Scaling of domestic semiconductor and microchip initiatives

Governments and private firms are increasing investment in semiconductor research, testing, and specialized chip manufacturing. While large-scale fabrication remains limited, new facilities support design, prototyping, compound semiconductors, and industrial sensors. These technologies are essential for automotive systems, telecommunications, medical devices, and aerospace applications. Expanding domestic capacity reduces reliance on overseas suppliers during global shortages. Universities and research institutes play a major role in training engineers and supporting advanced materials research. As companies adopt more automation and AI-powered systems, demand for specialized chips continues to rise. This shift strengthens the technology ecosystem and improves competitiveness in high-growth sectors.
Expansion of AI development hubs and applied research labs

Artificial intelligence research centers in Toronto, Montreal, Edmonton, and Vancouver are scaling rapidly as companies seek practical applications for machine learning. Investments support projects in healthcare diagnostics, transportation optimization, and advanced manufacturing systems. Startups benefit from partnerships with universities and access to skilled graduates trained in data science. The growth of AI hubs attracts international companies that want collaborative environments for experimentation. As adoption increases, the technology supports productivity improvements across multiple sectors. The expansion of applied labs helps create new intellectual property, strengthens the innovation economy, and enhances economic resilience in a technology-driven global marketplace.
Increasing investment in life sciences research clusters

Research districts focused on genomics, medical imaging, biotechnology, and clinical innovation are gaining funding from both public and private sources. These clusters support cross-disciplinary collaboration between universities, hospitals, and companies working on new diagnostics and therapeutics. Growth in this sector attracts international researchers and strengthens domestic intellectual property creation. Infrastructure investments include new laboratories, clinical trial centers, and data analysis platforms. The expansion encourages the commercialization of research outputs, bringing new products to global markets. As life sciences clusters mature, they diversify local economies and create long-term, high-skilled jobs. This shift strengthens global competitiveness in health innovation.
Reorientation of trade toward Asia Pacific markets

Trade patterns are gradually shifting as exporters increase focus on the Asia Pacific markets for energy, agriculture, technology, and services. New trade agreements and infrastructure investments support this transition by improving port capacity and streamlining regulations. Companies see opportunities in markets with rising middle-class demand and strong industrial growth. Diversifying export destinations reduces vulnerability during downturns in traditional markets. Investments in logistics, shipping, and digital trade platforms help facilitate this shift smoothly. As relationships deepen, long-term supply agreements support stability for producers. This realignment broadens economic opportunities and strengthens resilience in global trade environments.
Rising development of renewable energy megaprojects

Large-scale wind, solar, and hydro projects are being planned or expanded in several provinces. These projects stabilize long-term energy costs and attract companies seeking reliable low low-carbon power. New transmission infrastructure supports the integration of renewable sources into regional grids. Local communities benefit from construction jobs and ongoing maintenance roles. The rise of renewable megaprojects also encourages partnerships with Indigenous communities that support regional development. As demand for clean electricity rises due to the electrification of vehicles and industrial processes, these projects position regions as competitive investment destinations. This shift strengthens energy security and encourages sustainable economic growth.
Strengthening of advanced manufacturing supply chains

Advanced manufacturing is gaining importance as companies work to shorten supply chains and reduce dependence on overseas suppliers. Investments in robotics, specialized components, additive manufacturing, and digital monitoring systems improve efficiency and reliability. Collaboration between manufacturers and research centers supports innovation in aerospace, automotive, and precision engineering sectors. Federal and provincial programs provide incentives for upgrading equipment and training workers for specialized roles. Strengthened domestic supply chains attract international companies seeking stable production locations. As the sector grows, it enhances export potential and creates long-term skilled employment. This shift supports a more resilient and diversified industrial base.
Growth in electric public transit manufacturing

Companies are expanding production of electric buses, rail systems, and charging infrastructure. Domestic manufacturers benefit from transit agencies seeking low-emission vehicles and from government programs encouraging fleet electrification. New facilities in Quebec, Ontario, and Manitoba produce components, power systems, and full vehicle assemblies. This shift creates engineering, manufacturing, and maintenance jobs while supporting related supply chains. As transit agencies replace older fleets, long-term demand strengthens. The industry also attracts international clients seeking reliable suppliers for electric mobility solutions. This expansion builds a competitive export sector and aligns transportation with broader climate and productivity goals.
Expansion of cybersecurity capabilities and firms
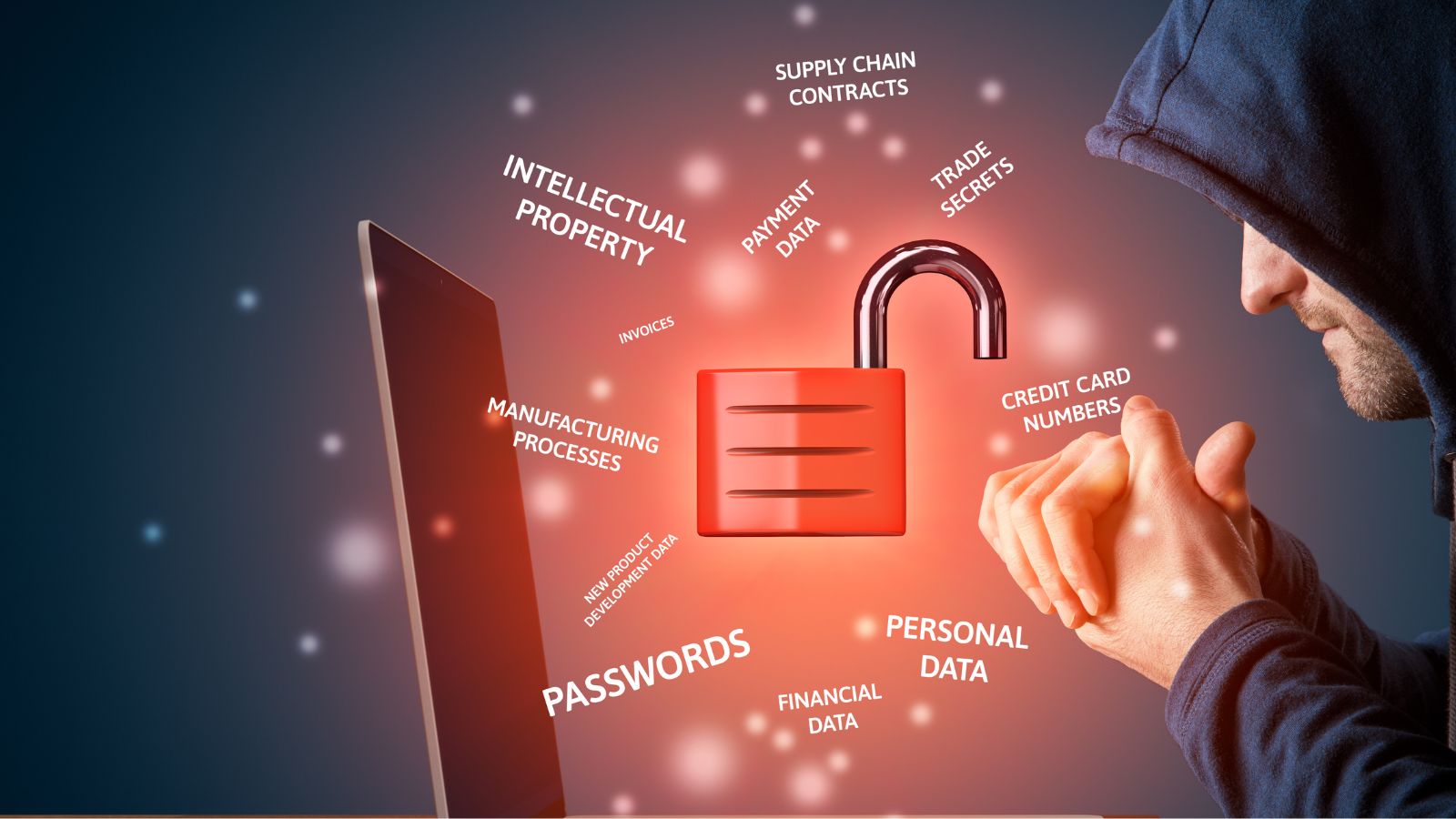

Cybersecurity demand is rising across government, finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure. Companies are investing in threat detection, penetration testing, and digital risk management services to address increasingly complex cyber threats. Universities have expanded cybersecurity programs to train more analysts and specialists. New startups develop defensive software tools while established firms handle large-scale security contracts. As digital systems expand across industries, the importance of local cybersecurity capacity grows. This shift supports high-wage employment and strengthens national resilience against attacks. Growth in this sector also positions the country as a trusted provider of secure digital services for global clients.
Large-scale housing construction to address supply shortages

Housing supply initiatives are shifting construction activity across provinces. Governments are accelerating permitting, encouraging higher-density developments, and investing in infrastructure to support growth. Private developers are building rental towers, purpose-built units, and mixed-use communities to meet rising demand. Expanded construction supports jobs in trades, engineering, design, and materials manufacturing. Increased supply stabilizes rental markets and benefits employers facing recruitment challenges in high-cost regions. New zoning reforms encourage more efficient land use and streamline approvals. As construction scales, it becomes a significant economic driver and supports long-term urban development strategies across major metropolitan areas.
Expansion of interprovincial trade reform and regulatory alignment

Efforts to reduce internal trade barriers are gaining momentum as provinces collaborate on simplifying regulations. These reforms make it easier for companies to transport goods, offer services, and access labour across provincial borders. Alignment of standards improves productivity and reduces administrative costs for businesses operating nationally. The shift also encourages smaller firms to expand into new markets without navigating inconsistent rules. As more provinces adopt shared frameworks, the economic impact becomes stronger. Improved internal trade efficiency supports growth in manufacturing, construction, transportation, and professional services. Over time, regulatory alignment contributes to a more integrated and competitive domestic market.
Increased investment in northern infrastructure and resource development

Northern regions are receiving investments in roads, ports, telecommunications, and energy systems to support long-term resource projects. Improved infrastructure reduces costs for mining, transportation, and supply delivery. The shift also supports local employment through training programs and long-term project operations. Better connectivity encourages new exploration and provides communities with opportunities to participate in development decisions. As infrastructure expands, northern regions become more attractive for private investment and diversified industries. These initiatives also strengthen national security by improving presence in remote areas. Over time, enhanced access creates new economic pathways and supports sustainable regional growth.
Rising focus on circular economy and recycling innovation
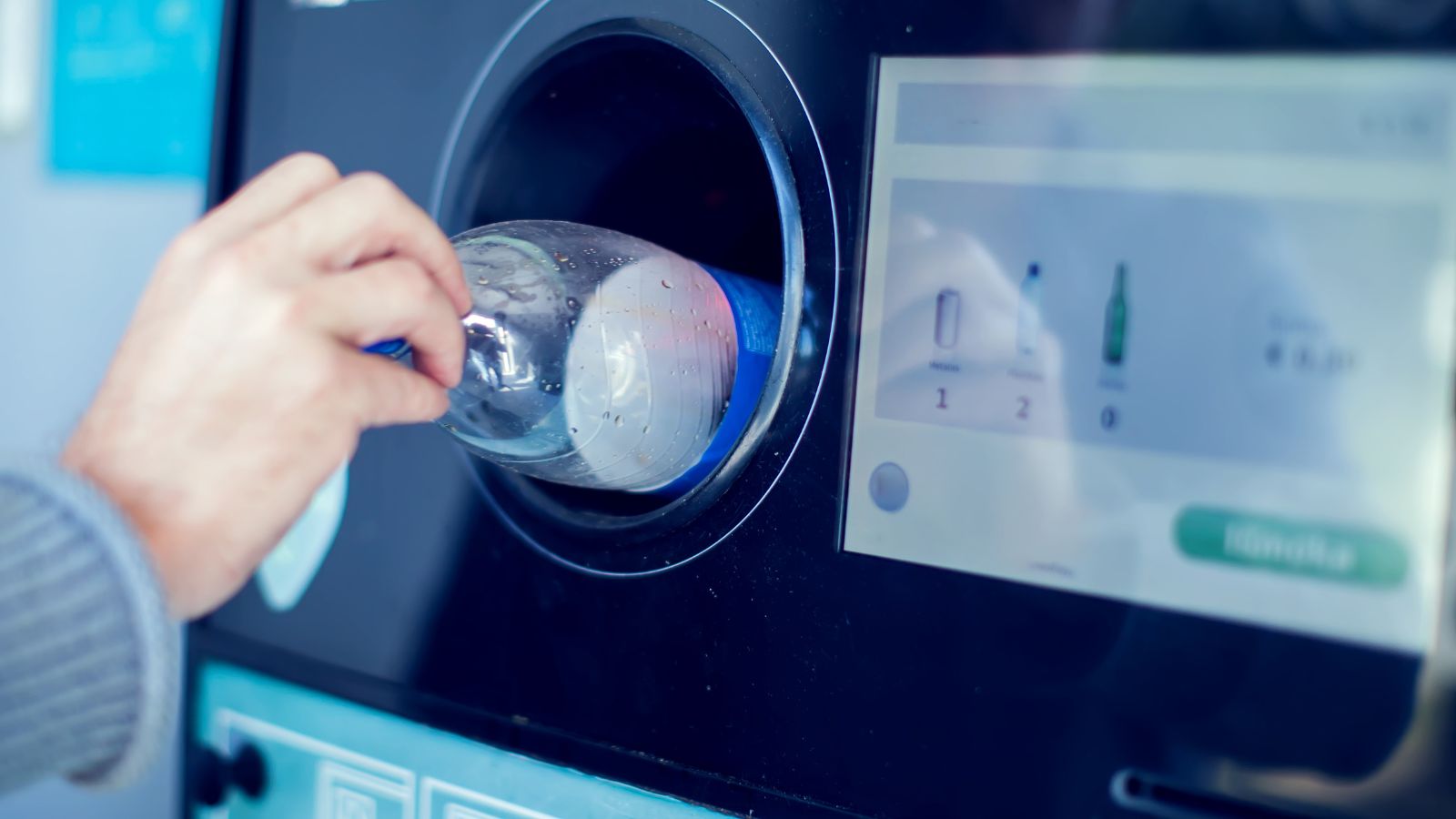

Companies and municipalities are scaling programs to recover plastics, metals, electronics, and construction materials. New recycling technologies increase the value extracted from waste streams and reduce the need for imported raw materials. Investments in sorting equipment, chemical recycling, and materials recovery facilities support local manufacturing that relies on consistent secondary materials. Universities research to improve recycling efficiency and create new products from recovered materials. Businesses benefit from reduced input costs and improved sustainability performance. As the circular economy expands, it contributes to job creation, resource conservation, and long-term competitiveness in manufacturing and environmental services.
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit

If trade tensions escalate between Canada and the U.S., everyday essentials can suddenly disappear or skyrocket in price. Products like pantry basics and tech must-haves that depend on are deeply tied to cross-border supply chains and are likely to face various kinds of disruptions
21 Products Canadians Should Stockpile Before Tariffs Hit
