More than merely an environmental problem, climate change significantly upset economies and international trade. Businesses, supply networks, and nations worldwide are facing serious issues as a result of the increase in extreme weather events, erratic climatic trends, and ecosystem changes. Here are 20 shocking facts about how climate change affects international trade unexpectedly.
Supply Chain Disruptions

As extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and wildfires increase frequency, global supply networks are severely disrupted. Businesses and consumers suffer significant losses as a result of factories being forced to close, transit routes being obstructed, and shipments being delayed.
A decline in agricultural exports

Crop yields are impacted by severe temperatures and shifting weather patterns, particularly in crucial agricultural export countries. Reduced harvests brought on by droughts, floods, and rising temperatures are increasing costs and making it more difficult for nations to supply the demand for food goods worldwide.
Rising Sea Levels Threaten Coastal Ports

Coastal regions are home to several of the busiest ports in the world, including those in Shanghai, Miami, and Rotterdam. These vital global trade centers are at risk from rising sea levels and more frequent floods brought on by climate change, which could result in billions of dollars in lost revenue and damage.
Higher Shipping Prices

Shipping routes are changing due to rising sea levels and an increase in severe weather. Increased transportation expenses are being passed on to customers due to longer journeys and the requirement to protect cargo from harsh environments.
Impact of Energy Shortages on Production

Energy shortages are becoming increasingly frequent as a result of climate change’s effects on the availability of resources like coal and water. Power outages are affecting trade by disrupting production and delaying exports, especially in developing country industries.
Water Scarcity Impacts Production

Water-intensive industries like mining and manufacturing are being impacted by the scarcity of water brought on by climate change. Because less water is available, businesses are compelled to reduce output, which lowers the quantity of commodities that can be traded.
The Cost of Insurance Is Exploding

Insurance rates for manufacturers and transportation industries are rising as a result of climate change’s heightened risk of natural disasters. Businesses are compelled to increase the prices of their products when insurance costs grow, which affects international trade flows.
Dropping Fishing Industries

Fish populations are dropping due to marine ecosystems being disrupted by warmer water temperatures. Reduced catches affect the economies of nations like Norway and Japan, which depend on fishing exports and the worldwide seafood trade.
Resources Struggled by Climate Refugees

Millions of people are displaced by climate change, especially from desert and coastal areas, increasing the burden on asylum-granting nations. The global economy is impacted by the strain this movement places on infrastructure, trade networks, and resources.
The Reevaluation of Trade Agreements

Many nations are reevaluating their trade agreements in light of the growing threat posed by climate change. Environmental laws and sustainability are becoming more critical, which could change how international trade is conducted.
Rising Commodity Prices

Prices are increasing due to climate change’s effects on the production of necessities, including food, metals, and oil. For example, mining disturbances affect the price of metals like copper and aluminum, while droughts in coffee-growing regions raise coffee costs.
Eco-friendly Technologies Are Changing Trade

Countries that export renewable energy technologies, including solar panels and wind turbines, are seeing an increase in trade as a result of the demand for cleaner technologies being driven by climate change. The trading environment and international markets are changing due to this change.
Slow Economic Growth

Roads, bridges, and railroads are examples of infrastructure being harmed by climate change and are essential to the efficient movement of products. In particular, developing nations experience sluggish economic growth due to climate-related disasters that harm their trade infrastructure.
Agricultural Shifts Create New Trade Patterns

New areas are becoming agricultural centers as some crops lose their viability in conventional growing areas as a result of climate change. With new companies entering the market and established ones disappearing, this change in crop production is changing the patterns of international trade.
Perishable Items Are More Dangerous

Transporting perishable items like fruits, vegetables, and medications is made more difficult by rising temperatures and erratic weather patterns. These difficulties raise the possibility of waste and spoiling, which increases the price of the global supply chain.
A Rise in the Need for Disaster Relief Products

The need for disaster relief materials like tents, potable water, and medical equipment is increasing as climate calamities occur more frequently. Certain items are finding a new market as a result, but supply networks are also under pressure to meet pressing needs.
Arctic Ice Shipping Routes
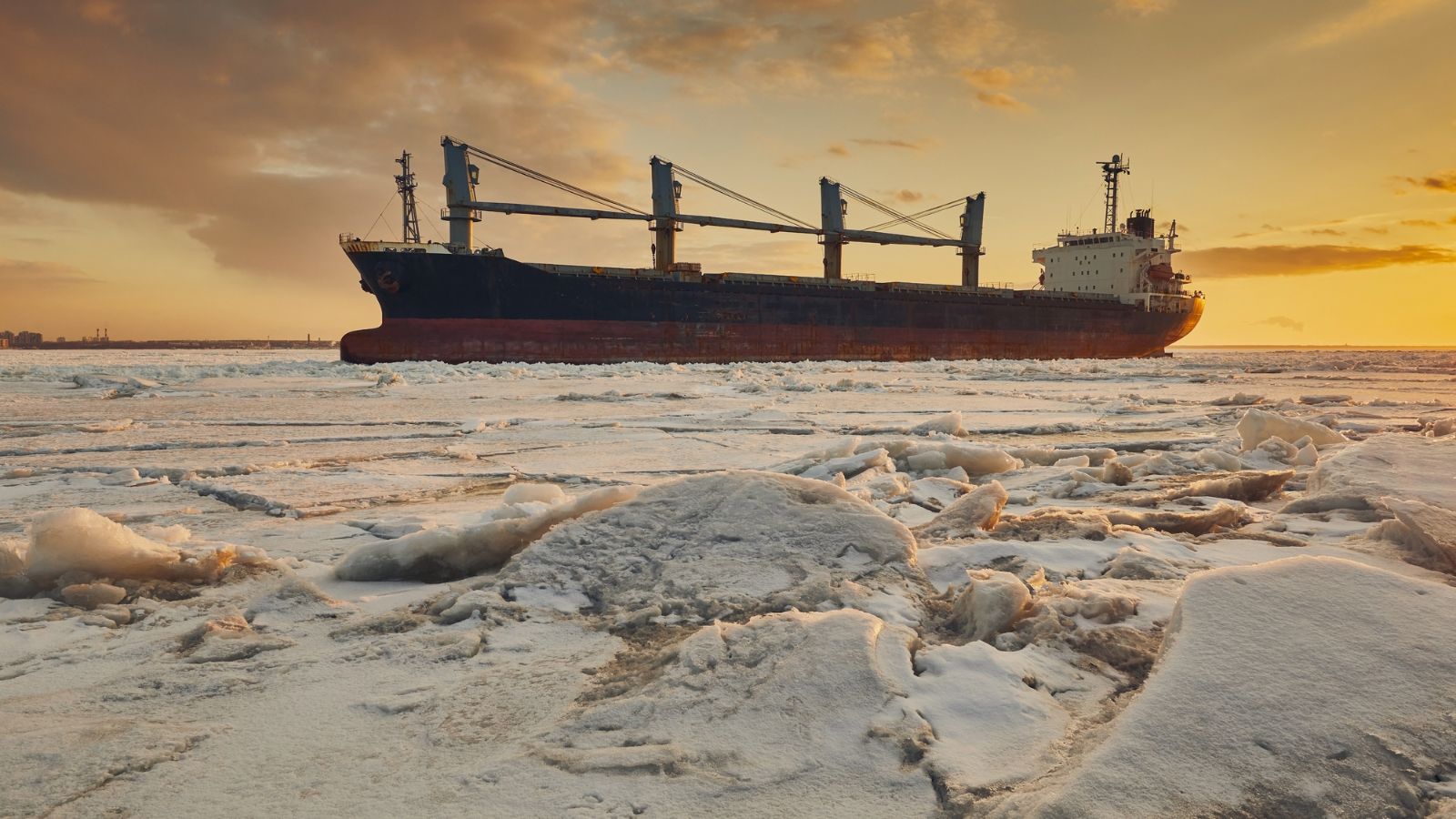

Some areas can now be reached sooner because of the emergence of new shipping lanes through the Arctic caused by the melting of polar ice. Although this offers a chance, it also brings up environmental issues and even geopolitical disputes over control of these new routes.
The Effect of Heat Waves on Worker Productivity
Heat waves are getting increasingly severe and frequent in many areas, which makes it harder for employees in industries like manufacturing, construction, and agriculture to do their duties effectively. Trade slows down when productivity declines because fewer goods are produced.
Regulations and Taxes on Carbon

Many nations are enacting stronger environmental laws and carbon levies to fight climate change. Despite being required, these regulations increase corporate expenses, which are frequently passed on to customers and affect trade competitiveness.
Climate Change Collaboration Worldwide

Countries are releasing more and more about how important international cooperation is as climate change continues to damage international trade. The global economy will probably change in the years to come as a result of the new trade agreements and policies being designed to address environmental issues collectively.
Conclusion

The Impact of Climate Change on International Trade With every year that goes by, the disruptive impacts of climate change on international trade become more apparent. Climate change is changing how things travel across borders, from changing shipping routes to increasing costs and causing damage to vital infrastructure. The future of international trade will undoubtedly look very different as nations and businesses struggle with these issues in a world that is becoming more and more influenced by the environment.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
