Dining out, whether at fine restaurants, grabbing fast food, or enjoying a quick coffee break, has become a standard part of modern life. Many people rely on food prepared outside their homes due to its convenience, taste, and social appeal. However, behind the enjoyment of eating out lies a range of hidden risks that could negatively impact your health. While an occasional meal at a restaurant may not harm you, making it a habit can seriously affect your physical and mental well-being. Here are 20 hidden dangers of eating out that may quietly damage your health.
Too Much Sodium

Restaurant foods, particularly fast foods, are usually highly processed and contain a lot of sodium. Excessive sodium leads to hypertension and increases the risk of heart disease and kidney problems. Generally, adults require no more than 2,300 milligrams (about twice the weight of a small paper clip) of sodium daily, but one restaurant meal alone can easily cross that limit.
Unhealthy Fats

Deep-fried foods and processed meats typically contain unhealthy fats such as trans fats and saturated fats, which elevate bad cholesterol, or LDL. These unhealthy fats contribute to cardiovascular disease. Even seemingly healthier dishes, grilled meats or salads, may be drenched in high-fat dressing or oil.
Sneaky Sugars

Of course, desserts expose one to a handsome amount of sugar. Still, many sauces, dressings, and marinades involved in restaurant-style meals comprise high levels of sugar that are not very visible to the consumer. Overconsumption of sugar leads to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic disorders. If you have sugary drinks accompanying your meal, that worsens things.
Overeating and Serving Sizes

Restaurant portions are often excessively large, significantly exceeding the recommended serving sizes. Overeating due to large portions is a cause of weight gain, digestive problems, and higher risks of diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
Food Additives

Food additives are usually added to the menu to make it taste and look presentable. Restaurants add preservatives, extra flavor enhancers such as MSG (monosodium glutamate), artificial coloring, etc. Some of the additives may trigger allergies in some individuals and result in headaches, allergic reactions, and, in some cases, gastrointestinal effects.
Low Nutrient Density

Additionally, dining out frequently can lead to nutritional imbalances. Many restaurant dishes focus more on flavor and presentation than on using nutrient-rich ingredients. As a result, these meals often lack essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are crucial for maintaining good health.
Foodborne Illness

Foodborne illness is always a risk when dining out. Food poisoning frequently occurs because of inappropriate handling, undercooking, or poor hygiene in the kitchen, which can lead to various symptoms, including nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. Complications in serious infections may further affect health in the long term.
High Caloric Content

Restaurant food, particularly those high in sauce, fried parts, or cheese, can be a calorific bomb. Even the seemingly healthy choices, like salads, when dressed to taste, have loads of added cheeses and croutons, turning them calorically dense. Too many calories without corresponding energy expenditure through exercise leads to weight gain.
Hormones and Antibiotics in Meat
Many restaurants serve meat from animals treated with growth hormones and antibiotics. These substances can add to antibiotic resistance in humans and may cause hormonal balances to be thrown off, leading to potential health problems that last a lifetime.
Processed Ingredients
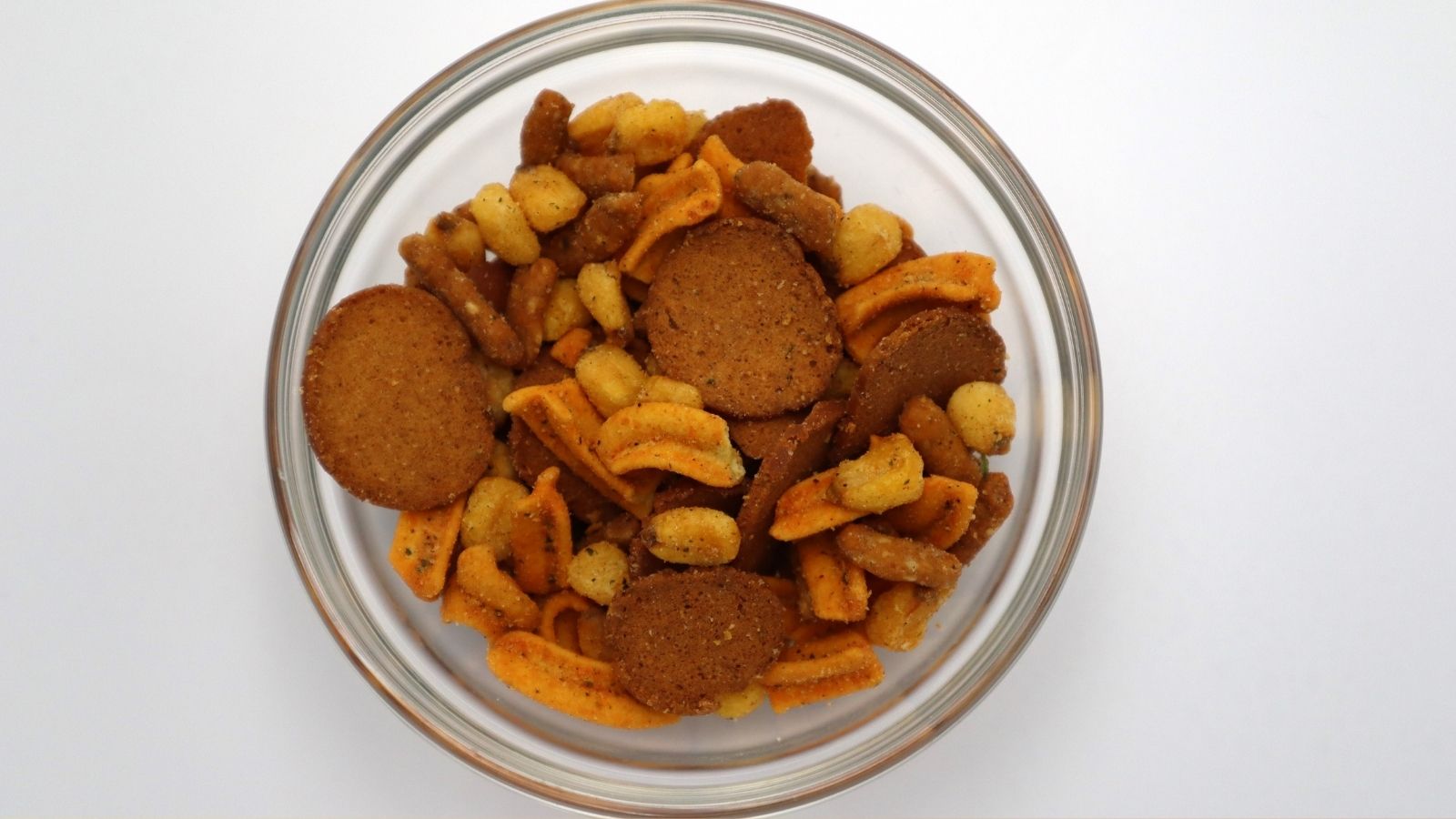

The ingredients are mainly processed for most restaurants, particularly for fast-food chains, so food is ready quickly, and costs are kept down. Processed foods are generally low in nutrients and high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and sugars, thus putting them at greater risk of obesity and other metabolic conditions.
Pesticide Residue

Fruits and vegetables served in restaurants are not always organic, meaning they may still contain pesticide residues. Even though produce is washed, it doesn’t always remove all traces of these chemicals, leaving a potential risk of harmful pesticide exposure.
Lack of Ingredient Transparency

You do not know what is used in the preparations, and you cannot control most of what goes into restaurant-prepared dishes. Most places do not give you that kind of information as to what is in your meal, so it is harder to avoid unwanted ingredients like sugar, salt, and artificial additives.
Increased Risk for Obesity

Combining high-calorie, low-nutrient foods with big portions, hidden sugars, and fats is an easy conduit to weight gain. Enjoying meals out regularly only exacerbates the energy imbalance, resulting in overweight and obesity.
Allergens and Cross-Contamination

The risk of exposure is much higher for those who suffer from food allergies or intolerances when consuming in an outside location. Though many food products are labeled as allergy-free, cross-contamination within the kitchen can sometimes occur, unintentionally exposing individuals to an allergen, possibly triggering a life-threatening allergic reaction.
Blood Sugar Spikes

Restaurant foods consist mostly of refined carbohydrates, which include white bread, pasta, and sweet beverages, thus causing a spike in blood sugar levels. Repeatedly spiking blood sugar will lead to a tendency toward insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Environmental Toxins

Restaurant foods are typically high in carbs and saturated fats but low in proteins and necessary fiber. This might contribute to dissatisfaction and subsequently cause undesirable cravings for poorly nourished food later in the day.
Stress and Poor Psychosomatic Condition

In our busy lives, we often get stressed or short of time. In this situation, we habitually consume fast food. Foods loaded with sugar and unhealthy fats are known to decrease one’s psychosomatic condition, which again reflects on the person’s mood and stress level. The psychotic problem can also be made worse due to emotional eating.
Alcoholic beverage intake

Dining out often involves consuming alcoholic beverages, and it’s easy to surpass safe limits due to drink promotions or social pressure. Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to liver disease, heart problems, and an increased risk of accidents or injuries.
Loss of mindful eating habits

People generally dine out and focus more on the companionship,
ambiance, or the convenience rather than the food itself. So, they do not pay attention to what they are eating. They continue eating without knowing their body would have sent the cue about satisfaction.
Imbalanced Macronutrient Consumption

Restaurant dishes often have excess carbohydrates and unhealthy fats while providing minimal amounts of beneficial protein and fiber that the body requires. This imbalance can lead to a calorie gap, leaving you unsatisfied and hungry later, which may cause cravings for more unhealthy foods.
Conclusion

Eating out can be fun and convenient, but it comes with various health risks due to high levels of sodium, unhealthy fats, hidden sugars, and overly processed ingredients. The large portions, unknown ingredients, and exposure to allergens, pesticides, and toxins only add to the concerns. To stay healthy, it’s important to make mindful choices: choose smaller portions, grilled over fried options, and avoid heavy sauces. Balancing restaurant meals with home-cooked food gives you more control over what you eat, helping to reduce these risks while still enjoying the experience of dining out.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses

Exploring factors that impact the desirability of living in Florida, this list delves into various challenges shaping residents’ experiences. From environmental concerns like rising sea levels to economic factors such as fluctuating job markets, these issues collectively contribute to a nuanced understanding of the state’s appeal.
18 Reasons Why People Are Leaving Florida in Masses
